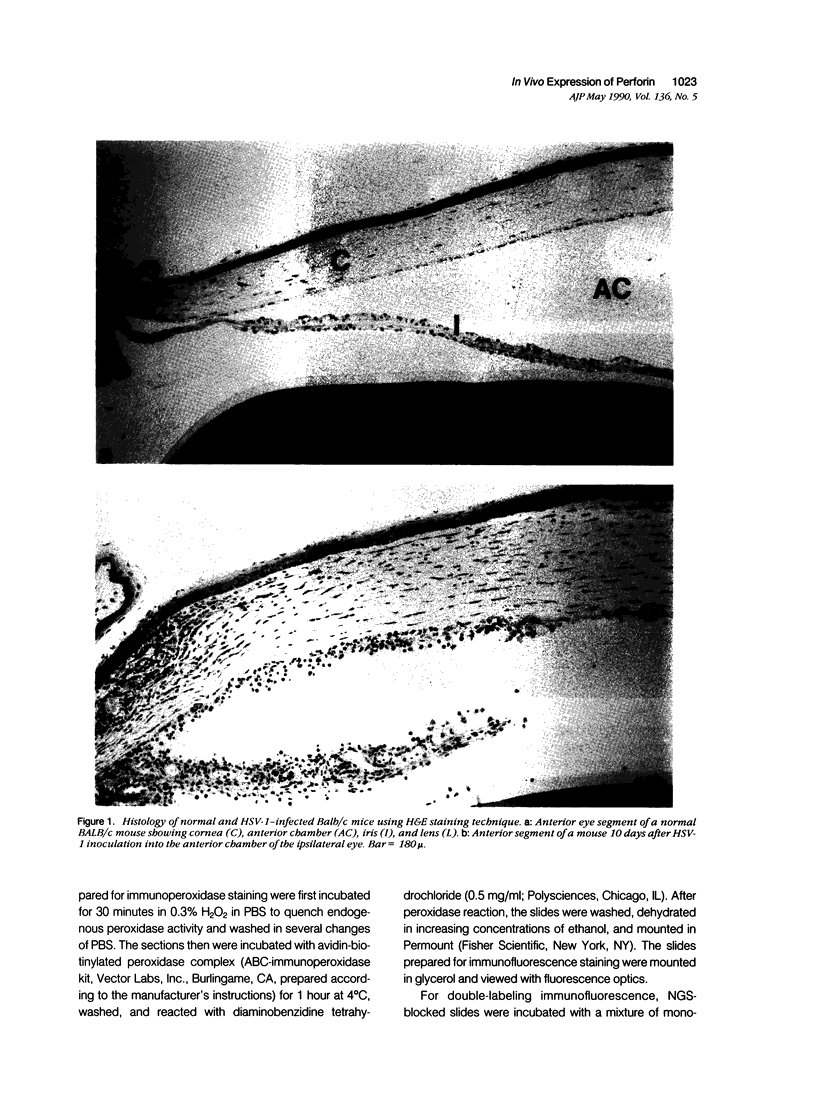
Abstract
A potent cytolytic pore-forming protein (PFP, perforin, or cytolysin) is associated with the cytoplasmic granules of cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTL) and natural killer (NK) cells. The role of PFP/perforin in cytolytic reactions carried out in vivo is still unclear. Here, the authors performed immunohistochemical analysis using antibodies monospecific for perforin and made use of a murine uveitis model produced by intracameral inoculation of herpes simplex virus I (HSV-I). The main cell infiltrate found in the anterior segment of virus-inoculated eyes consisted of Thy-1+/asialo GM1+/CD8-/CD4- cells, presumably representing NK cells. Perforin staining was detected mainly in cells bearing this phenotype. Perforin was only detected in cells displaying the large granular lymphocyte morphology. A small number of perforin-positive cells (less than 5%) colabeled as CD8+, indicating that these cells could have belonged to the CTL lineage. These observations show for the first time the presence of perforin-containing NK cells in tissues of animals undergoing acute viral infections.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berke G. Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes. How do they function? Immunol Rev. 1983;72:5–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01071.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biron C. A., Natuk R. J., Welsh R. M. Generation of large granular T lymphocytes in vivo during viral infection. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 15;136(6):2280–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop G. A., Glorioso J. C., Schwartz S. A. Relationship between expression of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and susceptibility of target cells to human natural killer activity. J Exp Med. 1983 May 1;157(5):1544–1561. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.5.1544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukowski J. F., Warner J. F., Dennert G., Welsh R. M. Adoptive transfer studies demonstrating the antiviral effect of natural killer cells in vivo. J Exp Med. 1985 Jan 1;161(1):40–52. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley M., Inaba K., Witmer-Pack M., Steinman R. M. The cell surface of mouse dendritic cells: FACS analyses of dendritic cells from different tissues including thymus. Cell Immunol. 1989 Jan;118(1):108–125. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90361-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djeu J. Y., Stocks N., Zoon K., Stanton G. J., Timonen T., Herberman R. B. Positive self regulation of cytotoxicity in human natural killer cells by production of interferon upon exposure to influenza and herpes viruses. J Exp Med. 1982 Oct 1;156(4):1222–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Fukui H., Shimamura K., Kasai M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tamaoki N. In vivo effects of anti-asialo GM1. I. Reduction of NK activity and enhancement of transplanted tumor growth in nude mice. J Immunol. 1981 Jul;127(1):34–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkart P. A. Mechanism of lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:31–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo G. C., Peppard J. R. Establishment of monoclonal anti-Nk-1.1 antibody. Hybridoma. 1984 Fall;3(3):301–303. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1984.3.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon B. S., Wakulchik M., Liu C. C., Persechini P. M., Trapani J. A., Haq A. K., Kim Y., Young J. D. The structure of the mouse lymphocyte pore-forming protein perforin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80168-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenheld M. G., Olsen K. J., Lu P., Lowrey D. M., Hameed A., Hengartner H., Podack E. R. Structure and function of human perforin. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):448–451. doi: 10.1038/335448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C., Kirkpatrick D., Read S. E., Fitzgerald P. A., Pitt J., Pahwa S., Ching C. Y., Smithwick E. M. Correlation between low natural killing of fibroblasts infected with herpes simplex virus type 1 and susceptibility to herpesvirus infections. J Infect Dis. 1983 Jun;147(6):1030–1035. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.6.1030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowrey D. M., Aebischer T., Olsen K., Lichtenheld M., Rupp F., Hengartner H., Podack E. R. Cloning, analysis, and expression of murine perforin 1 cDNA, a component of cytolytic T-cell granules with homology to complement component C9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):247–251. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Welsh R. M. Accumulation of natural killer and cytotoxic T large granular lymphocytes in the liver during virus infection. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1667–1681. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The molecular basis of target cell killing by human lymphocytes and of killer cell self-protection. Immunol Rev. 1988 Mar;103:87–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1988.tb00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepose J. S., Whittum-Hudson J. A. An immunogenetic analysis of resistance to herpes simplex virus retinitis in inbred strains of mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1549–1552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini P. M., Young J. D. The primary structure of the lymphocyte pore-forming protein perforin: partial amino acid sequencing and determination of isoelectric point. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 31;156(2):740–745. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80905-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds C. W., Reichardt D., Henkart M., Millard P., Henkart P. Inhibition of NK and ADCC activity by antibodies against purified cytoplasmic granules from rat LGL tumors. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Dec;42(6):642–652. doi: 10.1002/jlb.42.6.642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandstrom I. K., Foster C. S., Wells P. A., Knipe D., Caron L., Greene M. I. Previous immunization of mice with herpes simplex virus type-1 strain MP protects against secondary corneal infection. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1986 Aug;40(2):326–334. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(86)90037-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Koprowski H. Mechanisms of activation of human natural killer cells against tumor and virus-infected cells. Immunol Rev. 1979;44:125–163. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00269.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoli D., Trinchieri G., Lief F. S. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity against virus-infected target cells in humans. I. Characterization of the effector lymphocyte. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinkai Y., Takio K., Okumura K. Homology of perforin to the ninth component of complement (C9). Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):525–527. doi: 10.1038/334525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Perussia B. Human natural killer cells: biologic and pathologic aspects. Lab Invest. 1984 May;50(5):489–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Jongeneel C. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated cytolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2641–2646. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Masson D., Stanley K. K. Structural/functional similarity between proteins involved in complement- and cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):831–834. doi: 10.1038/322831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M. Regulation and role of large granular lymphocytes in arenavirus infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1987;134:185–209. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71726-0_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum-Hudson J. A., Pepose J. S. Immunologic modulation of virus-induced pathology in a murine model of acute herpetic retinal necrosis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1987 Sep;28(9):1541–1548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum-Hudson J., Farazdaghi M., Prendergast R. A. A role for T lymphocytes in preventing experimental herpes simplex virus type 1-induced retinitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985 Nov;26(11):1524–1532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittum J. A., McCulley J. P., Niederkorn J. Y., Streilein J. W. Ocular disease induced in mice by anterior chamber inoculation of herpes simplex virus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1984 Sep;25(9):1065–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang H., Yogeeswaran G., Bukowski J. F., Welsh R. M. Expression of asialo GM1 and other antigens and glycolipids on natural killer cells and spleen leukocytes in virus-infected mice. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1985;4(1):21–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A. Cellular and humoral mechanisms of cytotoxicity: structural and functional analogies. Adv Immunol. 1987;41:269–332. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60033-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Cohn Z. A., Podack E. R. The ninth component of complement and the pore-forming protein (perforin 1) from cytotoxic T cells: structural, immunological, and functional similarities. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):184–190. doi: 10.1126/science.2425429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Hengartner H., Podack E. R., Cohn Z. A. Purification and characterization of a cytolytic pore-forming protein from granules of cloned lymphocytes with natural killer activity. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):849–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. D., Liu C. C., Leong L. G., Cohn Z. A. The pore-forming protein (perforin) of cytolytic T lymphocytes is immunologically related to the components of membrane attack complex of complement through cysteine-rich domains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2077–2082. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Dowling J. E. Monoclonal antibodies distinguish subtypes of retinal horizontal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6255–6259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Klavinskis L. S., Oldstone M. B., Young J. D. In vivo expression of perforin by CD8+ lymphocytes during an acute viral infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2159–2171. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]