Abstract
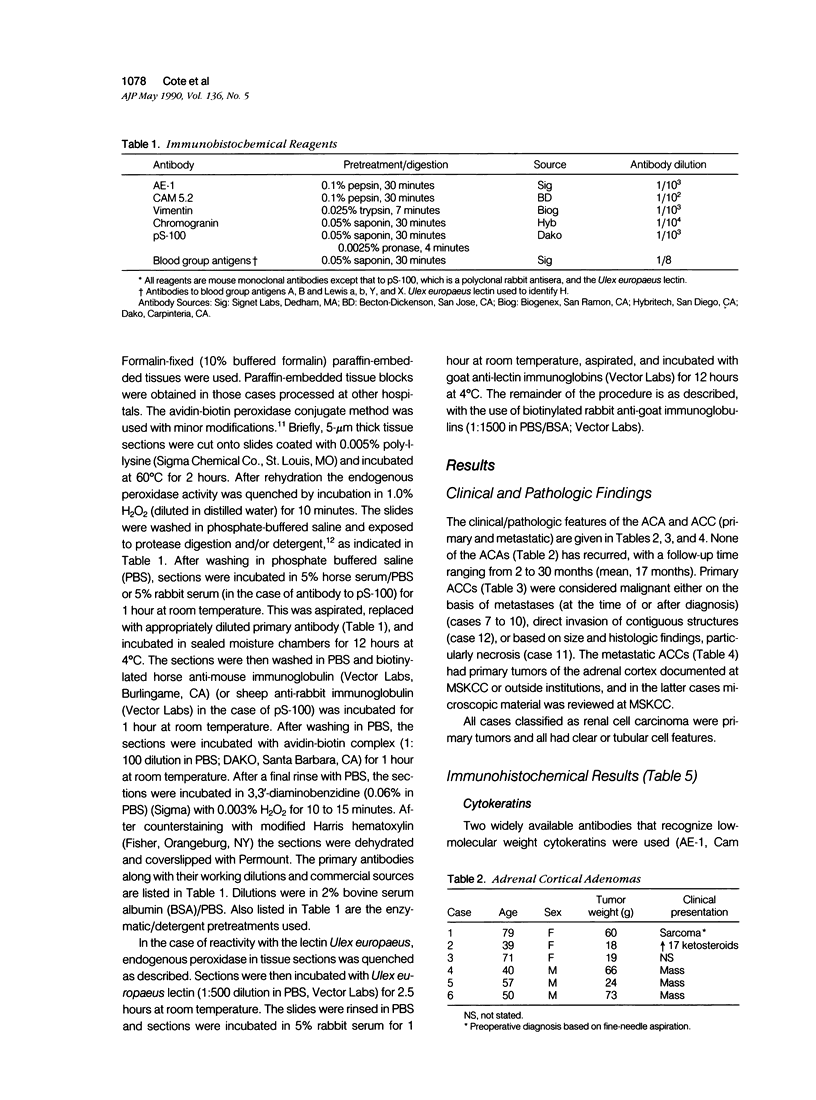
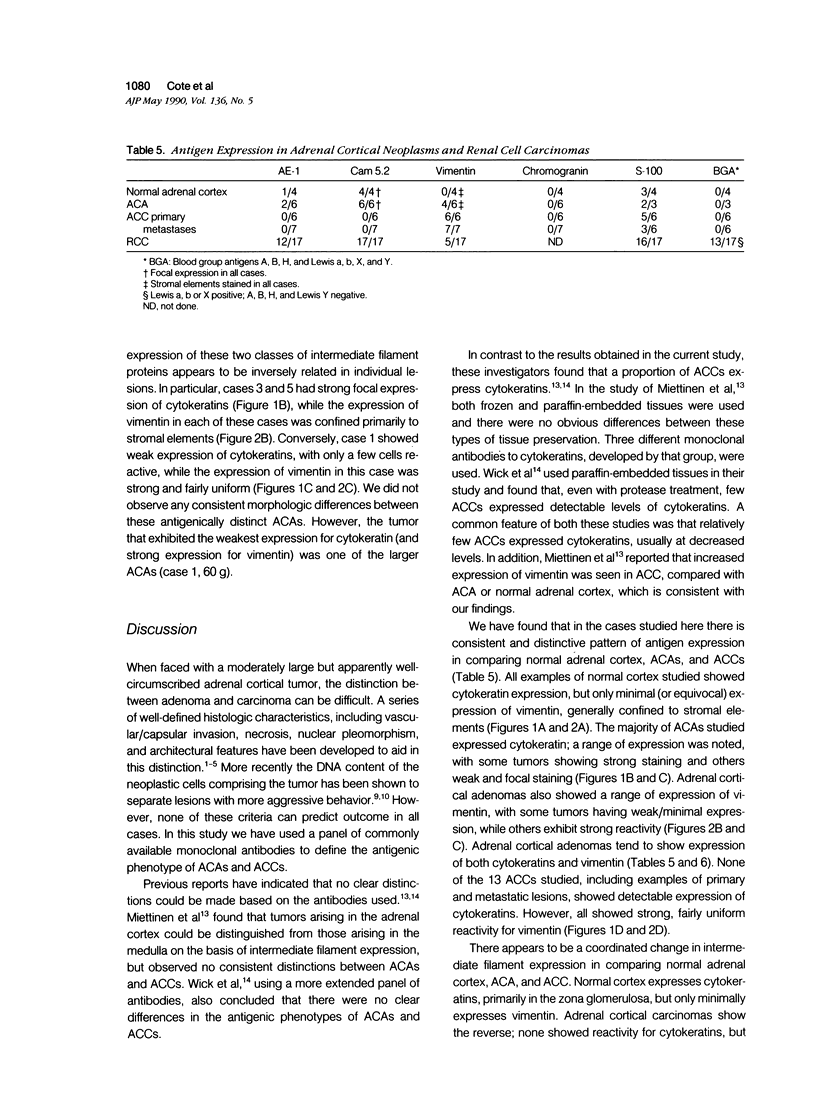
A series of adrenal cortical adenomas (ACA) and carcinomas (ACC), as well as normal adrenal cortex have been studied by a panel of 11 antibodies to characterize antigenic changes that may distinguish these morphologically similar entities. Normal adrenal cortex and ACA express low-molecular weight cytokeratin intermediate filaments. However, none of the six primary or seven metastatic ACCs were found to express detectable levels of cytokeratins. In contrast, vimentin was seen in all ACCs studied and was heterogeneously expressed by ACAs. However, its expression was usually confined to stromal elements of the normal adrenal cortex. We conclude that adrenal cortical cells undergo characteristic changes in intermediate filament expression during the process of neoplastic conversion and malignant transformation. Undetectable expression of cytokeratins and strong expression of vimentin is associated with malignant adrenal cortical lesions. In addition, we examined the antigenic phenotype of a series of primary renal cell carcinomas (RCC). Renal cell carcinomas express cytokeratins, while ACCs do not. The majority of primary RCCs express Lewis blood group isoantigens (most commonly Lewis X), while ACAs and ACCs do not. The panel of antibodies described here may help to distinguish morphologically similar lesions of like histogenesis (ACAs vs. ACCs) and lesions of different histogenesis (adrenal vs. renal) on the basis of their composite antigenic phenotypes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amberson J. B., Vaughan E. D., Jr, Gray G. F., Naus G. J. Flow cytometric analysis of nuclear DNA from adrenocortical neoplasms. A retrospective study using paraffin-embedded tissue. Cancer. 1987 Jun 15;59(12):2091–2095. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870615)59:12<2091::aid-cncr2820591221>3.0.co;2-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Bander N. H., Fradet Y., Finstad C. L., Whitmore W. F., Lloyd K. O., Oettgen H. F., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Immunoanatomic dissection of the human urinary tract by monoclonal antibodies. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Oct;32(10):1035–1040. doi: 10.1177/32.10.6384360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Finstad C. L., Bander N. H., Melamed M. R. Immunoanatomic distribution of cytostructural and tissue-associated antigens in the human urinary tract. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):269–284. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordon-Cardo C., Reuter V. E., Finstad C. L., Sheinfeld J., Lloyd K. O., Fair W. R., Melamed M. R. Blood group-related antigens in human kidney: modulation of Lewis determinants in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):212–218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finstad C. L., Cordon-Cardo C., Bander N. H., Whitmore W. F., Melamed M. R., Old L. J. Specificity analysis of mouse monoclonal antibodies defining cell surface antigens of human renal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2955–2959. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEINBECKER P., O'NEAL L. W., ACKERMAN L. V. Functioning and nonfunctioning adrenal cortical tumors. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1957 Jul;105(1):21–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough A. J., Hollifield J. W., Page D. L., Hartmann W. H. Prognostic factors in adrenal cortical tumors. A mathematical analysis of clinical and morphologic data. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979 Sep;72(3):390–399. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/72.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlimann J., Gardiol D., Scazziga B. Immunohistology of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. A study of 43 cases. Histopathology. 1987 Jun;11(6):567–580. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1987.tb02667.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huvos A. G., Hajdu S. I., Brasfield R. D., Foote F. W., Jr Adrenal cortical carcinoma. Clinicopathologic study of 34 cases. Cancer. 1970 Feb;25(2):354–361. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197002)25:2<354::aid-cncr2820250212>3.0.co;2-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato K., Haimoto H., Ariyoshi Y., Horisawa M., Washida H., Kimura S. High levels of S-100a0 (alpha alpha) protein in tumor tissues and in sera of patients with renal cell carcinoma. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1985 Sep;76(9):856–862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay S. Hyperplasia and neoplasia of the adrenal gland. Pathol Annu. 1976;11:103–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. R., Lack E. E. Adrenal cortical carcinoma: a clinical and pathologic study of 49 cases. Cancer. 1979 Jul;44(1):239–244. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197907)44:1<239::aid-cncr2820440139>3.0.co;2-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LiVolsi V. A., Brooks J. J., Arendash-Durand B. Anaplastic thyroid tumors. Immunohistology. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Apr;87(4):434–442. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.4.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medeiros L. J., Michie S. A., Johnson D. E., Warnke R. A., Weiss L. M. An immunoperoxidase study of renal cell carcinomas: correlation with nuclear grade, cell type, and histologic pattern. Hum Pathol. 1988 Aug;19(8):980–987. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(88)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meis J. M., Ordóez N. G., Gallager H. S. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the breast: an immunohistochemical study of six cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;410(5):415–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00712761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberman H. A. Metaplastic carcinoma of the breast. A clinicopathologic study of 29 patients. Am J Surg Pathol. 1987 Dec;11(12):918–929. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198712000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santeusanio G., Pascal R. R., Bisceglia M., Costantino A. M., Bosman C. Metaplastic breast carcinoma with epithelial phenotype of pseudosarcomatous components. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1988 Jan;112(1):82–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schteingart D. E., Oberman H. A., Friedman B. A., Conn J. W. Adrenal cortical neoplasms producing cushing's syndrome. A clinicopathologic study. Cancer. 1968 Nov;22(5):1005–1013. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196811)22:5<1005::aid-cncr2820220516>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. K., Gray G. F. Adrenocortical neoplasms. Prognosis and morphology. Urology. 1975 May;5(5):691–695. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(75)90135-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. R., Roederer M., Murphy R. F. Flow cytometric DNA analysis of adrenocortical tumors in children. Cancer. 1987 Jun 15;59(12):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19870615)59:12<2059::aid-cncr2820591216>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanstapel M. J., Gatter K. C., de Wolf-Peeters C., Mason D. Y., Desmet V. D. New sites of human S-100 immunoreactivity detected with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Feb;85(2):160–168. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/85.2.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M. Comparative histologic study of 43 metastasizing and nonmetastasizing adrenocortical tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Mar;8(3):163–169. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198403000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick M. R., Cherwitz D. L., McGlennen R. C., Dehner L. P. Adrenocortical carcinoma. An immunohistochemical comparison with renal cell carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 1986 Feb;122(2):343–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





