Abstract
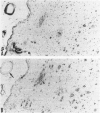
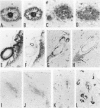
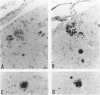
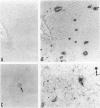
Here we report on a monoclonal antibody, H6-33, that labels various beta-amyloid plaques, including diffuse plaques in the formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded section from the brain affected with Alzheimer's disease (AD), without formic acid pretreatment. H6-33 also labels some neurofibrillary tangles and all kuru plaques in Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker disease. In sharp contrast, H6-33 did not stain beta amyloid in the leptomeningeal vessel. For specific staining, H6-33 required the presence of fetal calf serum and it was necessary for beta amyloid to be formalin fixed. These results suggest that a novel protein in the calf serum, CSX, binds formalin-fixed beta amyloid, followed by H6-33 binding. The detection of beta amyloid by CSX was nullified by formic acid pretreatment of the tissue section. In accordance with this, CSX reacted only with a polymer form of synthetic beta peptide after fixation, but not with native beta-protein or beta-peptide monomer. These observations strongly suggest that 1) meningovascular beta amyloid should have a beta-pleated sheet structure somewhat dissimilar to that of beta-amyloid cores; and 2) most, if not all, of beta-protein immunoreactivities of diffuse plaques in AD sections are presumably derived from small amounts of amyloid fibrils scattered in the normal-looking neurohil.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham C. R., Selkoe D. J., Potter H. Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor alpha 1-antichymotrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):487–501. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90462-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gorevic P. D., Migheli A., Frangione B. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. H., Johnson F. B., Whiting J., Roller P. P. Formaldehyde fixation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Aug;33(8):845–853. doi: 10.1177/33.8.3894502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. N., Merz P., Bennett-Gray J., Menezes A. H., Goeken J. A., Schelper R. L., Wisniewski H. M. beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer's disease is found in cerebral and spinal cord vascular malformations. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jul;132(1):167–172. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y. Massive somatodendritic sprouting of cortical neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 1988 Aug 30;459(1):138–144. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90293-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda K., Haga C., Kosaka K., Oyanagi S. Senile plaque-like structures: observation of a probably unknown type of senile plaque by periodic-acid methenamine silver (PAM) electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(2):137–142. doi: 10.1007/BF00688201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Morris J. H., Selkoe D. J. Diffuse senile plaques occur commonly in the cerebellum in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1989 Aug;135(2):309–319. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. X-ray diffraction from intraneuronal paired helical filaments and extraneuronal amyloid fibers in Alzheimer disease indicates cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Inouye H., Duffy L. K., Sinclair A., Lind M., Selkoe D. J. Synthetic peptide homologous to beta protein from Alzheimer disease forms amyloid-like fibrils in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Immunohistochemical confirmation of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with a long clinical course with amyloid plaque core antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jun;131(3):435–443. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J., Honda T., Mori H., Hamada Y., Miura R., Ogawara M., Ihara Y. The carboxyl third of tau is tightly bound to paired helical filaments. Neuron. 1988 Nov;1(9):827–834. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90130-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luben R. A., Mohler M. A. In vitro immunization as an adjunct to the production of hybridomas producing antibodies against the lymphokine osteoclast activating factor. Mol Immunol. 1980 May;17(5):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(80)90161-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann D. M., Esiri M. M. The site of the earliest lesions of Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):789–790. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norling B., Westermark G. T., Westermark P. Immunohistochemical identification of heparan sulphate proteoglycan in secondary systemic amyloidosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Aug;73(2):333–337. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogomori K., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Sato Y., Suetsugu M., Abe M. Beta-protein amyloid is widely distributed in the central nervous system of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1989 Feb;134(2):243–251. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogomori K., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Sato Y., Tashima T. Aging and cerebral amyloid: early detection of amyloid in the human brain using biochemical extraction and immunostain. J Gerontol. 1988 Nov;43(6):B157–B162. doi: 10.1093/geronj/43.6.b157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmert M. R., Podlisny M. B., Witker D. S., Oltersdorf T., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. Antisera to an amino-terminal peptide detect the amyloid protein precursor of Alzheimer's disease and recognize senile plaques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):432–437. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80859-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters T., Jr Serum albumin. Adv Protein Chem. 1985;37:161–245. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Allsop D., Bruton C. The occult aftermath of boxing. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1990 May;53(5):373–378. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.53.5.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roher A., Wolfe D., Palutke M., KuKuruga D. Purification, ultrastructure, and chemical analysis of Alzheimer disease amyloid plaque core protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2662–2666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R., Podlisny M. B., Duffy L. K. Isolation of low-molecular-weight proteins from amyloid plaque fibers in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1820–1834. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Podlisny M. B., Joachim C. L., Vickers E. A., Lee G., Fritz L. C., Oltersdorf T. Beta-amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer disease occurs as 110- to 135-kilodalton membrane-associated proteins in neural and nonneural tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7341–7345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Kisilevsky R., Willmer J., Prusiner S. B., DeArmond S. J. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans in amyloid plaques of prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(4):337–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00687367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Wight T. N. Proteoglycans in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease and other amyloidoses. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):481–497. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90108-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Willmer J. P., Kisilevsky R. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Pathol. 1987 May;18(5):506–510. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(87)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow A. D., Willmer J., Kisilevsky R. Sulfated glycosaminoglycans: a common constituent of all amyloids? Lab Invest. 1987 Jan;56(1):120–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Hasegawa M., Titani K., Ihara Y. Identification of beta protein precursor in newborn rat brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 May 15;160(3):1296–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80144-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hirai S., Morimatsu M., Shoji M., Ihara Y. A variety of cerebral amyloid deposits in the brains of the Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostaining. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(6):541–549. doi: 10.1007/BF00689591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Hirai S., Morimatsu M., Shoji M., Nakazato Y. Diffuse type of senile plaques in the cerebellum of Alzheimer-type dementia demonstrated by beta protein immunostain. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(3):314–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00687584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi H., Nakazato Y., Hirai S., Shoji M., Harigaya Y. Electron micrograph of diffuse plaques. Initial stage of senile plaque formation in the Alzheimer brain. Am J Pathol. 1989 Oct;135(4):593–597. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duinen S. G., Castaño E. M., Prelli F., Bots G. T., Luyendijk W., Frangione B. Hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis in patients of Dutch origin is related to Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5991–5994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]