Abstract
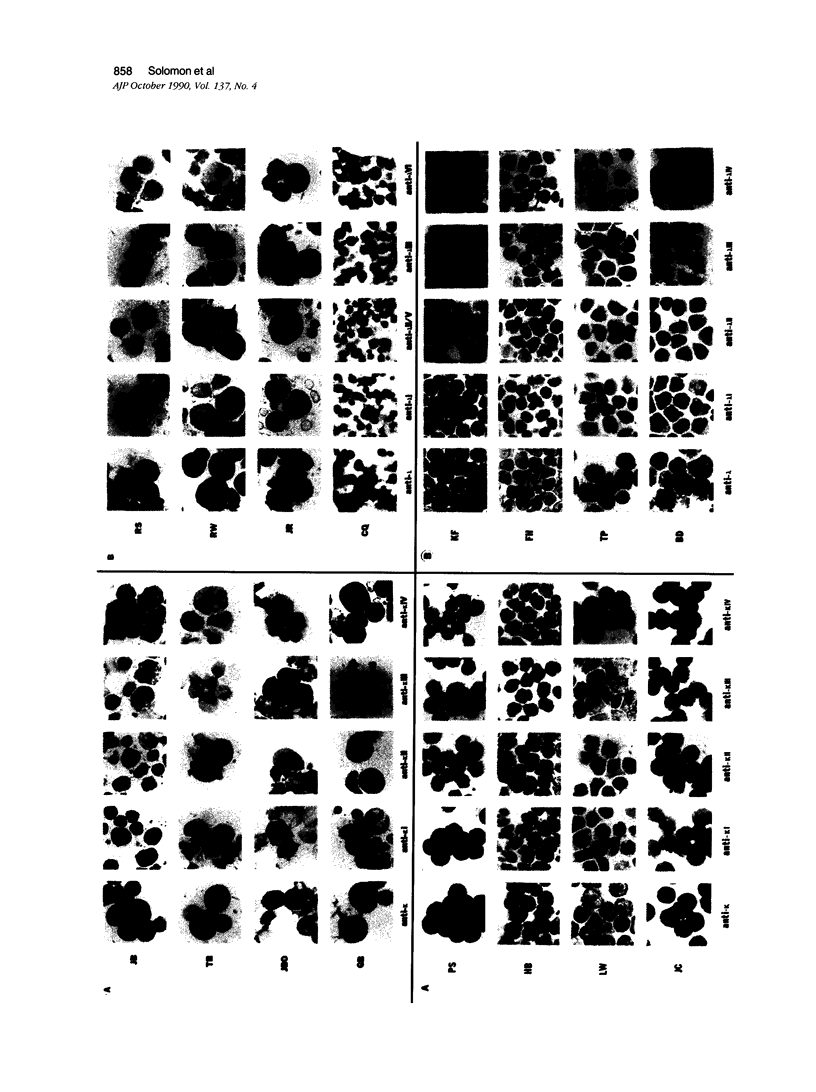
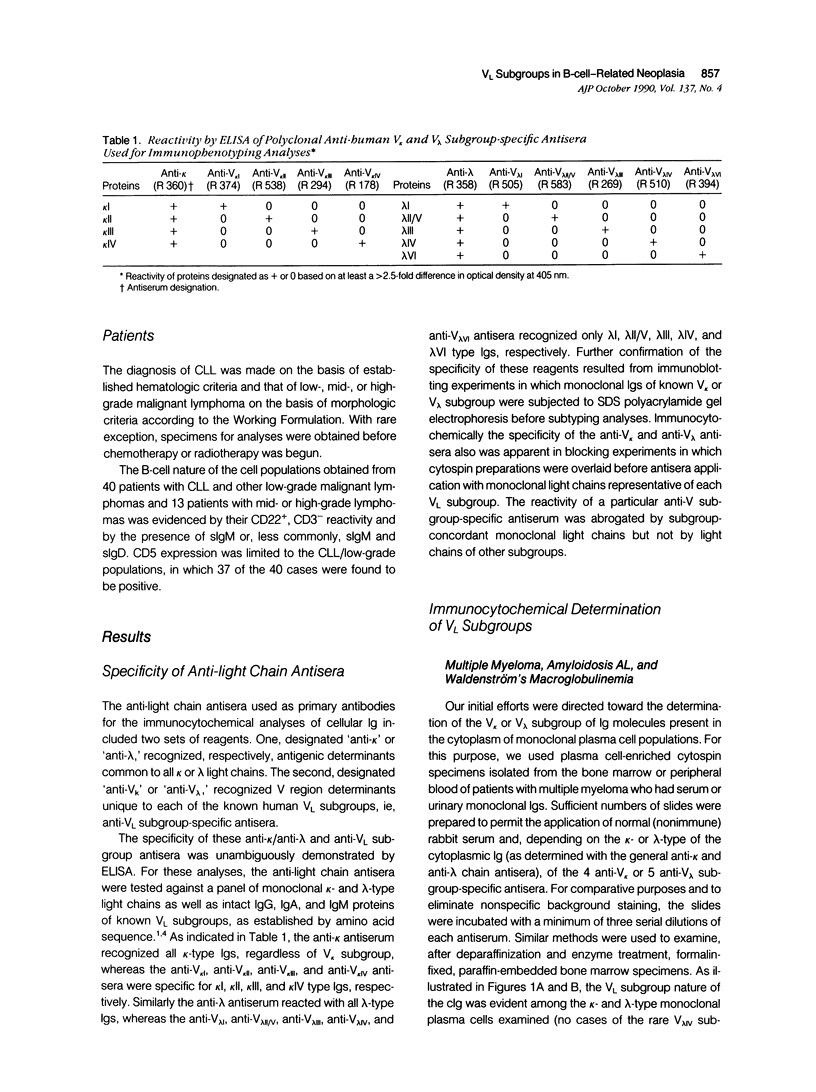
We have used a sensitive immunoperoxidase method and highly specific anti-light chain antisera to determine the light chain variable region (VL) subgroup nature of cytoplasmic (c) and cell surface (s) Ig expressed by human monoclonal plasma cells and B lymphocytes. The immunocytochemical characterization of cIg and sIg used antisera specific for the established kappa light chain V kappa subgroups (V kappa I, V kappa II, V kappa III, and V kappa IV) and the lambda light chain V lambda subgroups (V lambda I, V lambda II/V, V lambda IV, and V lambda VI). Studies were performed using cytospin preparations of bone marrow-, peripheral blood-, and lymph node-derived cells from patients with multiple myeloma, amyloidosis AL, and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia and with low-, mid-, and high-grade B-cell malignancies. The V kappa or V lambda subgroup of the cIg or sIg also could be identified after deparaffinization and enzyme treatment of formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens. For those patients who had monoclonal serum or urinary Igs, there was complete concordance between the VL subgroup of the secreted Ig and that of the cIg or sIg. The percentage distribution of V kappa or V lambda subgroups on the sIg of cells from patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and other cytomorphologic types of B-cell malignancies differed from that found for kappa- or lambda-type Bence Jones proteins obtained from patients with multiple myeloma, amyloidosis AL, and Waldenström's macroglobulinemia. In contrast to the plasma cell and lymphocytoid plasma cell diseases, a relative predominance of certain VL subgroups, ie, V kappa IV, V lambda III, and V lambda IV, and the absence of the amyloid-associated V lambda VI subgroup were found in CLL and related diseases. The immunocytochemical techniques used make possible a rapid means to demonstrate B-cell monoclonality and provide further evidence for the selective expression of certain VL genes in human B-cell neoplasia.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carson D. A., Fong S. A common idiotope on human rheumatoid factors identified by a hybridoma antibody. Mol Immunol. 1983 Oct;20(10):1081–1087. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casali P., Burastero S. E., Nakamura M., Inghirami G., Notkins A. L. Human lymphocytes making rheumatoid factor and antibody to ssDNA belong to Leu-1+ B-cell subset. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):77–81. doi: 10.1126/science.3105056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Robbins D. L., Jirik F. R., Kipps T. J., Carson D. A. Isolation and characterization of a light chain variable region gene for human rheumatoid factors. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1900–1905. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen P. P., Siminovitch K. A., Olsen N. J., Erger R. A., Carson D. A. A highly informative probe for two polymorphic Vh gene regions that contain one or more autoantibody-associated Vh genes. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):706–710. doi: 10.1172/JCI114218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S., Chen P. P., Gilbertson T. A., Fox R. I., Vaughan J. H., Carson D. A. Structural similarities in the kappa light chains of human rheumatoid factor paraproteins and serum immunoglobulins bearing a cross-reactive idiotype. J Immunol. 1985 Sep;135(3):1955–1960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Freeman G., Whitman J., Segil J., Daley J., Nadler L. M. Studies of in vitro activated CD5+ B cells. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):202–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Shimizu M., Yamasaki K., Kishimoto T. Rheumatoid factor secretion from human Leu-1+ B cells. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):81–83. doi: 10.1126/science.3105057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Fong S., Tomhave E., Chen P. P., Goldfien R. D., Carson D. A. High-frequency expression of a conserved kappa light-chain variable-region gene in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Robbins B. A., Kuster P., Carson D. A. Autoantibody-associated cross-reactive idiotypes expressed at high frequency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia relative to B-cell lymphomas of follicular center cell origin. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):422–428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J. The CD5 B cell. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:117–185. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Tomhave E., Chen P. P., Carson D. A. Autoantibody-associated kappa light chain variable region gene expressed in chronic lymphocytic leukemia with little or no somatic mutation. Implications for etiology and immunotherapy. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):840–852. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipps T. J., Tomhave E., Pratt L. F., Duffy S., Chen P. P., Carson D. A. Developmentally restricted immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene expressed at high frequency in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5913–5917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel H. G., Winchester R. J., Joslin F. G., Capra J. D. Similarities in the light chains of anti-gamma-globulins showing cross-idiotypic specificities. J Exp Med. 1974 Jan 1;139(1):128–136. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledford D. K., Goñi F., Pizzolato M., Franklin E. C., Solomon A., Frangione B. Preferential association of kappa IIIb light chains with monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Immunol. 1983 Sep;131(3):1322–1325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natvig J. B., Thompson K., Randen I., Steinitz M., Taussig M., Beale D., Barker P., Sletten K., Waalen K., Førre O. Partial amino acid sequence analysis and variable subgroup determination (VH and VL) of a monoclonal rheumatoid factor derived from a rheumatoid arthritis patient. Scand J Rheumatol Suppl. 1988;75:127–132. doi: 10.3109/03009748809096753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plater-Zyberk C., Maini R. N., Lam K., Kennedy T. D., Janossy G. A rheumatoid arthritis B cell subset expresses a phenotype similar to that in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Sep;28(9):971–976. doi: 10.1002/art.1780280903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons-Estel B., Goñi F., Solomon A., Frangione B. Sequence similarities among kappa IIIb chains of monoclonal human IgM kappa autoantibodies. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):893–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Seligmann M. Anti-human immunoglobulin G activity of membrane-bound monoclonal immunoglobulin M in lymphoproliferative disorders. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2132–2135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radoux V., Chen P. P., Sorge J. A., Carson D. A. A conserved human germline V kappa gene directly encodes rheumatoid factor light chains. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):2119–2124. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roelcke D. Cold agglutination. Antibodies and antigens. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Jan;2(2):266–280. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royston I., Majda J. A., Baird S. M., Meserve B. L., Griffiths J. C. Human T cell antigens defined by monoclonal antibodies: the 65,000-dalton antigen of T cells (T65) is also found on chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells bearing surface immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):725–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch K. A., Misener V., Kwong P. C., Song Q. L., Chen P. P. A natural autoantibody is encoded by germline heavy and lambda light chain variable region genes without somatic mutation. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1675–1678. doi: 10.1172/JCI114347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., Frangione B., Franklin E. C. Bence Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins. Preferential association of the V lambda VI subgroup of human light chains with amyloidosis AL (lambda). J Clin Invest. 1982 Aug;70(2):453–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI110635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. Light chains of human immunoglobulins. Methods Enzymol. 1985;116:101–121. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)16008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A. Light chains of immunoglobulins: structural-genetic correlates. Blood. 1986 Sep;68(3):603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., McLaughlin C. L. Bence Jones proteins and light chains of immunoglobulins. IV. Immunochemical differentiation among proteins within each of the three established kappa-chain classes. J Immunol. 1971 Jan;106(1):120–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon A., Weiss D. T. Serologically defined V region subgroups of human lambda light chains. J Immunol. 1987 Aug 1;139(3):824–830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. Y., Good R. A., Ammirati P., Dymbort G., Evans R. L. Identification of a p69,71 complex expressed on human T cells sharing determinants with B-type chronic lymphatic leukemic cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1539–1544. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



