Abstract
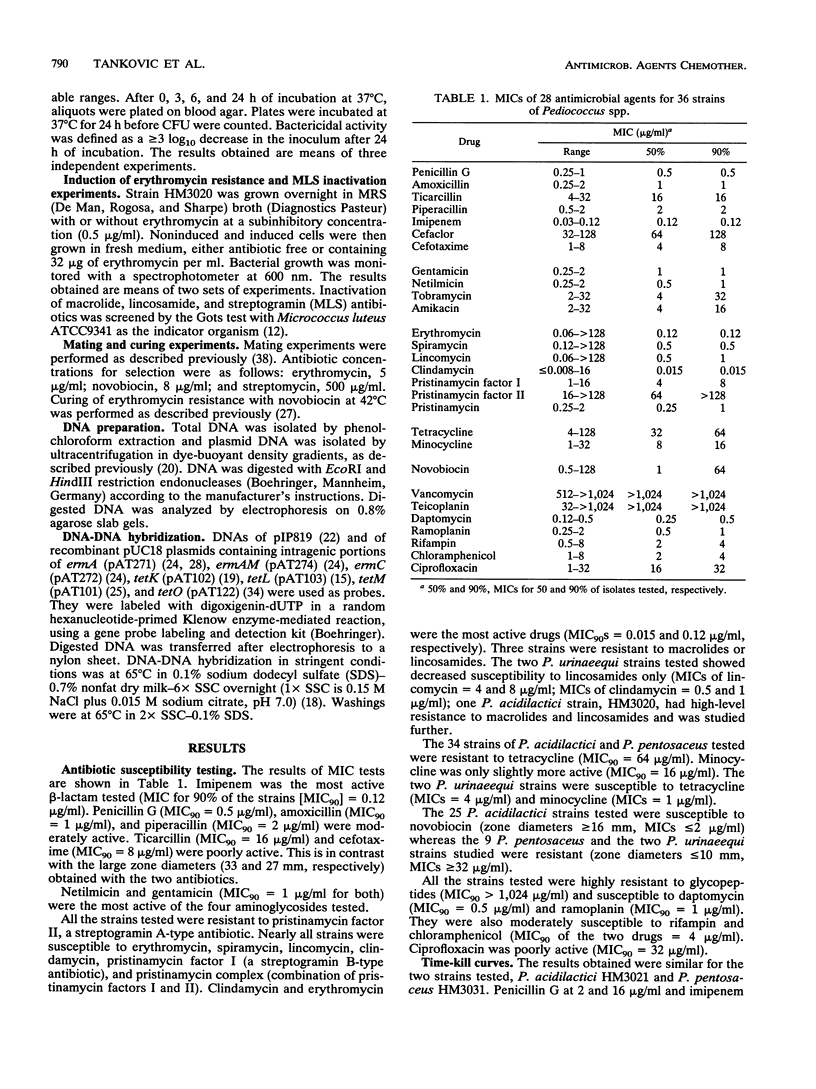
We determined the MICs of 28 antimicrobial agents against 36 clinical strains of Pediococcus spp. (25 P. acidilactici, 9 P. pentosaceus, and 2 P. urinaeequi strains). Penicillin G, imipenem, gentamicin, netilmicin, erythromycin, clindamycin, rifampin, chloramphenicol, daptomycin, and ramoplanin were the most active. All strains of P. acidilactici were susceptible to novobiocin, whereas all isolates of P. pentosaceus were resistant. Novobiocin could therefore be helpful for differentiation of these two closely related species. P. acidilactici HM3020 was inducibly resistant to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin B-type (MLS) antibiotics. Resistance was due to a determinant homologous to ermAM and carried by a nontransferable 46-kb plasmid, pVM20. This plasmid was structurally distinct from two enterococcal MLS resistance plasmids, pIP819 and pAM beta 1. The 34 strains of P. acidilactici and P. pentosaceus were resistant to tetracycline, and total DNA of these strains did not hybridize to probes specific for tetK, tetL, tetM, and tetO.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axelsson L. T., Ahrné S. E., Andersson M. C., Ståhl S. R. Identification and cloning of a plasmid-encoded erythromycin resistance determinant from Lactobacillus reuteri. Plasmid. 1988 Sep;20(2):171–174. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(88)90023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buu-Hoï A., Le Bouguénec C., Horaud T. Genetic basis of antibiotic resistance in Aerococcus viridans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):529–534. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Yagi Y., Dunny G. M., Schultz S. K. Characterization of three plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid molecules in a strain of Streptococcus faecalis: identification of a plasmid determining erythromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):283–289. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.283-289.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colman G., Efstratiou A. Vancomycin-resistant leuconostocs, lactobacilli and now pediococci. J Hosp Infect. 1987 Jul;10(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0195-6701(87)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran G. D., Gibbons N., Mulvihill T. E. Septicaemia caused by Pediococcus pentosaceus: a new opportunistic pathogen. J Infect. 1991 Sep;23(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(91)92190-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courvalin P., Carlier C. Transposable multiple antibiotic resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):291–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00430441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Facklam R., Hollis D., Collins M. D. Identification of gram-positive coccal and coccobacillary vancomycin-resistant bacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Apr;27(4):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.4.724-730.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golledge C. L., Stingemore N., Aravena M., Joske D. Septicemia caused by vancomycin-resistant Pediococcus acidilactici. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jul;28(7):1678–1679. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.7.1678-1679.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez C. F., Kunka B. S. Plasmid transfer in Pediococcus spp.: intergeneric and intrageneric transfer of pIP501. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):81–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.81-89.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gots J. S. THE DETECTION OF PENICILLINASE-PRODUCING PROPERTIES OF MICROORGANISMS. Science. 1945 Sep 21;102(2647):309–309. doi: 10.1126/science.102.2647.309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handwerger S., Horowitz H., Coburn K., Kolokathis A., Wormser G. P. Infection due to Leuconostoc species: six cases and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1990 Jul-Aug;12(4):602–610. doi: 10.1093/clinids/12.4.602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshino T., Ikeda T., Tomizuka N., Furukawa K. Nucleotide sequence of the tetracycline resistance gene of pTHT15, a thermophilic Bacillus plasmid: comparison with staphylococcal TcR controls. Gene. 1985;37(1-3):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90265-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg H. D., Vellozzi E. M., Shapiro J., Rubin L. G. Clinical laboratory challenges in the recognition of Leuconostoc spp. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Mar;26(3):479–483. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.479-483.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. P., Uttley A. H., Woodford N., George R. C. Resistance to vancomycin and teicoplanin: an emerging clinical problem. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jul;3(3):280–291. doi: 10.1128/cmr.3.3.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan S. A., Novick R. P. Complete nucleotide sequence of pT181, a tetracycline-resistance plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus. Plasmid. 1983 Nov;10(3):251–259. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouguénec C., de Cespédès G., Horaud T. Molecular analysis of a composite chromosomal conjugative element (Tn3701) of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3930–3936. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3930-3936.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Courvalin P. Bacterial resistance to macrolide, lincosamide, and streptogramin antibiotics by target modification. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jul;35(7):1267–1272. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.7.1267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclercq R., Derlot E., Weber M., Duval J., Courvalin P. Transferable vancomycin and teicoplanin resistance in Enterococcus faecium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):10–15. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. Evolution and spread of tetracycline resistance determinants. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1989 Jul;24(1):1–3. doi: 10.1093/jac/24.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mabilat C., Courvalin P. Gene heterogeneity for resistance to macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins in Enterobacteriaceae. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;139(6):677–681. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin P., Trieu-Cuot P., Courvalin P. Nucleotide sequence of the tetM tetracycline resistance determinant of the streptococcal conjugative shuttle transposon Tn1545. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):7047–7058. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.7047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastro T. D., Spika J. S., Lozano P., Appel J., Facklam R. R. Vancomycin-resistant Pediococcus acidilactici: nine cases of bacteremia. J Infect Dis. 1990 May;161(5):956–960. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.5.956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Elimination of plasmids from several bacterial species by novobiocin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):423–426. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. Nucleotide sequence of ermA, a macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B determinant in Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.633-640.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raccach M. Pediococci and biotechnology. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;14(4):291–309. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riebel W. J., Washington J. A. Clinical and microbiologic characteristics of pediococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1348–1355. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1348-1355.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoff K. L., Kuritzkes D. R., Wolfson J. S., Ferraro M. J. Vancomycin-resistant gram-positive bacteria isolated from human sources. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2064–2068. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2064-2068.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahm D. F., Baker C. N., Jones R. N., Thornsberry C. Medium-dependent zone size discrepancies associated with susceptibility testing of group D streptococci against various cephalosporins. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Oct;18(4):858–865. doi: 10.1128/jcm.18.4.858-865.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims W. The isolation of pediococci from human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1966 Oct;11(10):967–972. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(66)90198-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson J. M., Facklam R. R., Thornsberry C. Antimicrobial susceptibility of vancomycin-resistant Leuconostoc, Pediococcus, and Lactobacillus species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):543–549. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomich P. K., An F. Y., Clewell D. B. Properties of erythromycin-inducible transposon Tn917 in Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1366–1374. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1366-1374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trieu-Cuot P., Carlier C., Courvalin P. Conjugative plasmid transfer from Enterococcus faecalis to Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4388–4391. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4388-4391.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane N., Jones R. N. In vitro activity of 43 antimicrobial agents tested against ampicillin-resistant enterococci and gram-positive species resistant to vancomycin. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jul-Aug;14(4):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(91)90025-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


