Abstract
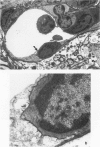
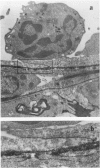
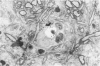
Most of the central nervous system (CNS) endothelium regulates the passage of solutes and functions as a blood-brain barrier (BBB). During experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an inflammatory demyelinating disease of the CNS, loss of BBB function occurs. The authors have previously shown an increase in endothelial transcytotic activity associated with decreased mitochondrial content as evidence of BBB dysfunction in EAE. These changes occurred in the capillary bed and correlated with CNS edema and clinical signs. In the present report, a fixation procedure before infusion of the intravascular tracer horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in rats at the height of clinical EAE has been used. In these animals, tracer leakage was only noted in inflamed venules with diameters of 12 to 19 mu. The authors detected several mechanisms of passive leakage: 1) increased junctional permeability; 2) increased interendothelial space; 3) leakage alongside migrating inflammatory cells. Some small capillaries showed necrotic changes with minimal tracer leakage. This report demonstrates that BBB disruption also occurs via nonendocytic mechanisms that may be induced by inflammatory cells.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aström K. E., Webster H. D., Arnason B. G. The initial lesion in experimental allergic neuritis. A phase and electron microscopic study. J Exp Med. 1968 Sep 1;128(3):469–495. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.3.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUBIS J. J., LUSE S. A. AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS IN THE RAT. Am J Pathol. 1964 Feb;44:299–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balin B. J., Broadwell R. D., Salcman M., el-Kalliny M. Avenues for entry of peripherally administered protein to the central nervous system in mouse, rat, and squirrel monkey. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Sep 8;251(2):260–280. doi: 10.1002/cne.902510209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A. Gamma-interferon: the match that lights the fire? Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91256-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brett J., Gerlach H., Nawroth P., Steinberg S., Godman G., Stern D. Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):1977–1991. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Bornstein M. B., Bloom B. R. The effects of macrophage depletion on the clinical and pathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):614–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Cammer W., Norton W. T., Bloom B. R. Proteinase inhibitors suppress the development of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Nature. 1980 May 22;285(5762):235–237. doi: 10.1038/285235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claudio L., Kress Y., Norton W. T., Brosnan C. F. Increased vesicular transport and decreased mitochondrial content in blood-brain barrier endothelial cells during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1989 Dec;135(6):1157–1168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R. T-cell vaccination against autoimmune disease. Hosp Pract (Off Ed) 1989 Feb 15;24(2):57–64. doi: 10.1080/21548331.1989.11703657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig S. W., Pardo J. V. alpha-Actinin localization in the junctional complex of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jan;80(1):203–210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.1.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorovini-Zis K., Sato M., Goping G., Rapoport S., Brightman M. Ionic lanthanum passage across cerebral endothelium exposed to hyperosmotic arabinose. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(1-2):49–60. doi: 10.1007/BF00685347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffey M. E., Hainau B., Ho S., Bentzel C. J. Regulation of epithelial tight junction permeability by cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Dec 3;294(5840):451–453. doi: 10.1038/294451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux E., Joó F. Effects of histamine on brain capillaries. Fine structural and immunohistochemical studies after intracarotid infusion. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00239384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faustmann P. M., Dermietzel R. Extravasation of polymorphonuclear leukocytes from the cerebral microvasculature. Inflammatory response induced by alpha-bungarotoxin. Cell Tissue Res. 1985;242(2):399–407. doi: 10.1007/BF00214554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmuntz E. A., Brosnan C. F., Norton W. T. Prazosin treatment suppresses increased vascular permeability in both acute and passively transferred experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3444–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M., Becker N. H., Levine S., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structural alterations of the blood-brain barrier in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jul;29(3):432–440. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Nong Y. H., Remold H. G. IFN-gamma, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and urokinase regulate the expression of urokinase receptors on human monocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4229–4234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPERT P., CARPENTER S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE VASCULAR PERMEABILITY AND THE MECHANISM OF DEMYELINATION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965 Jan;24:11–24. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196501000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Burridge K. Alpha-actinin: immunofluorescent localization of a muscle structural protein in nonmuscle cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):289–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S., Kennedy L. Cerebral vascular permeability and cellular infiltration in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):859–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Munoz J. J., Blaskett A. Acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. I. Adjuvant action of Bordetella pertussis is due to vasoactive amine sensitization and increased vascular permeability of the central nervous system. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 1;73(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzo A. V., Hedley-Whyte E. T., Eisenberg H. M., Hsu D. W. Increased penetration of horseradish peroxidase across the blood-brain barrier induced by Metrazol seizures. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):136–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90961-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marker O., Nielsen M. H., Diemer N. H. The permeability of the blood-brain barrier in mice suffering from fatal lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;63(3):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00685249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Maruta K., Burkart V., Gillis S., Kolb H. IL-1 and IFN-gamma increase vascular permeability. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):301–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Fujiwara M. Adoptively transferred experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in chimeric rats: identification of transferred cells in the lesions of the central nervous system. Immunology. 1988 Sep;65(1):23–29. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meldolesi J., Castiglioni G., Parma R., Nassivera N., De Camilli P. Ca++-dependent disassembly and reassembly of occluding junctions in guinea pig pancreatic acinar cells. Effect of drugs. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):156–172. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Mathieson G., Hüttner I. Blood-brain barrier opening to horseradish peroxidase in acute arterial hypertension. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Oct;48(1):45–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00691790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Peters H., Hüttner I. Charge-related alterations of the cerebral endothelium. Lab Invest. 1983 Dec;49(6):662–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy Z., Peters H., Hüttner I. Fracture faces of cell junctions in cerebral endothelium during normal and hyperosmotic conditions. Lab Invest. 1984 Mar;50(3):313–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):749–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oláh Z., Novák R., Lengyel I., Dux E., Joó F. Kinetics of protein phosphorylation in microvessels isolated from rat brain: modulation by second messengers. J Neurochem. 1988 Jul;51(1):49–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb04834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. E., Simionescu M., Simionescu N. Structural aspects of the permeability of the microvascular endothelium. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1979;463:11–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panitch H. S., McFarlin D. E. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: enhancement of cell-mediated transfer by concanavalin A. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):1134–1137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Howes E. L., Jr, Rubin R. M., Samples J. R. Ocular inflammatory effects of intravitreally-injected tumor necrosis factor. Am J Pathol. 1988 Oct;133(1):47–53. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Samples J. R., Hefeneider S. H., Howes E. L., Jr Ocular inflammatory effects of intravitreal interleukin 1. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Aug;105(8):1117–1120. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060080119040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstein M., Ettinghausen S. E., Rosenberg S. A. Extravasation of intravascular fluid mediated by the systemic administration of recombinant interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1735–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneeberger E. E., Lynch R. D. Tight junctions. Their structure, composition, and function. Circ Res. 1984 Dec;55(6):723–733. doi: 10.1161/01.res.55.6.723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick J., Brostoff S., Mason D. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the absence of a classical delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction. Severe paralytic disease correlates with the presence of interleukin 2 receptor-positive cells infiltrating the central nervous system. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):1058–1075. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simionescu M., Simionescu N., Palade G. E. Segmental differentiations of cell junctions in the vascular endothelium. The microvasculature. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):863–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Kaplan M. S., Gonatas N. K. A quantitative assay for experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat based on permeability of spinal cords to 125I-human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun D., Meyermann R., Wekerle H. Cytotoxic T cells in autoimmune disease of the central nervous system. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;532:221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb36341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werdelin O., McCluskey R. T. The nature and the specificity of mononuclear cells in experimental autoimmune inflammations and the mechanisms leading to their accumulation. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1242–1263. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]