Abstract
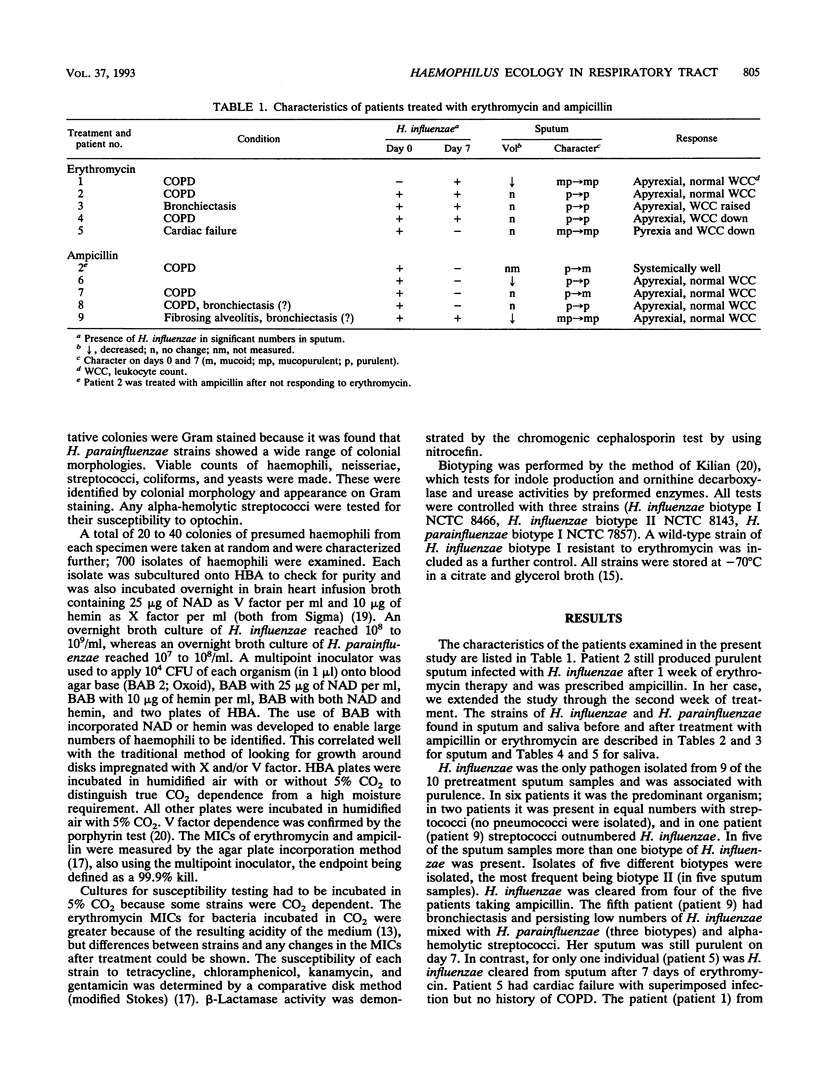
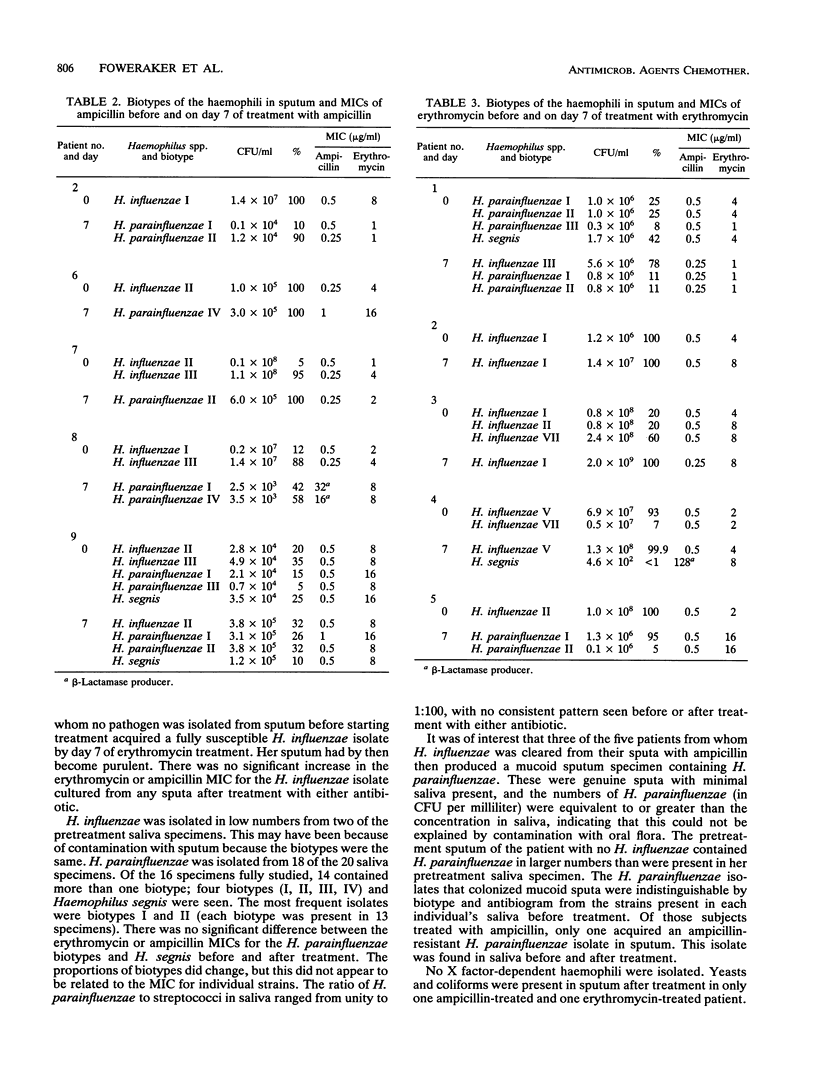
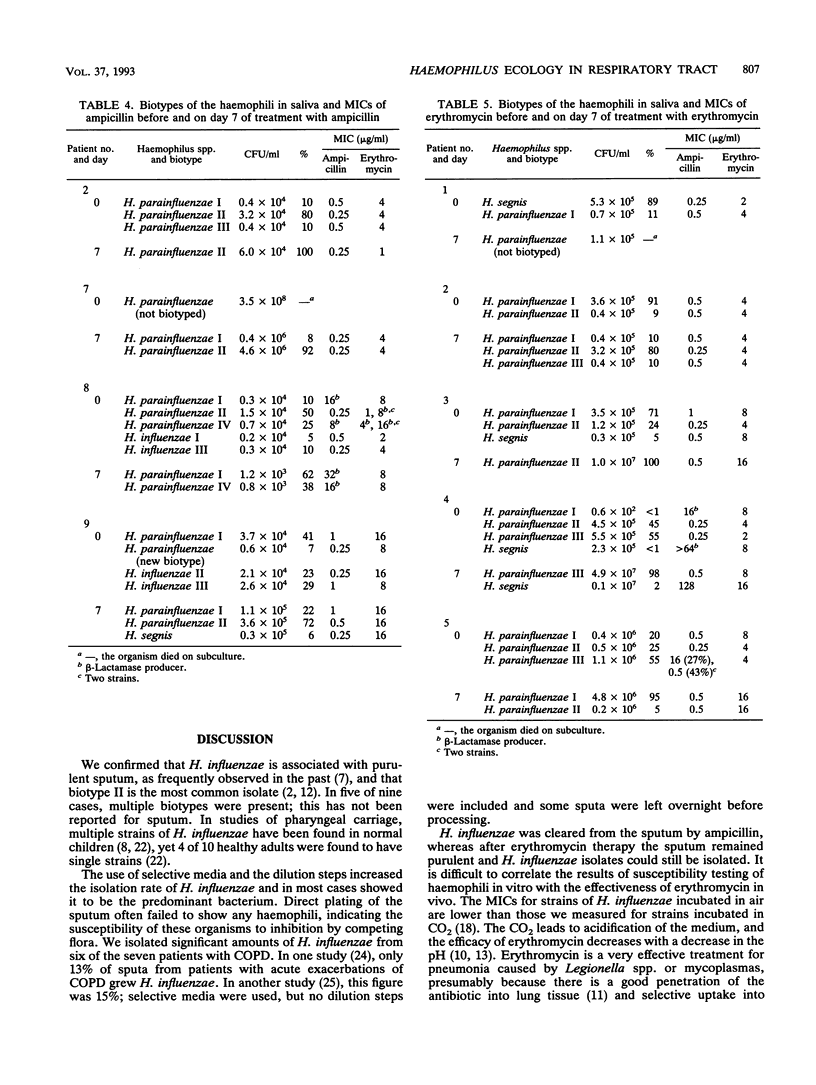
Nine patients with lower respiratory tract infections were used to study in detail the effect of ampicillin or erythromycin on the colonization patterns of Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae in sputum and saliva. H. influenzae was isolated from purulent sputum of eight patients before the start of treatment. Ampicillin was more effective than erythromycin at clearing H. influenzae from sputum and in decreasing purulence. By careful characterization of multiple strains, the changes in biotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility patterns were shown. Five biotypes of H. influenzae were associated with chest infection, with type II predominating. Mixed biotype infections occurred in five patients. Most saliva contained multiple biotypes of H. parainfluenzae. Neither antibiotic selected resistant haemophili in saliva or sputum. After treatment with ampicillin, the mucoid sputum was colonized with ampicillin-susceptible H. parainfluenzae biotypes previously found in saliva. We postulate that as inflammation decreases at the bronchial mucosa, the ampicillin concentration drops, allowing ampicillin-susceptible oral H. parainfluenzae isolates to seed the residual mucoid sputum.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton W. L., Brunton J. L., Meier M., Bowman M. N., Slaney L. A. Haemophilus influenzae: comparison of respiratory tract isolates with genitourinary tract isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Nov;16(5):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.5.826-831.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton W. L. Infections due to Haemophilus species other than H. influenzae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:199–216. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.001215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergogne-Berezin E. Penetration of antibiotics into the respiratory tree. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Sep;8(3):171–174. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.3.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumfitt W., Franklin I., Grady D., Hamilton-Miller J. M. Effect of amoxicillin-clavulanate and cephradine on the fecal flora of healthy volunteers not exposed to a hospital environment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):335–337. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Forey F., Gamondes J. P., Tebib A., Brune J., Fleurette J. Levels of erythromycin in pulmonary tissue and bronchial mucus compared to those of amoxycillin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Dec;8(6):459–466. doi: 10.1093/jac/8.6.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns M. W., May J. R. Haemophilus influenzae precipitins in the serum of patients with chronic bronchial disorders. Lancet. 1967 Feb 18;1(7486):354–358. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92895-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin K. C., Doern G. V. Selective media for recovery of Haemophilus influenzae from specimens contaminated with upper respiratory tract microbial flora. J Clin Microbiol. 1983 Jun;17(6):1163–1165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.17.6.1163-1165.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devalia J. L., Grady D., Harmanyeri Y., Tabaqchali S., Davies R. J. Histamine synthesis by respiratory tract micro-organisms: possible role in pathogenicity. J Clin Pathol. 1989 May;42(5):516–522. doi: 10.1136/jcp.42.5.516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb W. L., Digranes A., Bottolfsen K. L. Effects of carbon dioxide upon the in vitro activity of erythromycin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand B. 1986 Jun;94(3):173–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1986.tb03038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraschini F., Braga P. O., Copponi V., Gattei G., Guerrasco E., Scaglione F., Villa F., Scarpazza G. The tropism of erythromycin for the respiratory system. J Int Med Res. 1980;8 (Suppl 2):36–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groeneveld K., van Alphen L., Eijk P. P., Visschers G., Jansen H. M., Zanen H. C. Endogenous and exogenous reinfections by Haemophilus influenzae in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the effect of antibiotic treatment on persistence. J Infect Dis. 1990 Mar;161(3):512–517. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.3.512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAIGHT T. H., FINLAND M. The antibacterial action of erythromycin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Oct;81(1):175–183. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass H., Morris J. F., Samson S., Kilbourn J. P., Kim P. J. Bacterial flora of the respiratory tract in chronic bronchitis: comparison of transtracheal, fiberbronchoscopic, and oropharyngeal sampling methods. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jul;116(1):41–47. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimdahl A., Nord C. E. Effect of erythromycin and clindamycin on the indigenous human anaerobic flora and new colonization of the gastrointestinal tract. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Feb;1(1):38–48. doi: 10.1007/BF02014139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard A. J., Williams H. M. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Haemophilus influenzae in Wales. Report from the Standing Specialist Advisory Group for Microbiology in Wales. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1988 Feb;21(2):251–260. doi: 10.1093/jac/21.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilian M., Schiott C. R. Haemophili and related bacteria in the human oral cavity. Arch Oral Biol. 1975 Dec;20(12):791–796. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(75)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuklinska D., Kilian M. Relative proportions of Haemophilus species in the throat of healthy children and adults. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Jun;3(3):249–252. doi: 10.1007/BF02014895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey R. W., Lord V. L., Howson G. L., Luxton D. E., Trotter I. S. Double-blind study to compare the selection of antibiotic resistance by amoxycillin or cephradine in the commensal flora. Lancet. 1983 Sep 3;2(8349):529–532. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90566-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. R., Holt H. A., Reeves D. S., Hodson M. E. Cefaclor and amoxycillin in the treatment of infective exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1983 Jan;11(1):83–88. doi: 10.1093/jac/11.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHardy V. U., Inglis J. M., Calder M. A., Crofton J. W., Gregg I., Ryland D. A., Taylor P., Chadwick M., Coombs D., Riddell R. W. A study of infective and other factors in exacerbations of chronic bronchitis. Br J Dis Chest. 1980 Jul;74(3):228–238. doi: 10.1016/0007-0971(80)90048-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy T. F., Apicella M. A. Nontypable Haemophilus influenzae: a review of clinical aspects, surface antigens, and the human immune response to infection. Rev Infect Dis. 1987 Jan-Feb;9(1):1–15. doi: 10.1093/clinids/9.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prokesch R. C., Hand W. L. Antibiotic entry into human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Mar;21(3):373–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.21.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhind G. B., Gould G. A., Ahmad F., Croughan M. J., Calder M. A. Haemophilus parainfluenzae and H influenzae respiratory infections: comparison of clinical features. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1985 Sep 14;291(6497):707–708. doi: 10.1136/bmj.291.6497.707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims W. Oral haemophili. J Med Microbiol. 1970 Nov;3(4):615–625. doi: 10.1099/00222615-3-4-615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. B., Golden C. A., Kanner R. E., Renzetti A. D. Haemophilus influenzae and haemophilus parainfluenzae in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet. 1976 Jun 12;1(7972):1253–1255. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91733-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. M., Fisher M., Young J. E., Lutz W. Ampicillin levels in sputum, serum, and saliva. Thorax. 1970 May;25(3):304–311. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.3.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempro P. J., Slots J. Selective medium for the isolation of Haemophilus aphrophilus from the human periodontium and other oral sites and the low proportion of the organism in the oral flora. J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;23(4):777–782. doi: 10.1128/jcm.23.4.777-782.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



