Abstract
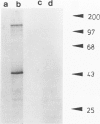
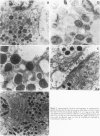
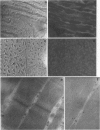
Any explanation of the causes of Alzheimer's disease and of its unique cerebral pathologic features must take into account the distribution and ultrastructural localization of the pre-A4 amyloid proteins in tissues and organs. The authors have analyzed the expression of the pre-A4 amyloid proteins in several tissues by immunogold electron microscopy and by immunofluorescence. For this purpose, they have used a mouse monoclonal antibody and a guinea pig antiserum raised against two synthetic peptides corresponding to two different sequences common to all the full-length forms of the A4 amyloid precursors. They observed a tissue-specific distribution of the secreted and the transmembrane form of the precursors. The authors could determine that the secreted form is generated in vivo within the cytoplasm. In the salivary glands and in the adenohypophysis, all the immunoreactivity is associated with the process of secretion, whereas in the muscle, a staining pattern compatible with the presence of the pre-A4 amyloid proteins in the sarcoplasmic reticulum has been observed. This difference in the localization may reflect tissue-specific processing pathways and suggests that posttranslational modifications such as proteolytic removal of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains contribute to the structural and thus functional diversity of the A4 amyloid precursors.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbach J. P. Action of proteolytic enzymes on lipotropins and endorphins: biosynthesis, biotransformation and fate. Pharmacol Ther. 1984;24(3):321–354. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(84)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Aebersold R., Ziltener H., Schrader J. W., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Automated chemical synthesis of a protein growth factor for hemopoietic cells, interleukin-3. Science. 1986 Jan 10;231(4734):134–139. doi: 10.1126/science.3079915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L., Wolska B., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Martins R., Simms G., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: prevalence in aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1688–1693. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyrks T., Weidemann A., Multhaup G., Salbaum J. M., Lemaire H. G., Kang J., Müller-Hill B., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, transmembrane orientation and biogenesis of the amyloid A4 precursor of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):949–957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02900.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. J., Hastings G. Z., Syred A. D., McGinn B., Brown F., Rowlands D. J. Non-responsiveness to a foot-and-mouth disease virus peptide overcome by addition of foreign helper T-cell determinants. Nature. 1987 Nov 12;330(6144):168–170. doi: 10.1038/330168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M., Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G. Correlation between scores for dementia and counts of 'senile plaques' in cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Nature. 1966 Jan 1;209(5018):109–110. doi: 10.1038/209109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., LaCorbiere M., Saitoh T., Cole G. Characterization of an amyloid beta precursor protein that binds heparin and contains tyrosine sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):2066–2069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert D., Schroeder R., LaCorbiere M., Saitoh T., Cole G. Amyloid beta protein precursor is possibly a heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein. Science. 1988 Jul 8;241(4862):223–226. doi: 10.1126/science.2968652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Selby M., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Bell G. I., Rutter W. J. Isolation and nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the precursor of mouse nerve growth factor. Nature. 1983 Apr 7;302(5908):538–540. doi: 10.1038/302538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J., Urdea M., Quiroga M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Fong N., Selby M., Rutter W. J., Bell G. I. Structure of a mouse submaxillary messenger RNA encoding epidermal growth factor and seven related proteins. Science. 1983 Jul 15;221(4607):236–240. doi: 10.1126/science.6602382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimonkevitz R., Colon S., Kappler J. W., Marrack P., Grey H. M. Antigen recognition by H-2-restricted T cells. II. A tryptic ovalbumin peptide that substitutes for processed antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2067–2074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivers B. D., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Salbaum M., Beyreuther K., Seeburg P. H. Alzheimer's disease amyloidogenic glycoprotein: expression pattern in rat brain suggests a role in cell contact. EMBO J. 1988 May;7(5):1365–1370. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02952.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., McClatchey A. I., Lamperti E. D., Villa-Komaroff L., Gusella J. F., Neve R. L. Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):528–530. doi: 10.1038/331528a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1983 Nov;14(5):497–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tierney M. C., Fisher R. H., Lewis A. J., Zorzitto M. L., Snow W. G., Reid D. W., Nieuwstraten P. The NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group criteria for the clinical diagnosis of probable Alzheimer's disease: a clinicopathologic study of 57 cases. Neurology. 1988 Mar;38(3):359–364. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.3.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidemann A., König G., Bunke D., Fischer P., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Beyreuther K. Identification, biogenesis, and localization of precursors of Alzheimer's disease A4 amyloid protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. T., Winchell L. F., McCune B. K., Earp H. S., Teixidó J., Massagué J., Herman B., Lee D. C. The TGF-alpha precursor expressed on the cell surface binds to the EGF receptor on adjacent cells, leading to signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann K., Herget T., Salbaum J. M., Schubert W., Hilbich C., Cramer M., Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Kang J., Lemaire H. G. Localization of the putative precursor of Alzheimer's disease-specific amyloid at nuclear envelopes of adult human muscle. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):367–372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02822.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sauvage F., Octave J. N. A novel mRNA of the A4 amyloid precursor gene coding for a possibly secreted protein. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):651–653. doi: 10.1126/science.2569763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]