Abstract
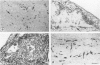
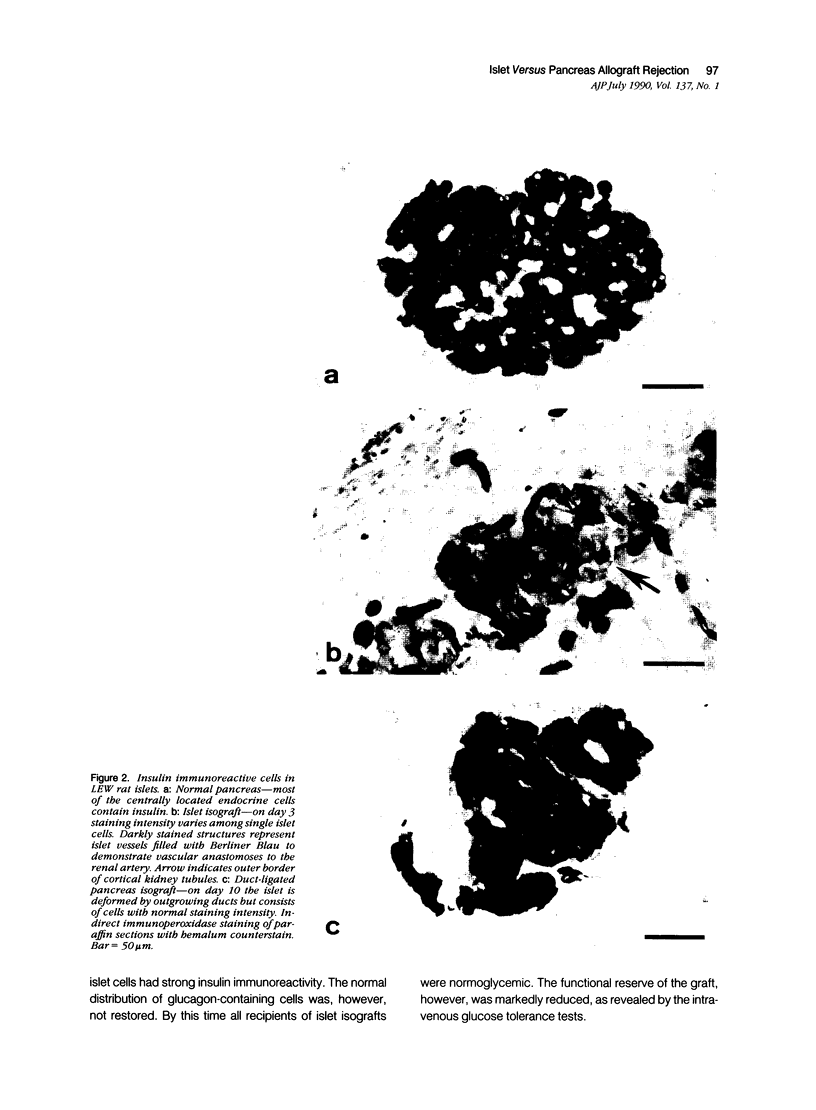
The course of acute rejection of major histocompatibility complex (MHC)-incompatible isolated rat pancreatic islets transplanted under the kidney capsule was monitored functionally and histologically from day 1 to 10. The patterns observed were compared to those of vascularized whole-pancreas transplants with preserved and suppressed exocrine secretion. In addition the morphologic reactions after isogenic transplantation of islets or whole-pancreas transplants are described. The sequential patterns of acute rejection were found to be essentially identical in isolated islet and whole-pancreas allografts. This was also true for the process of I-A-like class II MHC antigen induction. Endocrine cell necrosis and reduced insulin content of beta cells were detected in isolated islets but not in whole-organ isografts. Thus ischemic damage may have occurred to be transplanted islets on days 1 and 2 because connections to the renal vasculature were not demonstrated before day 3. Islet cell loss was, however, functionally compensated by beta cell proliferation beginning on day 4. From the first day after transplantation, an altered spacial distribution of insulin- and glucagon-containing cells was present in islet isografts. This phenomenon was, however, not unique to islets, but also occurred in duct-ligated whole-organ isografts on days 6 to 10.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buus S., Sette A., Grey H. M. The interaction between protein-derived immunogenic peptides and Ia. Immunol Rev. 1987 Aug;98:115–141. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00522.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christova T., Daskalova R. Intra-splenic transplantation of allogenic isolated pancreatic islets in nonimmunosuppressed rats. A morphological immunocytochemical study. Anat Anz. 1985;158(5):395–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean B. M., Walker R., Bone A. J., Baird J. D., Cooke A. Pre-diabetes in the spontaneously diabetic BB/E rat: lymphocyte subpopulations in the pancreatic infiltrate and expression of rat MHC class II molecules in endocrine cells. Diabetologia. 1985 Jul;28(7):464–466. doi: 10.1007/BF00280892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. W., Morris P. J. Developments in isolated pancreatic islet transplantation. Transplantation. 1987 Mar;43(3):321–331. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198703000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. W., Sutton R., McShane P., Peters M., Morris P. J. Exocrine contamination impairs implantation of pancreatic islets transplanted beneath the kidney capsule. J Surg Res. 1988 Nov;45(5):432–442. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(88)90193-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith R. C., Scharp D. W., Hartman B. K., Ballinger W. F., Lacy P. E. A morphologic study of intrahepatic portal-vein islet isografts. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):201–214. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart D. N., Fabre J. W. Major histocompatibility complex antigens in rat kidney, ureter, and bladder. Localization with monoclonal antibodies and demonstration of Ia-positive dendritic cells. Transplantation. 1981 May;31(5):318–325. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198105010-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart T. K., Pino R. M. Pseudoislet vascularization. Induction of diaphragm-fenestrated endothelia from the hepatic sinusoids. Lab Invest. 1986 Mar;54(3):304–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer J., Settje A. Vascularized pancreas transplantation in the rat--details of the microsurgical techniques, results, and complications. Transpl Int. 1989 Aug;2(2):84–91. doi: 10.1007/BF02459325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBAEK K. Intravenous glucose tolerance as a tool in definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Br Med J. 1962 Jun 2;1(5291):1507–1513. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5291.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster W. R., Williams A. F. Identification of Ia glycoproteins in rat thymus and purification from rat spleen. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jun;9(6):426–433. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard P. R., Reece-Smith H., Clark A., Jeffery E. L., McShane P., Morris P. J. The long-term allografted rat islet. A histologic and immunohistologic study. Am J Pathol. 1983 May;111(2):166–173. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pujol-Borrell R., Todd I., Doshi M., Bottazzo G. F., Sutton R., Gray D., Adolf G. R., Feldmann M. HLA class II induction in human islet cells by interferon-gamma plus tumour necrosis factor or lymphotoxin. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):304–306. doi: 10.1038/326304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., Falk P., Van der Meide P. H. Interferon-gamma in vivo. Induction and loss of class II MHC antigens and immature myelomonocytic cells in rat organs. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):661–669. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., Klempnauer J. Distinct histologic patterns of acute, prolonged, and chronic rejection in vascularized rat pancreas allografts. Am J Pathol. 1986 Aug;124(2):253–262. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., Klempnauer J., Wonigeit K. Altered distribution of class I and class II MHC antigens during acute pancreas allograft rejection in the rat. Transplantation. 1985 Sep;40(3):234–239. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198509000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D. E. Pancreas transplantation. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989 Aug;1(6):1195–1206. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Clark-Lewis I., Harris A. W., Schrader J. W. Effect of cloned interferon-gamma on expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on cell lines of hemopoietic, lymphoid, epithelial, fibroblastic and neuronal origin. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jan;14(1):52–56. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]