Abstract
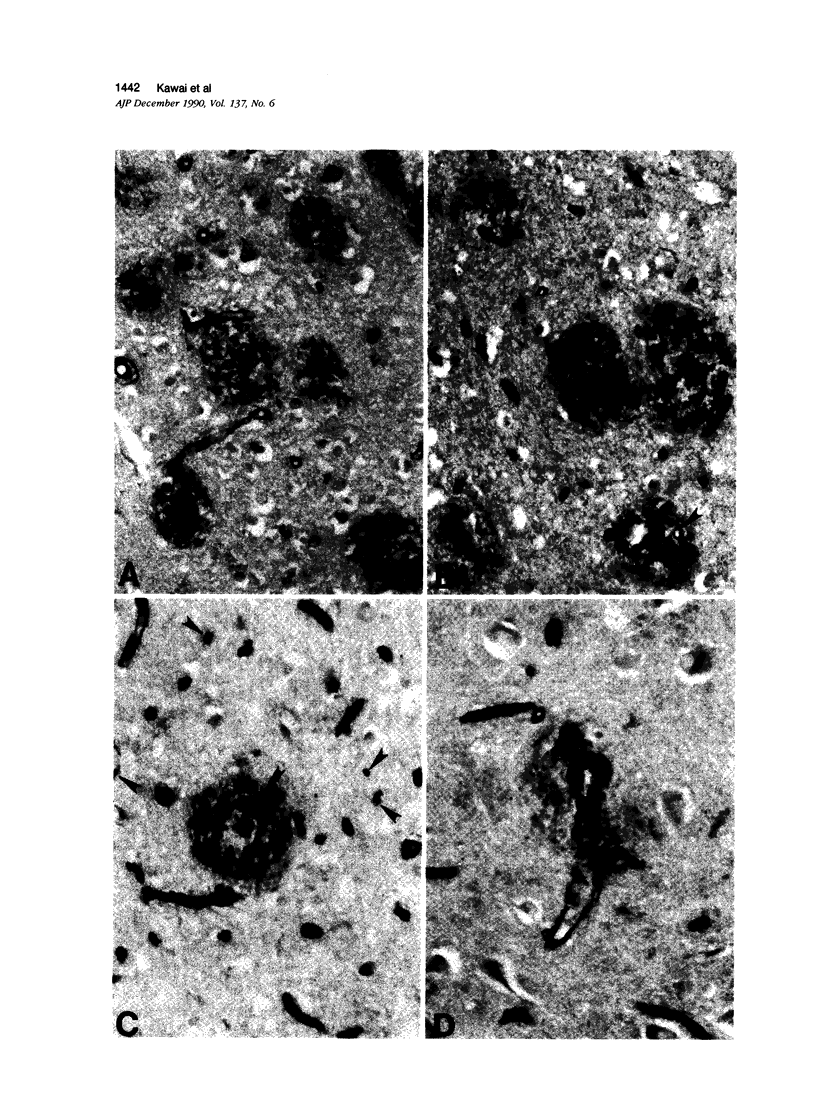
The authors examined the hypothesis that senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease (AD) are formed by abnormal leakage of amyloidogenic precursors from brain capillaries by quantitative analysis of the spatial relationship between capillaries and amyloid plaques. Vibratome sections (40 mu) of the hippocampus, including the entorhinal cortex, obtained at autopsy from AD subjects, were immunostained with a monoclonal antibody to beta-protein and counterstained with rabbit serum to either the glucose transporter protein, a cerebral endothelial marker, or collagen type IV, a basal lamina marker. The authors found that while 60% to 77% of amyloid plaques were associated with capillaries, only 8% to 13% were penetrated by a capillary, the remainder being adjacent. To test whether 1) the area occupied by amyloid plaques or 2) the border zone (10-mu rim) surrounding amyloid plaques has a statistically higher density of capillaries than 3) the remaining gray matter, similarly double-stained 6-mu sections from five AD subjects were photographed and the capillary densities in the three areas calculated. Capillary density was significantly lower in 1) than in 3) and higher in 2) than in 3), while the combined area of 1) and 2) showed the same capillary density as 3). Similar results were obtained by using either the glucose transporter or the collagen type IV antibodies. Because capillary density is low within, and high in regions that immediately surround amyloid plaques, our findings suggest that amyloid plaques exclude capillaries or lead to their degeneration, or both. The latter possibility was investigated by triple-staining tissue sections with antibodies to beta-protein, glucose transporter, and collagen type IV. The proportion of glucose transporter-negative capillaries was not significantly different in areas inside or outside of the plaques. Thus, the authors found no evidence of basal lamina remnants consistent with capillary degeneration preferential to amyloid plaques. Although a small number of capillaries showed amyloid deposition just beneath the basement membrane, the authors conclude that capillaries play only a limited direct role, if any, in amyloid plaque formation, and that the apparent association of amyloid plaques and capillaries is no more than a chance contact.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L., Lundahl P. C-terminal-specific monoclonal antibodies against the human red cell glucose transporter. Epitope localization with synthetic peptides. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11414–11420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arai H., Sagi N., Noguchi I., Haga S., Ishii T., Makino Y., Kosaka K. An immunohistochemical study of beta-protein in Alzheimer-type dementia brains. J Neurol. 1989 May;236(4):214–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00314502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsky S. H., Baker A., Siegal G. P., Togo S., Liotta L. A. Use of anti-basement membrane antibodies to distinguish blood vessel capillaries from lymphatic capillaries. Am J Surg Pathol. 1983 Oct;7(7):667–677. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198310000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach T. G., McGeer E. G. Lamina-specific arrangement of astrocytic gliosis and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease visual cortex. Brain Res. 1988 Nov 1;463(2):357–361. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90410-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell M. A., Ball M. J. Laminar variation in the microvascular architecture of normal human visual cortex (area 17). Brain Res. 1985 May 27;335(1):139–143. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)90284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell M. A., Ball M. J. The correlation of vascular capacity with the parenchymal lesions of Alzheimer's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1986 Nov;13(4 Suppl):456–461. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100037124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendotti C., Forloni G. L., Morgan R. A., O'Hara B. F., Oster-Granite M. L., Reeves R. H., Gearhart J. D., Coyle J. T. Neuroanatomical localization and quantification of amyloid precursor protein mRNA by in situ hybridization in the brains of normal, aneuploid, and lesioned mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3628–3632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron C., Ranalli P. J., Miceli P. N. Amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Can J Neurol Sci. 1987 Nov;14(4):564–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braak H., Braak E., Kalus P. Alzheimer's disease: areal and laminar pathology in the occipital isocortex. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(5):494–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00687251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORSELLIS J. A., BRIERLEY J. B. An unusual type of pre-senile dementia (atypical Alzheimer's disease with amyloid vascular change). Brain. 1954 Dec;77(4):571–587. doi: 10.1093/brain/77.4.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J. L., Falini B., Erber W. N., Ghosh A. K., Abdulaziz Z., MacDonald S., Pulford K. A., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (APAAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Feb;32(2):219–229. doi: 10.1177/32.2.6198355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cras P., Kawai M., Siedlak S., Mulvihill P., Gambetti P., Lowery D., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Greenberg B., Perry G. Neuronal and microglial involvement in beta-amyloid protein deposition in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):241–246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies L., Wolska B., Hilbich C., Multhaup G., Martins R., Simms G., Beyreuther K., Masters C. L. A4 amyloid protein deposition and the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: prevalence in aged brains determined by immunocytochemistry compared with conventional neuropathologic techniques. Neurology. 1988 Nov;38(11):1688–1693. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.11.1688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delacourte A., Defossez A., Persuy P., Peers M. C. Observation of morphological relationships between angiopathic blood vessels and degenerative neurites in Alzheimer's disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1987;411(3):199–204. doi: 10.1007/BF00735024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDE R. L., MAGEE K. R. Alzheimer's disease. Presentation of a case with pathologic and enzymatic-histochemical observatins. Neurology. 1962 Mar;12:213–222. doi: 10.1212/wnl.12.3.213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Congophilic microangiopathy in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's syndrome (presenile dementia). Med Hypotheses. 1979 Nov;5(11):1231–1236. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(79)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harik S. I., Kalaria R. N., Whitney P. M., Andersson L., Lundahl P., Ledbetter S. R., Perry G. Glucose transporters are abundant in cells with "occluding" junctions at the blood-eye barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4261–4264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel H. C., Rosenfeld M. G., Rosen O. M. Characterization of antisera to a synthetic carboxyl-terminal peptide of the glucose transporter protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda S., Allsop D., Glenner G. G. Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. An immunohistochemical study using amyloid beta-protein antibody. Lab Invest. 1989 Jan;60(1):113–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joachim C. L., Morris J. H., Selkoe D. J. Clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease: autopsy results in 150 cases. Ann Neurol. 1988 Jul;24(1):50–56. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalaria R. N., Gravina S. A., Schmidley J. W., Perry G., Harik S. I. The glucose transporter of the human brain and blood-brain barrier. Ann Neurol. 1988 Dec;24(6):757–764. doi: 10.1002/ana.410240610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khachaturian Z. S. Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1985 Nov;42(11):1097–1105. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1985.04060100083029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. A., Campbell M. J., Terry R. D., Morrison J. H. Laminar and regional distributions of neurofibrillary tangles and neuritic plaques in Alzheimer's disease: a quantitative study of visual and auditory cortices. J Neurosci. 1987 Jun;7(6):1799–1808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-06-01799.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majocha R. E., Benes F. M., Reifel J. L., Rodenrys A. M., Marotta C. A. Laminar-specific distribution and infrastructural detail of amyloid in the Alzheimer disease cortex visualized by computer-enhanced imaging of epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6182–6186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandybur T. I. The incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1975 Feb;25(2):120–126. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Shimoji A., Kuramoto R., Higuchi Y. The relationship between senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels in Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia. Morphological mechanism of senile plaque production. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1982 Aug;40(2):121–129. doi: 10.1007/BF02932857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa T., Sumiyoshi S., Murayama E., Deshimaru M. Ultrastructure of capillary plaque-like degeneration in senile dementia. Mechanism of amyloid production. Acta Neuropathol. 1974;29(3):229–236. doi: 10.1007/BF00685258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountjoy C. Q., Tomlinson B. E., Gibson P. H. Amyloid and senile plaques and cerebral blood vessels. A semi-quantitative investigation of a possible relationship. J Neurol Sci. 1982 Nov-Dec;57(1):89–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90113-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANTELAKIS S. Un type particuliar d'angiopathie sénile du systeme nerveux central: l'angiopathie congophile; topographie et fréquence. Monatsschr Psychiatr Neurol. 1954 Oct;128(4):219–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peers M. C., Lenders M. B., Défossez A., Delacourte A., Mazzuca M. Cortical angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease: the formation of dystrophic perivascular neurites is related to the exudation of amyloid fibrils from the pathological vessels. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol. 1988;414(1):15–20. doi: 10.1007/BF00749733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Lipphardt S., Mulvihill P., Kancherla M., Mijares M., Gambetti P., Sharma S., Maggiora L., Cornette J., Lobl T. Amyloid precursor protein in senile plaques of Alzheimer disease. Lancet. 1988 Sep 24;2(8613):746–746. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Morrison J. H. Quantitative morphology and regional and laminar distributions of senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 1985 Oct;5(10):2801–2808. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-10-02801.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblum W. I., Haider A. Negative correlations between parenchymal amyloid and vascular amyloid in hippocampus. Am J Pathol. 1988 Mar;130(3):532–536. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D. E., Goldgaber D., Burkhart D. S., Gilbert J. R., Gajdusek D. C., Roses A. D. Cellular localization of messenger RNA encoding amyloid-beta-protein in normal tissue and in Alzheimer disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1988;2(2):96–111. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198802020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torack R. M., Lynch R. G. Cytochemistry of brain amyloid in adult dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(3):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00688021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Bancher C., Barcikowska M., Wen G. Y., Currie J. Spectrum of morphological appearance of amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(4):337–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00688170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Wen G. Y., Kim K. S. Comparison of four staining methods on the detection of neuritic plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;78(1):22–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00687398. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada M., Tsukagoshi H., Otomo E., Hayakawa M. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the aged. J Neurol. 1987 Aug;234(6):371–376. doi: 10.1007/BF00314080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]