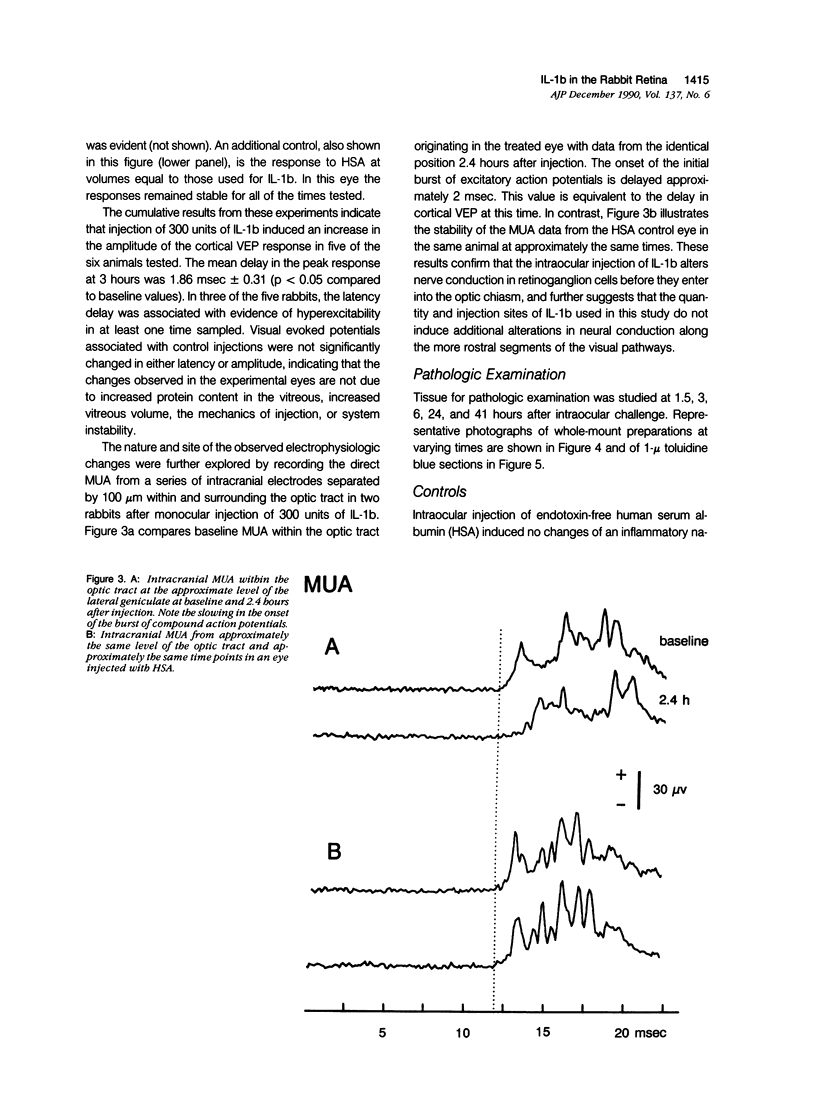
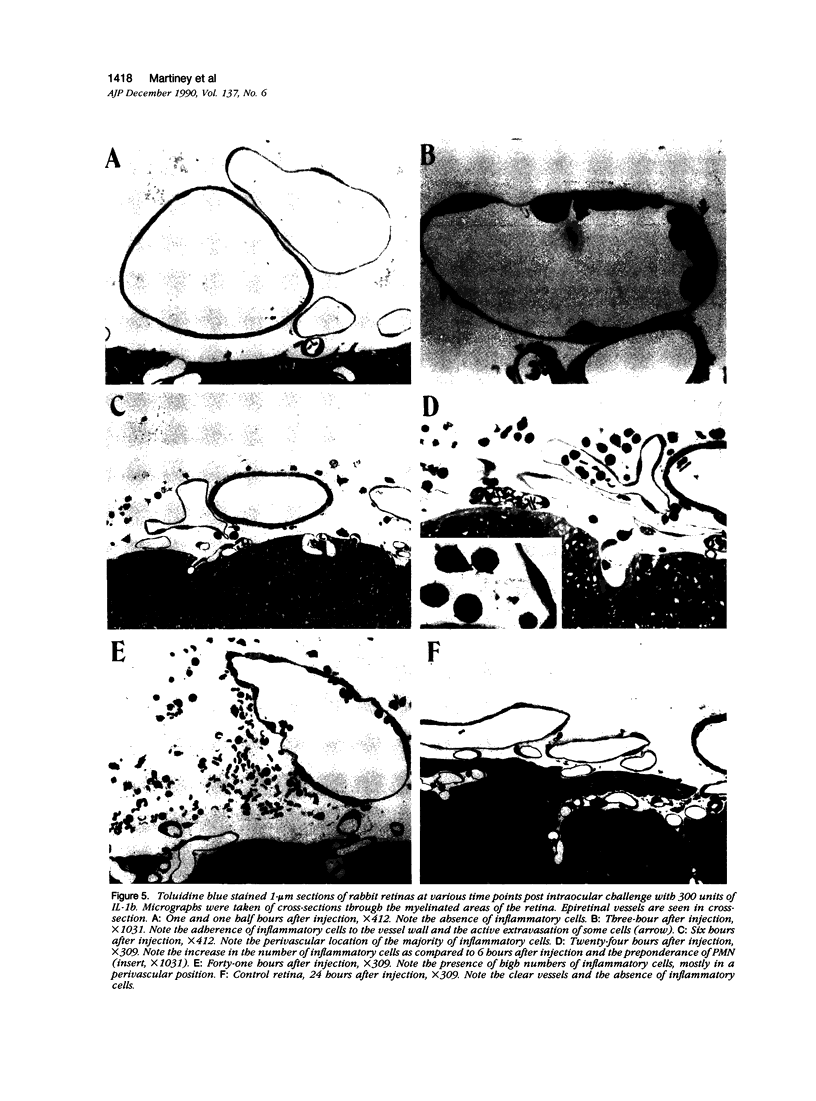
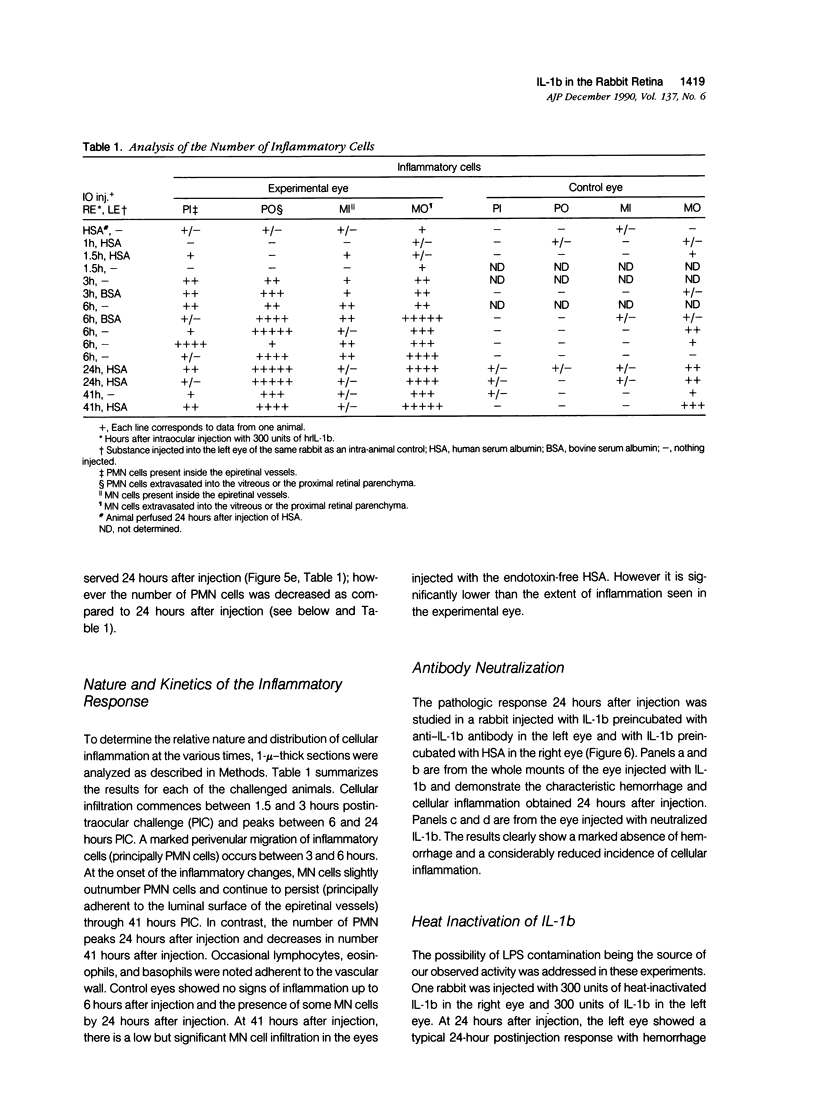
Abstract
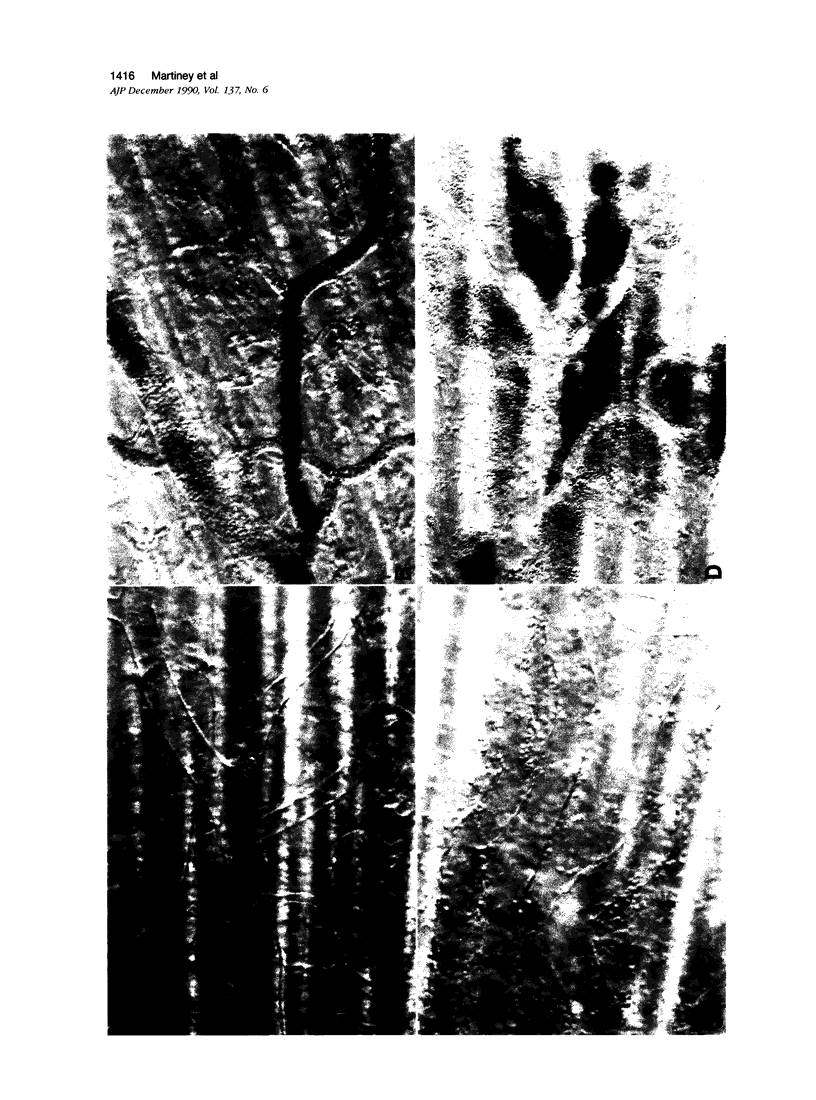
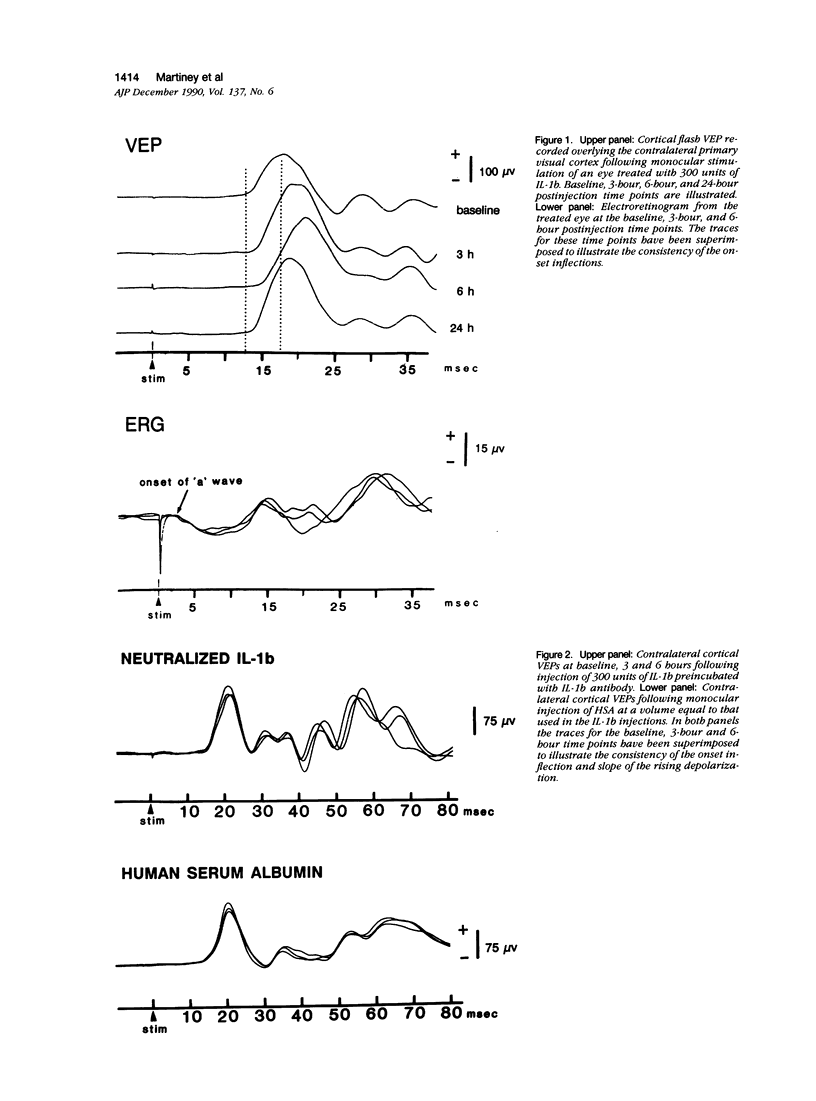
Interleukin-1 is a potent immunomodulator and has been shown to initiate many aspects of the inflammatory response. To determine the effects of IL-1b in the central nervous system (CNS), the rabbit retina was used, adjacent to which factors can be injected with minimal trauma and both pathologic and physiologic effects can be monitored. Intravitreal injection of 300 units of IL-1b induced an alteration in the visual evoked potentials (VEP) that was associated with marked intravascular red blood cell accumulations, hemorrhage, and cellular inflammation of the epiretinal vessels. Analysis of these events showed slowing and occasional hyper-excitability of the compound action potential of the optic tract and of the cortical VEP that correlate with the maximum inflammatory response. Histologic studies show the following: no apparent response occurs within the first 1.5 hours after intraocular challenge; and between 3 and 6 hours after injection an extensive intravascular red blood cell accumulation and progressive hemorrhage is accompanied by an increase in the number of mononuclear (MN) cells and the appearance of polymorphonuclear (PMN) cells. Polymorphonuclear cells continue to increase with time to give a single wave of inflammation that peaks 24 hours after injection, while the number of MN cells steadily increases. These events are associated with changes in the permeability of the blood-brain barrier and correlate with the electrophysiologic dysfunctions. Forty-one hours after injection, MN inflammation, reactive gliosis, and residual PMN inflammation are evident. Neutralization with specific antibody inhibited the responses through 6 hours after injection. It is concluded that the rabbit retina provides a valuable model for the in vivo analysis of CNS inflammation.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arezzo J. C., Brosnan C. F., Schroeder C. E., Litwak M. S., Bornstein M. B. Electrophysiological analysis of factors involved in the primary demyelinating diseases: the rabbit eye model system. Brain Res. 1988 Oct 18;462(2):286–300. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90557-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks W. A., Kastin A. J., Durham D. A. Bidirectional transport of interleukin-1 alpha across the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Bull. 1989 Dec;23(6):433–437. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90185-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 (IL-1) induces biosynthesis and cell surface expression of procoagulant activity in human vascular endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1984 Aug 1;160(2):618–623. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Wheeler M. E., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Interleukin 1 acts on cultured human vascular endothelium to increase the adhesion of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and related leukocyte cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):2003–2011. doi: 10.1172/JCI112200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., Saper C. B. Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3258444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Bornstein M. B., Bloom B. R. The effects of macrophage depletion on the clinical and pathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):614–620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Litwak M. S., Schroeder C. E., Selmaj K., Raine C. S., Arezzo J. C. Preliminary studies of cytokine-induced functional effects on the visual pathways in the rabbit. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Dec;25(2-3):227–239. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90141-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A., McFarlin D. E., Raine C. S. Chronologic neuropathology of relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1982 Feb;46(2):171–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavender D. E., Haskard D. O., Joseph B., Ziff M. Interleukin 1 increases the binding of human B and T lymphocytes to endothelial cell monolayers. J Immunol. 1986 Jan;136(1):203–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coceani F., Lees J., Dinarello C. A. Occurrence of interleukin-1 in cerebrospinal fluid of the conscious cat. Brain Res. 1988 Apr 19;446(2):245–250. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90883-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Colditz I. G., Movat H. Z. The role of interleukin-1 in neutrophil leukocyte emigration induced by endotoxin. Am J Pathol. 1986 Sep;124(3):367–372. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 and its biologically related cytokines. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:153–205. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60642-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Multiple biological properties of recombinant human interleukin 1 (beta). Immunobiology. 1986 Sep;172(3-5):301–315. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(86)80112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Schmidt J. A., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 1: an immunological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux E., Joó F. Effects of histamine on brain capillaries. Fine structural and immunohistochemical studies after intracarotid infusion. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00239384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emeis J. J., Kooistra T. Interleukin 1 and lipopolysaccharide induce an inhibitor of tissue-type plasminogen activator in vivo and in cultured endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1260–1266. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana A., Kristensen F., Dubs R., Gemsa D., Weber E. Production of prostaglandin E and an interleukin-1 like factor by cultured astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2413–2419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie M. B., McHugh D. D. Migration of neutrophils across endothelial monolayers is stimulated by treatment of the monolayers with interleukin-1 or tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3309–3317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallis B., Prickett K. S., Jackson J., Slack J., Schooley K., Sims J. E., Dower S. K. IL-1 induces rapid phosphorylation of the IL-1 receptor. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3235–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. II. The cellular source of potentiating mediator(s). J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):143–155. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., Lachman L. B. Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J Exp Med. 1986 Aug 1;164(2):594–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.2.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howes E. L., Jr, Wong K. L., Hartiala K. T., Webster R. O., Rosenbaum J. T. Complement and polymorphonuclear leukocytes do not determine the vascular permeability induced by intraocular LPS. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):35–42. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. C., Male D. K., Lantos P. L. Adhesion of lymphocytes to cerebral microvascular cells: effects of interferon-gamma, tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):677–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legatt A. D., Arezzo J., Vaughan H. G., Jr Averaged multiple unit activity as an estimate of phasic changes in local neuronal activity: effects of volume-conducted potentials. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Apr;2(2):203–217. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90061-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. Allergic encephalomyelitis: new form featuring polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Science. 1971 Feb 5;171(3970):498–499. doi: 10.1126/science.171.3970.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Kawai K., Fujiwara M. Hemorrhagic autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by adoptive transfer of activated semiallogeneic spleen cells into irradiated rats. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):306–315. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser R., Schleiffenbaum B., Groscurth P., Fehr J. Interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate human vascular endothelial cells to promote transendothelial neutrophil passage. J Clin Invest. 1989 Feb;83(2):444–455. doi: 10.1172/JCI113903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Hajjar K. A., Silverstein R. L., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawroth P. P., Handley D. A., Esmon C. T., Stern D. M. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell procoagulant while suppressing cell-surface anticoagulant activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3460–3464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberge F. G., Caspi R. R., Nussenblatt R. B. Glial retinal Müller cells produce IL-1 activity and have a dual effect on autoimmune T helper lymphocytes. Antigen presentation manifested after removal of suppressive activity. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2193–2196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. T., Samples J. R., Hefeneider S. H., Howes E. L., Jr Ocular inflammatory effects of intravitreal interleukin 1. Arch Ophthalmol. 1987 Aug;105(8):1117–1120. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1987.01060080119040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. M., Rosenbaum J. T. A platelet-activating factor antagonist inhibits interleukin 1-induced inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90704-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J. The development of astrocytes and blood vessels in the postnatal rabbit retina. J Neurocytol. 1988 Aug;17(4):433–449. doi: 10.1007/BF01189801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons J. A., Bundick R. V., Suckling A. J., Rumsby M. G. Cerebrospinal fluid interleukin 1 like activity during chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1987 Jun;68(3):648–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavoico G. B., Ewenstein B. M., Schafer A. I., Pober J. S. IL-1 and related cytokines enhance thrombin-stimulated PGI2 production in cultured endothelial cells without affecting thrombin-stimulated von Willebrand factor secretion or platelet-activating factor biosynthesis. J Immunol. 1989 Jun 1;142(11):3993–3999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]