Abstract
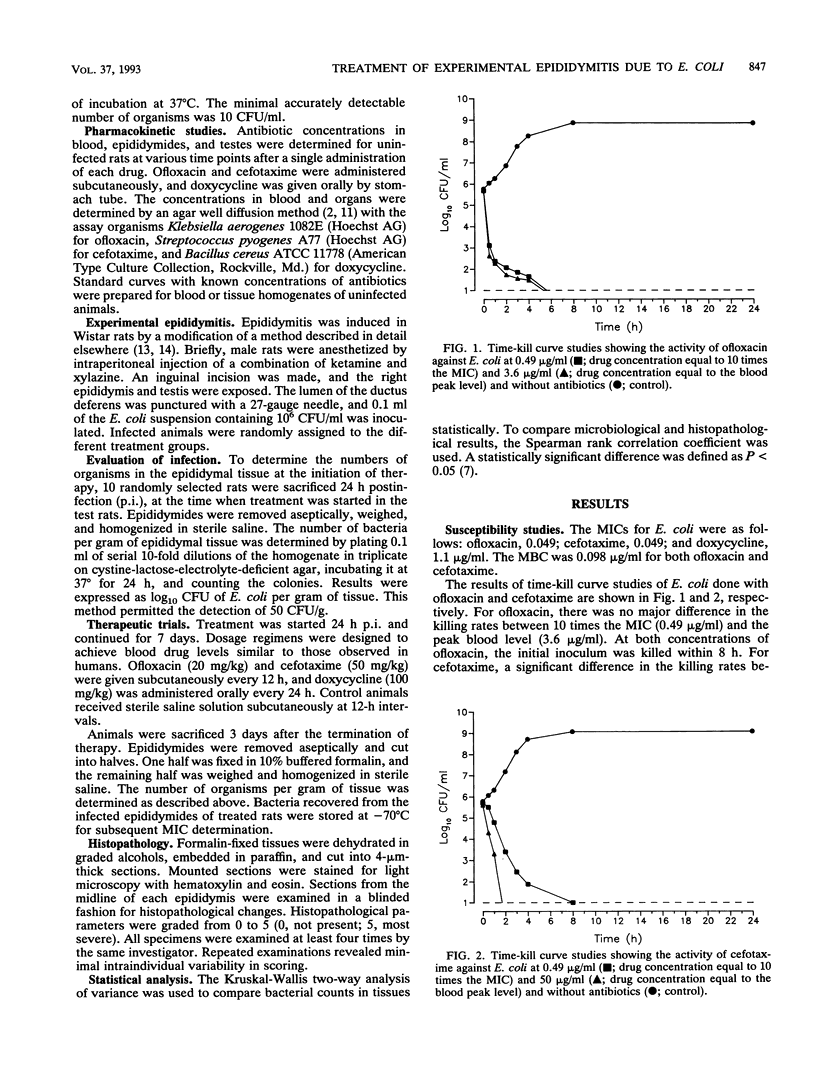
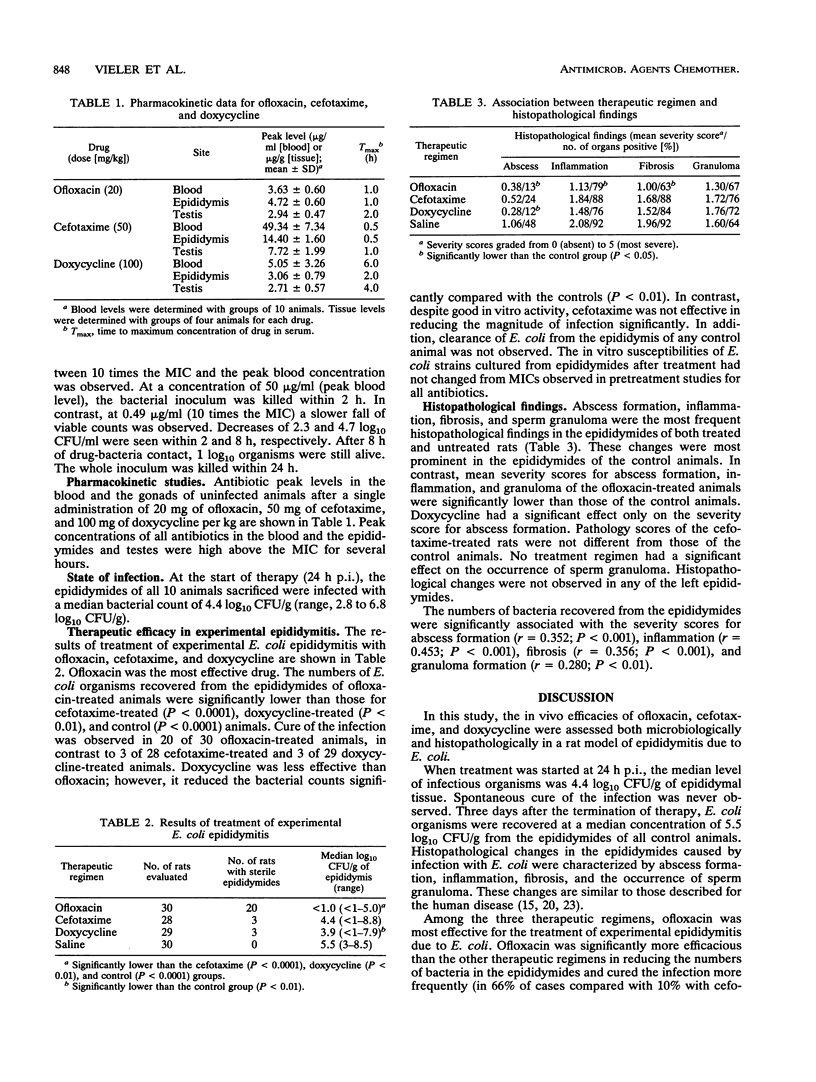
The in vivo efficacy of ofloxacin was compared with those of cefotaxime and doxycycline in a rat model of epididymitis due to Escherichia coli. Treatment was started 24 h after infection and was continued for 7 days. Ofloxacin reduced the numbers of E. coli organisms in the epididymides significantly more than the other therapeutic regimens and cured the infection more frequently. Histopathological changes in the epididymides of ofloxacin-treated animals were significantly less severe than those observed in untreated animals. Doxycycline was less effective than ofloxacin but significantly reduced the titers of organisms in rat epididymides. In contrast, despite excellent in vitro activity, cefotaxime failed to reduce the magnitude of infection. The results of this study suggest that ofloxacin may be a very effective antimicrobial agent for the treatment of epididymitis due to E. coli.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker H. C., Weidner W., Schiefer H. G., Brunner H., Krause W. Epididymitis. Untersuchungen zur Atiologie und Pathogenese unter besonderer Berücksichtigung von Chlamydia trachomatis und Ureaplasma urealyticum. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1984 Apr 13;109(15):569–575. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1069234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. V., Brodie J. L., Benner E. J., Kirby W. M. Simplified, accurate method for antibiotic assay of clinical specimens. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):170–177. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.170-177.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger R. E., Alexander E. R., Harnisch J. P., Paulsen C. A., Monda G. D., Ansell J., Holmes K. K. Etiology, manifestations and therapy of acute epididymitis: prospective study of 50 cases. J Urol. 1979 Jun;121(6):750–754. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)56978-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunha B. A., Garabedian-Ruffalo S. M. Tetracyclines in urology: current concepts. Urology. 1990 Dec;36(6):548–556. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(90)80201-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalhoff A., Ullmann U. Correlation between pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and efficacy of antibacterial agents in animal models. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;9(7):479–487. doi: 10.1007/BF01964287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng R. H., Smith S. M., Cherubin C. E., Tan E. N. Evaluation of two methods for overcoming the antibiotic carry-over effect. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Jan;10(1):34–38. doi: 10.1007/BF01967095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Avonts D., Piot P. Treatment of genital chlamydial infection with ofloxacin. Infection. 1986;14 (Suppl 4):S318–S320. doi: 10.1007/BF01661307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber A. U., Brugger H. P., Feller C., Stritzko T., Stalder B. Antibiotic therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa in normal and granulocytopenic mice: comparison of murine and human pharmacokinetics. J Infect Dis. 1986 Jan;153(1):90–97. doi: 10.1093/infdis/153.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. K., Berger R. E., Alexander E. R. Acute epididymitis: etiology and therapy. Arch Androl. 1979 Dec;3(4):309–316. doi: 10.3109/01485017908988421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantos C., Baumgärtner W., Durchfeld B., Schiefer H. G. Experimental epididymitis due to Chlamydia trachomatis in rats. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2324–2328. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2324-2328.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantos C., Krauss H., Altmannsberger M., Thiele D., Weidner W., Schiefer H. G. Experimental chlamydial epididymitis. Urol Int. 1989;44(5):279–283. doi: 10.1159/000281523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiviat M. D., Kiviat N. B., Berger R. E. Chlamydia trachomatis epididymitis diagnosed by fluorescent monoclonal antibody. Urology. 1987 Oct;30(4):395–397. doi: 10.1016/0090-4295(87)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leggett J. E., Fantin B., Ebert S., Totsuka K., Vogelman B., Calame W., Mattie H., Craig W. A. Comparative antibiotic dose-effect relations at several dosing intervals in murine pneumonitis and thigh-infection models. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meylan P. R., Francioli P., Glauser M. P. Discrepancies between MBC and actual killing of viridans group streptococci by cell-wall-active antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):418–423. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk J. P., Campoli-Richards D. M. Ofloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1987 Apr;33(4):346–391. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198733040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen O. S. An experimental study of the treatment of bacterial epididymitis. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1987;104:115–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saivin S., Houin G. Clinical pharmacokinetics of doxycycline and minocycline. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1988 Dec;15(6):355–366. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198815060-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- See W. A., Taylor T. O., Mack L. A., Tartaglione T. A., Opheim K. E., Berger R. E. Bacterial epididymitis in the rat: a model for assessing the impact of acute inflammation on epididymal antibiotic penetration. J Urol. 1990 Sep;144(3):780–784. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)39591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartaglione T. A., Taylor T. O., Opheim K. E., See W. A., Berger R. E. Antimicrobial tissue penetration in a rat model of E. coli epididymitis. J Urol. 1991 Nov;146(5):1413–1417. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)38126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelman B., Gudmundsson S., Leggett J., Turnidge J., Ebert S., Craig W. A. Correlation of antimicrobial pharmacokinetic parameters with therapeutic efficacy in an animal model. J Infect Dis. 1988 Oct;158(4):831–847. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.4.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner W., Garbe C., Weissbach L., Harbrecht J., Kleinschmidt K., Schiefer H. G., Friedrich H. J. Initiale Therapie der akuten einseitigen Epididymitis mit Ofloxacin. I. Klinische und mikrobiologische Befunde. Urologe A. 1990 Sep;29(5):272–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weidner W., Schiefer H. G., Garbe C. Acute nongonococcal epididymitis. Aetiological and therapeutic aspects. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):111–117. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson J. S., Hooper D. C. Treatment of genitourinary tract infections with fluoroquinolones: activity in vitro, pharmacokinetics, and clinical efficacy in urinary tract infections and prostatitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Oct;33(10):1655–1661. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.10.1655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


