Abstract
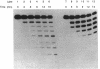
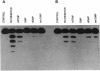
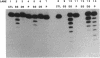
A 3'-exonuclease(s) that excised 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) monophosphate (AZTMP) from the 3' terminus of DNA was partially purified from two human cell lines. AZTMP inhibited the hydrolysis of AZTMP-terminated single-stranded and double-stranded DNA substrates. Thus, high levels of AZTMP might inhibit the exonuclease and trigger the toxicity of AZT by impairing the repair of AZTMP-terminated DNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzarini J., Pauwels R., Baba M., Herdewijn P., de Clercq E., Broder S., Johns D. G. The in vitro and in vivo anti-retrovirus activity, and intracellular metabolism of 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine are highly dependent on the cell species. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 1;37(5):897–903. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger D., Ståhle L., Li S. L., Oberg B. Long-term tolerance and efficacy of 3'-azidothymidine and 3'-fluorothymidine treatment of asymptomatic monkeys infected with simian immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1770–1772. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Cheng Y. C. Herpes simplex virus type I DNA polymerase. Kinetic properties of the associated 3'-5' exonuclease activity and its role in araAMP incorporation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8525–8530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Schooley R. T. The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):185–191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridland A., Connelly M. C., Ashmun R. Relationship of deoxynucleotide changes to inhibition of DNA synthesis induced by the antiretroviral agent 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine and release of its monophosphate by human lymphoid cells (CCRF-CEM). Mol Pharmacol. 1990 May;37(5):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho H. T., Hitchcock M. J. Cellular pharmacology of 2',3'-dideoxy-2',3'-didehydrothymidine, a nucleoside analog active against human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jun;33(6):844–849. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.6.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang P., Chubb S., Plunkett W. Termination of DNA synthesis by 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine. A mechanism for cytotoxicity. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16617–16625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Tsushita K., Itoh T., Ogura M., Hotta T., Saneyoshi M., Yoshida S., Saitoh H., Tomoda Y., Nagai Y. In vitro bone marrow toxicity of nucleoside analogs against human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Apr;33(4):576–579. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.4.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Soni A. Exonucleolytic proofreading enhances the fidelity of DNA synthesis by chick embryo DNA polymerase-gamma. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4450–4459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. D., Beattie K. L. Influence of divalent metal activator on the specificity of misincorporation during DNA synthesis catalyzed by DNA polymerase I of Escherichia coli. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;198(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langen P., Kowollik G., Etzold G., Venner H., Reinert H. The phosphorylation of 3'-deoxy-3'-fluorothymidine and its incorporation into DNA in a cellfree system from tumor cells. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1972;29(4):483–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansuri M. M., Hitchcock M. J., Buroker R. A., Bregman C. L., Ghazzouli I., Desiderio J. V., Starrett J. E., Sterzycki R. Z., Martin J. C. Comparison of in vitro biological properties and mouse toxicities of three thymidine analogs active against human immunodeficiency virus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Apr;34(4):637–641. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.4.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. E., Miller W. H. Human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Substrate and inhibitor kinetics with thymidine 5'-triphosphate and 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine 5'-triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20302–20307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R., Schinazi R. F., Zhou Z. Uridine reverses the toxicity of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine in normal human granulocyte-macrophage progenitor cells in vitro without impairment of antiretroviral activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Jul;32(7):997–1001. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.7.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommadossi J. P., Carlisle R., Zhou Z. Cellular pharmacology of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine with evidence of incorporation into DNA of human bone marrow cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;36(1):9–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi P., Calabresi P., Goulette F. A., Renaud C. A., Darnowski J. W. Azidothymidine-induced cytotoxicity and incorporation into DNA in the human colon tumor cell line HCT-8 is enhanced by methotrexate in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 1;52(15):4069–4073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez-Padua M. A., Starnes M. C., Cheng Y. C. Incorporation of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine into cellular DNA and its removal in a human leukemic cell line. Cancer Commun. 1990;2(1):55–62. doi: 10.3727/095535490820874740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veloso D., Guynn R. W., Oskarsson M., Veech R. L. The concentrations of free and bound magnesium in rat tissues. Relative constancy of free Mg 2+ concentrations. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4811–4819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Broder S. Anti-retroviral therapy of AIDS and related disorders: general principles and specific development of dideoxynucleosides. Pharmacol Ther. 1989;40(3):329–348. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(89)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Klecker R. W., Weinhold K. J., Markham P. D., Lyerly H. K., Durack D. T., Gelmann E., Lehrman S. N., Blum R. M., Barry D. W. Administration of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine, an inhibitor of HTLV-III/LAV replication, to patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1986 Mar 15;1(8481):575–580. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92808-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z., Hitchcock M. J., Sommadossi J. P. Metabolism and DNA interaction of 2',3'-didehydro-2',3'-dideoxythymidine in human bone marrow cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Nov;40(5):838–845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]