Abstract
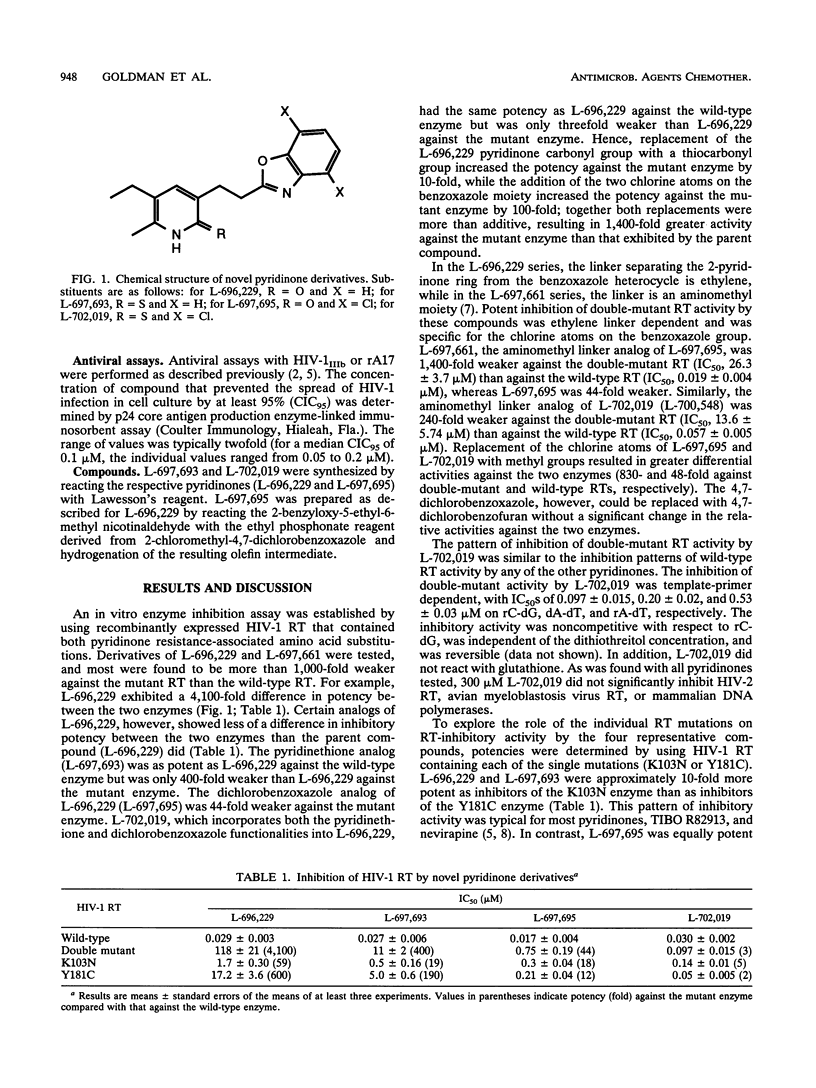
Pyridinone derivatives are potent and specific inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT) and HIV-1 replication in cell culture. However, the potential clinical usefulness of these compounds as monotherapeutic agents may be limited by the selection of inhibitor-resistant viral variants. Resistance in cell culture is due primarily to mutational alterations at RT amino acid residues 103 and 181. A recombinant HIV-1 RT containing both of these mutations was used to screen a panel of pyridinone analogs for inhibitory activity. L-696,229 and L-697,661, pyridinones currently undergoing clinical evaluation, were more than 4,000-fold weaker against the mutant enzyme than against the wild-type enzyme. In contrast, one derivative of L-696,229, L-702,019 (3-[2-(4,7-dichlorobenzoxazol-2-yl)ethyl]-5-ethyl-6-methylpyrid in-2(1H)-thione), showed only three-fold different potencies against the two enzymes. L-702,019 was also a potent inhibitor of the replication of mutant HIV-1 containing the individual mutations at amino acid 103 or 181 as well as of clinical isolates resistant to L-697,661 and L-696,229. Isolation and analysis of resistant viral variants in cell culture showed that significant resistance to L-702,019 could be engendered only by multiple amino acid substitutions in RT. Accordingly, these studies demonstrated the potential of identifying second-generation specific HIV-1 RT inhibitors that can overcome the viral resistance selected by the first generation of inhibitors.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coen D. M. Antiviral drug resistance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;616:224–237. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb17843.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. E., Nunberg J. H., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Schleif W. A., Freund K. F., Gaul S. L., Saari W. S., Wai J. S., Hoffman J. M. Pyridinone derivatives: specific human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors with antiviral activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6863–6867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. E., O'Brien J. A., Ruffing T. L., Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Quintero J. C., Siegl P. K., Hoffman J. M., Smith A. M., Emini E. A. L-696,229 specifically inhibits human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and possesses antiviral activity in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 May;36(5):1019–1023. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.5.1019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Hargrave K. D., Labadia M., Grozinger K., Skoog M., Wu J. C., Shih C. K., Eckner K., Hattox S., Adams J. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.1701568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Schols D., Kukla M. J., Breslin H. J., Raeymaeckers A., Van Gelder J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. Potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in vitro by a novel series of TIBO derivatives. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):470–474. doi: 10.1038/343470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saari W. S., Hoffman J. M., Wai J. S., Fisher T. E., Rooney C. S., Smith A. M., Thomas C. M., Goldman M. E., O'Brien J. A., Nunberg J. H. 2-Pyridinone derivatives: a new class of nonnucleoside, HIV-1-specific reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 1991 Sep;34(9):2922–2925. doi: 10.1021/jm00113a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardana V. V., Emini E. A., Gotlib L., Graham D. J., Lineberger D. W., Long W. J., Schlabach A. J., Wolfgang J. A., Condra J. H. Functional analysis of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase amino acids involved in resistance to multiple nonnucleoside inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17526–17530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


