Abstract
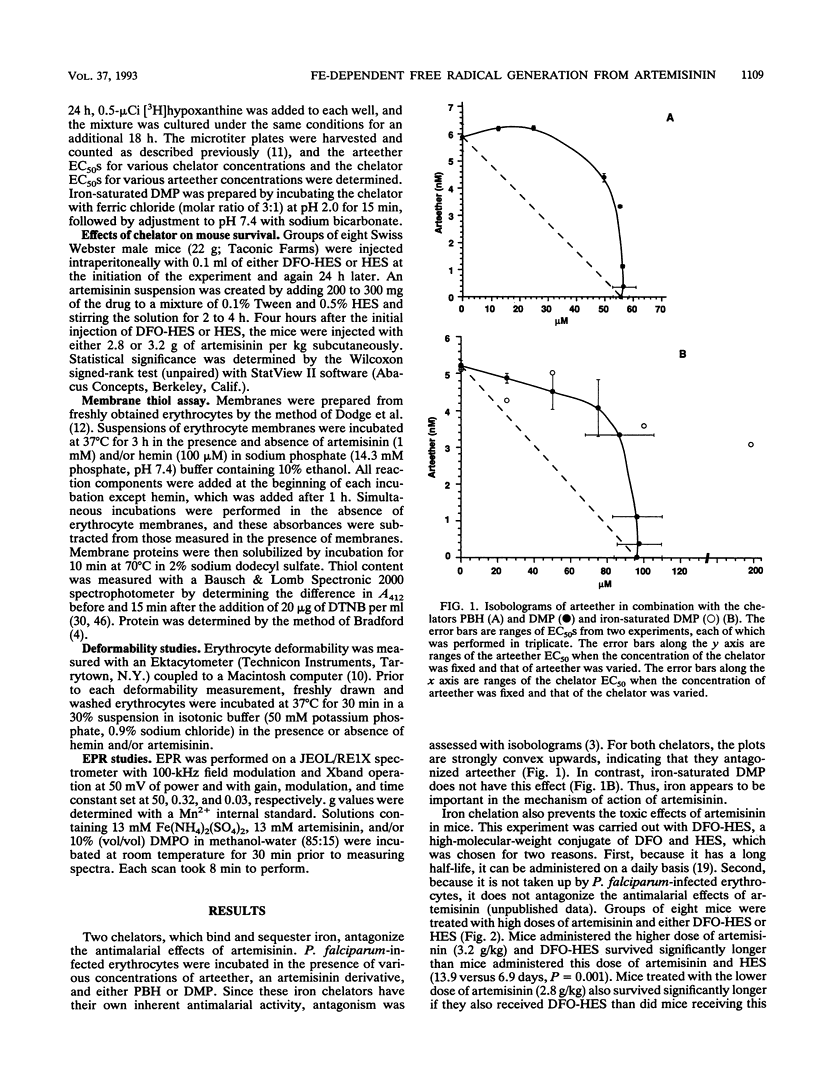
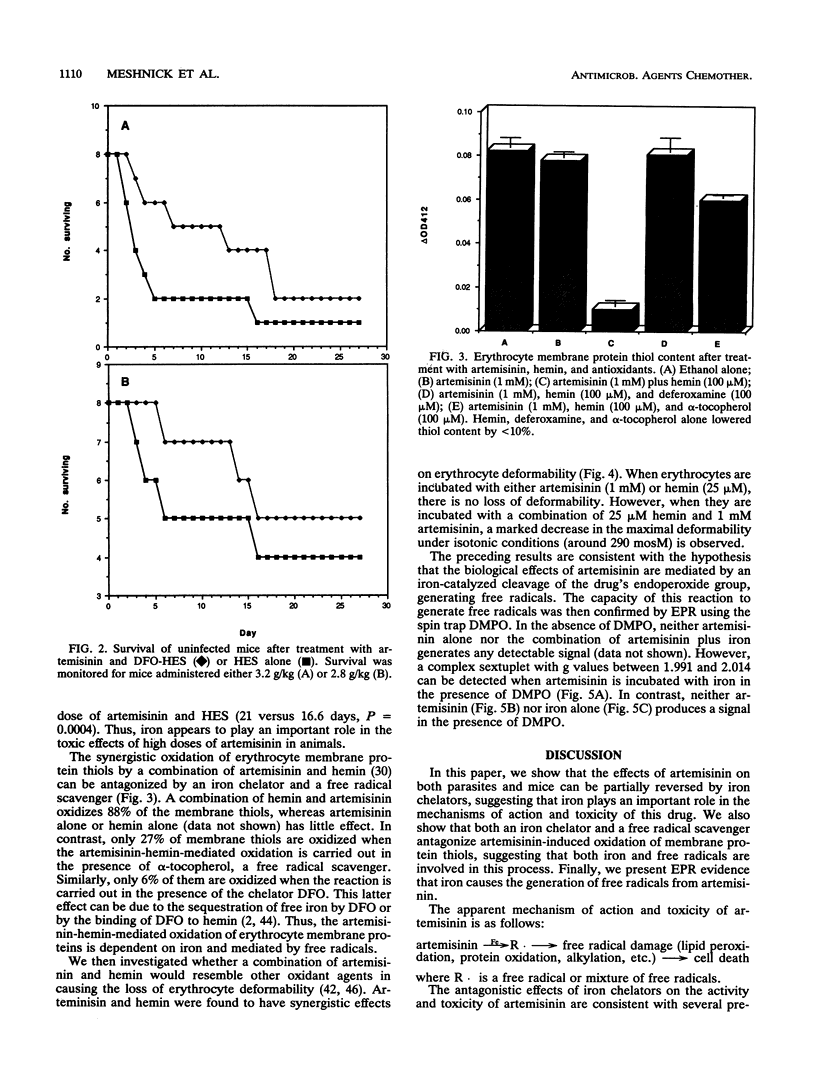
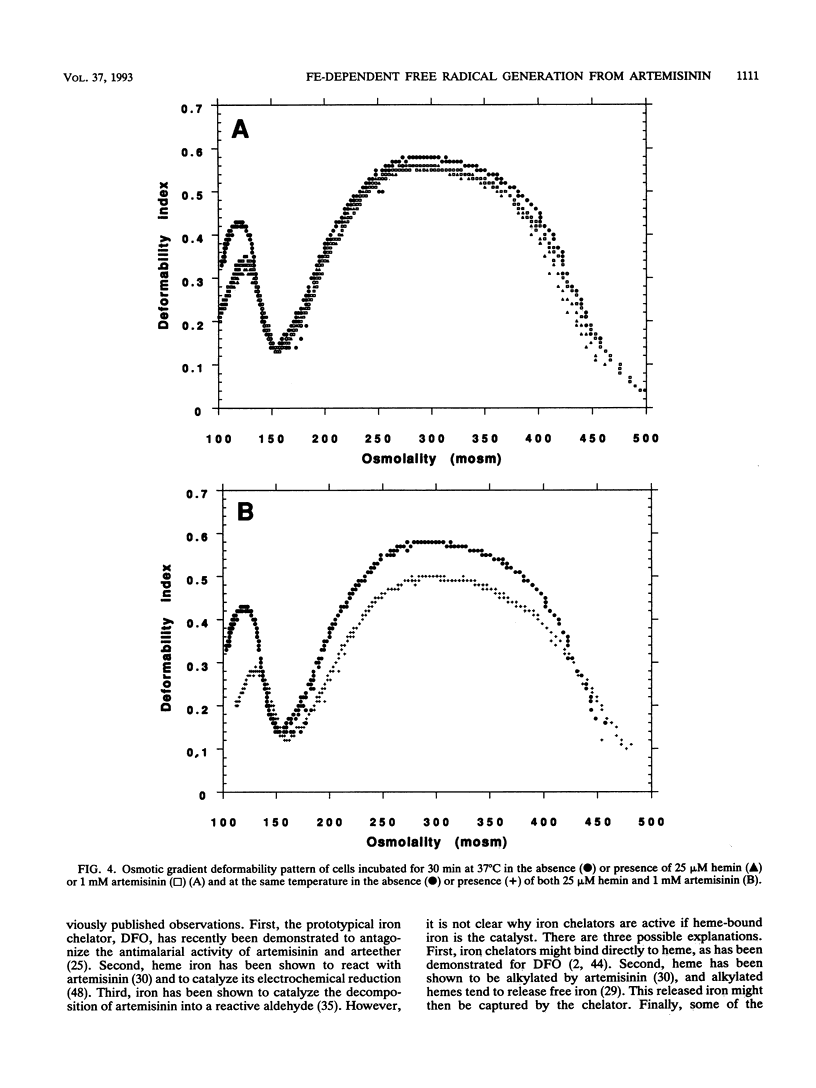
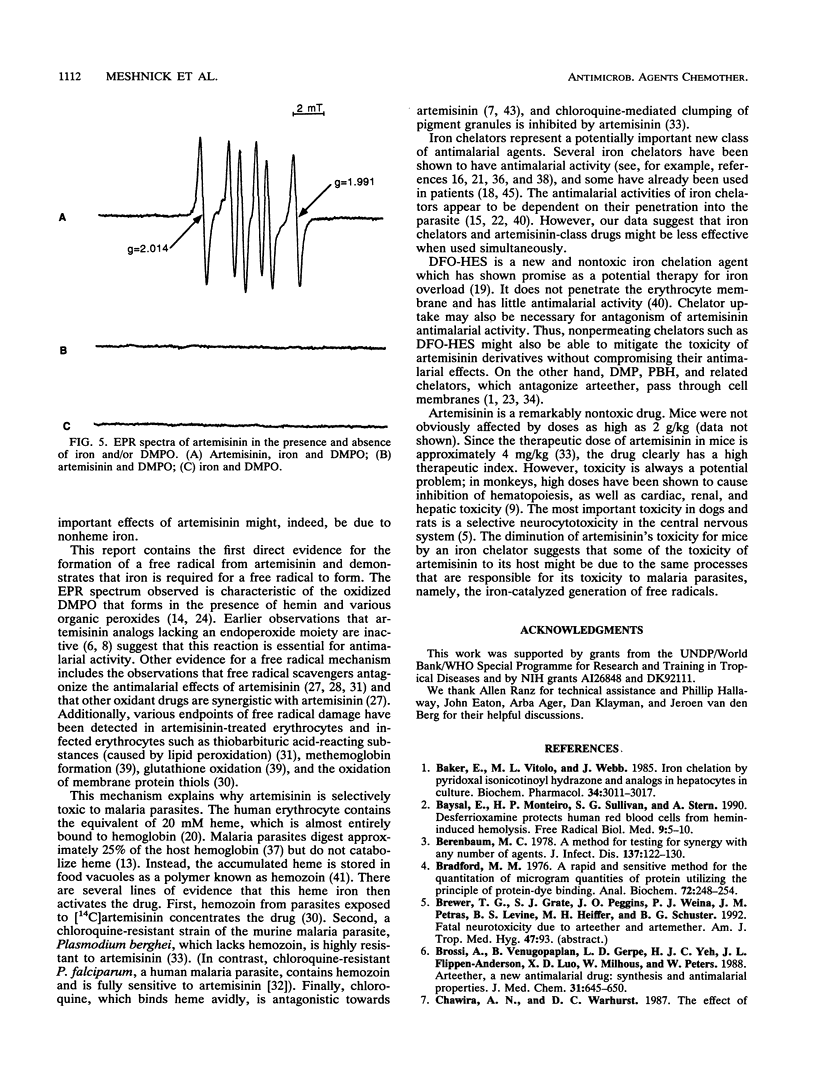
Artemisinin is an important new antimalarial agent containing a bridged endoperoxide. The in vitro antimalarial activity of an artemisinin derivative, arteether, is antagonized by two iron chelators, pyridoxal benzoylhydrazone and 1,2-dimethyl-3-hydroxypyrid-4-one. Similarly, the acute toxicity of artemisinin in mice is antagonized by another chelator, deferoxamine-hydroxyethylstarch. A combination of artemisinin and hemin oxidizes erythrocyte membrane thiols in vitro, and this oxidation is also inhibited by an iron chelator. Thus, iron plays a role in the mechanisms of action and toxicity of artemisinin. The combination of artemisinin and hemin also decreases erythrocyte deformability. Iron probably catalyzes the generation of free radicals from artemisinin since alpha-tocopherol antagonizes the thiol-oxidizing activity of artemisinin and since a spin-trapped free radical signal can be seen by electron paramagnetic resonance only when artemisinin is incubated in the presence of iron.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker E., Vitolo M. L., Webb J. Iron chelation by pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone and analogues in hepatocytes in culture. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Sep 1;34(17):3011–3017. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90142-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baysal E., Monteiro H. P., Sullivan S. G., Stern A. Desferrioxamine protects human red blood cells from hemin-induced hemolysis. Free Radic Biol Med. 1990;9(1):5–10. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(90)90043-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berenbaum M. C. A method for testing for synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):122–130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brossi A., Venugopalan B., Dominguez Gerpe L., Yeh H. J., Flippen-Anderson J. L., Buchs P., Luo X. D., Milhous W., Peters W. Arteether, a new antimalarial drug: synthesis and antimalarial properties. J Med Chem. 1988 Mar;31(3):645–650. doi: 10.1021/jm00398a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chawira A. N., Warhurst D. C. The effect of artemisinin combined with standard antimalarials against chloroquine-sensitive and chloroquine-resistant strains of Plasmodium falciparum in vitro. J Trop Med Hyg. 1987 Feb;90(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark M. R., Mohandas N., Shohet S. B. Osmotic gradient ektacytometry: comprehensive characterization of red cell volume and surface maintenance. Blood. 1983 May;61(5):899–910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins R. E., Canfield C. J., Haynes J. D., Chulay J. D. Quantitative assessment of antimalarial activity in vitro by a semiautomated microdilution technique. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1979 Dec;16(6):710–718. doi: 10.1128/aac.16.6.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckman J. R., Modler S., Eaton J. W., Berger E., Engel R. R. Host heme catabolism in drug-sensitive and drug-resistant malaria. J Lab Clin Med. 1977 Oct;90(4):767–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. A., Soong L. M. Spin trapping in biological systems. Oxidation of the spin trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-1-oxide by a hydroperoxide-hematin-system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch G., Jung A. 14C-desferrioxamine B: uptake into erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(6):709–713. doi: 10.1007/BF00925092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritsch G., Sawatzki G., Treumer J., Jung A., Spira D. T. Plasmodium falciparum: inhibition in vitro with lactoferrin, desferriferrithiocin, and desferricrocin. Exp Parasitol. 1987 Feb;63(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(87)90072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Slater A. F., Cerami A., Henderson G. B. Hemoglobin degradation in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum: an ordered process in a unique organelle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordeuk V. R., Thuma P. E., Brittenham G. M., Zulu S., Simwanza G., Mhangu A., Flesch G., Parry D. Iron chelation with desferrioxamine B in adults with asymptomatic Plasmodium falciparum parasitemia. Blood. 1992 Jan 15;79(2):308–312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallaway P. E., Eaton J. W., Panter S. S., Hedlund B. E. Modulation of deferoxamine toxicity and clearance by covalent attachment to biocompatible polymers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10108–10112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebbel R. P., Eaton J. W. Pathobiology of heme interaction with the erythrocyte membrane. Semin Hematol. 1989 Apr;26(2):136–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppner D. G., Hallaway P. E., Kontoghiorghes G. J., Eaton J. W. Antimalarial properties of orally active iron chelators. Blood. 1988 Jul;72(1):358–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko C., Peto T. E. Deferoxamine inhibition of malaria is independent of host iron status. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):375–387. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. R., Ponka P. A study of the mechanism of action of pyridoxal isonicotinoyl hydrazone at the cellular level using reticulocytes loaded with non-heme 59Fe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jun 9;757(3):306–315. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalyanaraman B., Mottley C., Mason R. P. A direct electron spin resonance and spin-trapping investigation of peroxyl free radical formation by hematin/hydroperoxide systems. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3855–3858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klayman D. L. Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science. 1985 May 31;228(4703):1049–1055. doi: 10.1126/science.3887571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krungkrai S. R., Yuthavong Y. The antimalarial action on Plasmodium falciparum of qinghaosu and artesunate in combination with agents which modulate oxidant stress. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1987;81(5):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(87)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levander O. A., Ager A. L., Jr, Morris V. C., May R. G. Qinghaosu, dietary vitamin E, selenium, and cod-liver oil: effect on the susceptibility of mice to the malarial parasite Plasmodium yoelii. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Aug;50(2):346–352. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/50.2.346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks G. S., McCluskey S. A., Mackie J. E., Riddick D. S., James C. A. Disruption of hepatic heme biosynthesis after interaction of xenobiotics with cytochrome P-450. FASEB J. 1988 Sep;2(12):2774–2783. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.12.3044903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshnick S. R., Thomas A., Ranz A., Xu C. M., Pan H. Z. Artemisinin (qinghaosu): the role of intracellular hemin in its mechanism of antimalarial action. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Dec;49(2):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90062-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meshnick S. R., Tsang T. W., Lin F. B., Pan H. Z., Chang C. N., Kuypers F., Chiu D., Lubin B. Activated oxygen mediates the antimalarial activity of qinghaosu. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;313:95–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhous W. K., Gerena L., Kyle D. E., Oduola A. M. In vitro strategies for circumventing antimalarial drug resistance. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1989;313:61–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters W., Li Z. L., Robinson B. L., Warhurst D. C. The chemotherapy of rodent malaria, XL. The action of artemisinin and related sesquiterpenes. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1986 Oct;80(5):483–489. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1986.11812054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter J. B., Gyparaki M., Burke L. C., Huehns E. R., Sarpong P., Saez V., Hider R. C. Iron mobilization from hepatocyte monolayer cultures by chelators: the importance of membrane permeability and the iron-binding constant. Blood. 1988 Nov;72(5):1497–1503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raventos-Suarez C., Pollack S., Nagel R. L. Plasmodium falciparum: inhibition of in vitro growth by desferrioxamine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1982 Sep;31(5):919–922. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1982.31.919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth E. F., Jr, Brotman D. S., Vanderberg J. P., Schulman S. Malarial pigment-dependent error in the estimation of hemoglobin content in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cells: implications for metabolic and biochemical studies of the erythrocytic phases of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1986 Sep;35(5):906–911. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1986.35.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheibel L. W., Stanton G. G. Antimalarial activity of selected aromatic chelators. IV. Cation uptake by Plasmodium falciparum in the presence of oxines and siderochromes. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Oct;30(4):364–369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Meshnick S. R., Williams R. A., Chiu D. T., Pan H. C., Lubin B. H., Kuypers F. A. Qinghaosu-mediated oxidation in normal and abnormal erythrocytes. J Lab Clin Med. 1989 Oct;114(4):401–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. D., Ranz A., Kuypers F. A., Lubin B. H., Meshnick S. R. Parasite uptake of desferroxamine: a prerequisite for antimalarial activity. Br J Haematol. 1990 Aug;75(4):598–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1990.tb07805.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater A. F., Cerami A. Inhibition by chloroquine of a novel haem polymerase enzyme activity in malaria trophozoites. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):167–169. doi: 10.1038/355167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. M., Fortier N. L., Trainor J., Jacobs J., Leb L., Lubin B., Chiu D., Shohet S., Mohandas N. Effect of hydrogen peroxide exposure on normal human erythrocyte deformability, morphology, surface characteristics, and spectrin-hemoglobin cross-linking. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1971–1977. doi: 10.1172/JCI112196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahel E., Druilhe P., Gentilini M. Antagonism of chloroquine with other antimalarials. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(2):221–221. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traore O., Carnevale P., Kaptue-Noche L., M'Bede J., Desfontaine M., Elion J., Labie D., Nagel R. L. Preliminary report on the use of desferrioxamine in the treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Am J Hematol. 1991 Jul;37(3):206–208. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830370316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilsen B., Nielsen H. Reaction of phenylhydrazine with erythrocytes. Cross-linking of spectrin by disulfide exchange with oxidized hemoglobin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Sep 1;33(17):2739–2748. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90690-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Gosser D. K., Jr, Meshnick S. R. Hemin-catalyzed decomposition of artemisinin (qinghaosu). Biochem Pharmacol. 1992 Apr 15;43(8):1805–1809. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(92)90713-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



