Abstract
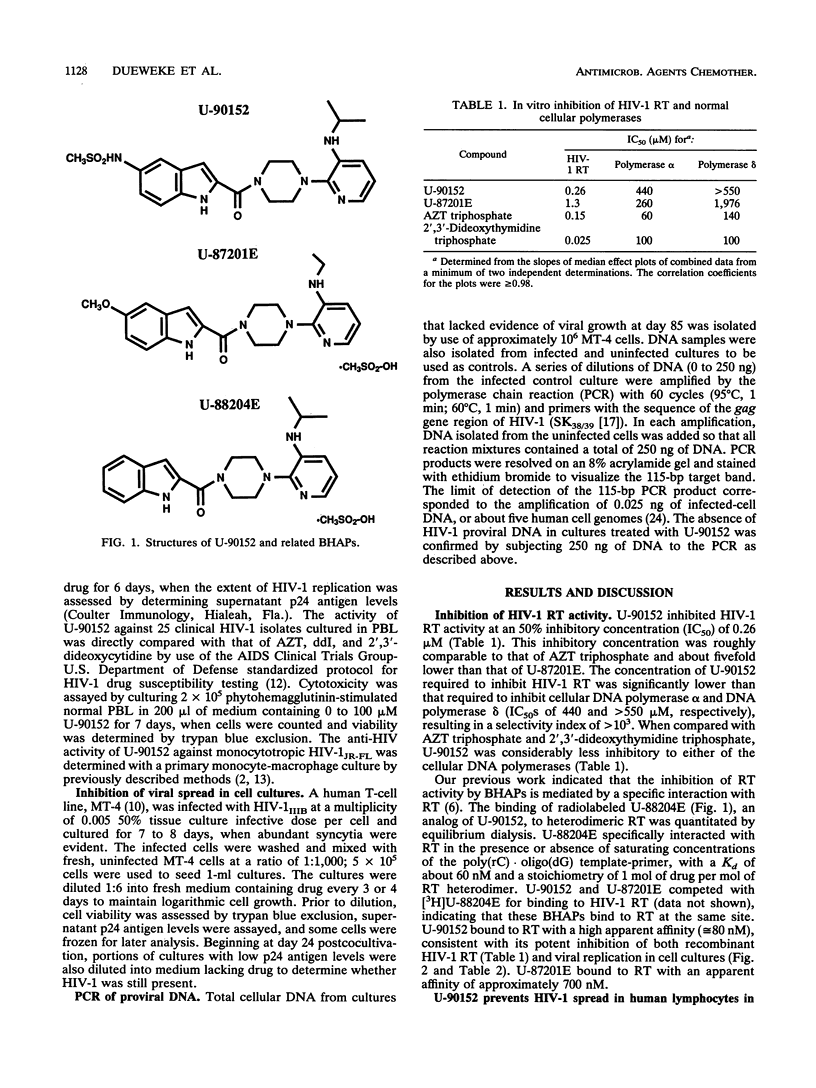
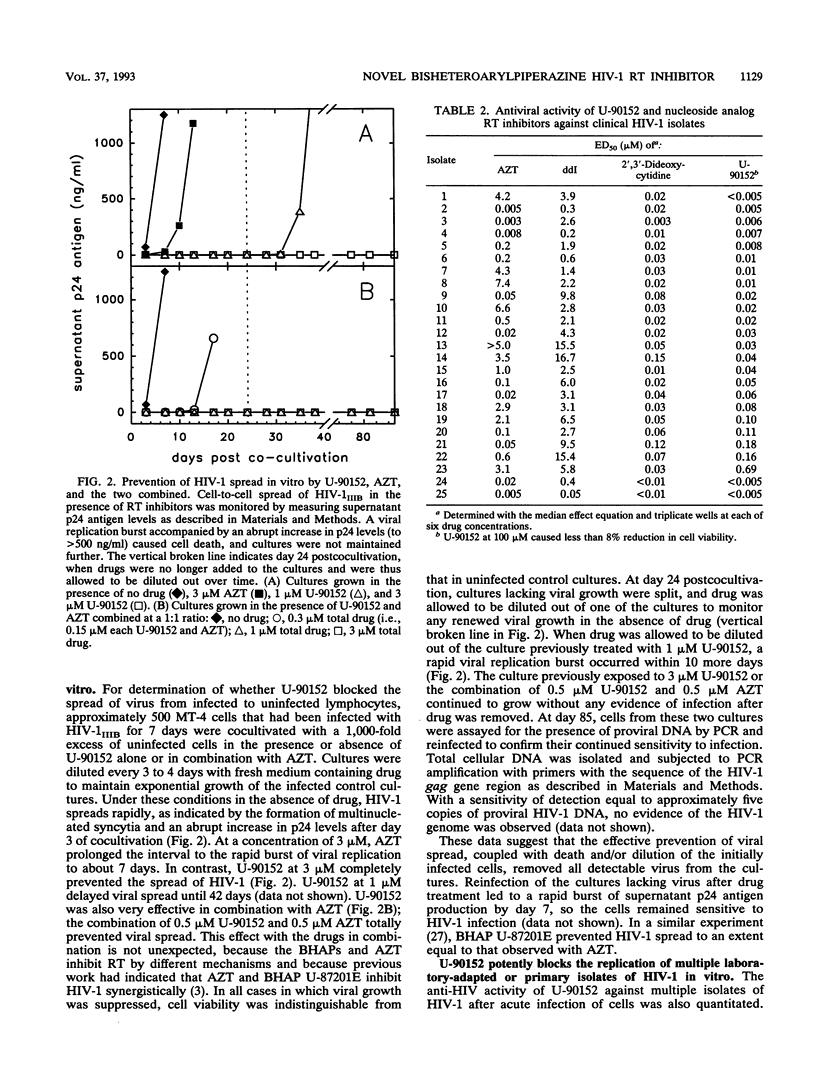
Bisheteroarylpiperazines are potent inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase (RT). We describe a novel bisheteroarylpiperazine, U-90152 [1-(5-methanesulfonamido-1H-indol-2-yl-carbonyl)-4-[3-(1-methyl eth yl-amino)pyridinyl]piperazine], which inhibited recombinant HIV-1 RT at a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.26 microM (compared with IC50s of > 440 microM for DNA polymerases alpha and delta). U-90152 blocked the replication in peripheral blood lymphocytes of 25 primary HIV-1 isolates, including variants that were highly resistant to 3'-azido-2',3'-dideoxythymidine (AZT) or 2',3'-dideoxyinosine, with a mean 50% effective dose of 0.066 +/- 0.137 microM. U-90152 had low cellular cytotoxicity, causing less than 8% reduction in peripheral blood lymphocyte viability at 100 microM. In experiments assessing inhibition of the spread of HIV-1IIIB in cell cultures, U-90152 was much more effective than AZT. When approximately 500 HIV-1IIIB-infected MT-4 cells were mixed 1:1,000 with uninfected cells, 3 microM AZT delayed the evidence of rapid viral growth for 7 days. In contrast, 3 microM U-90152 totally prevented the spread of HIV-1, and death and/or dilution of the original inoculum of infected cells prevented renewed viral growth after U-90152 was removed at day 24. The combination of U-90152 and AZT, each at 0.5 microM, also totally prevented viral spread. Finally, although the RT amino acid substitutions K103N (lysine 103 to asparagine) and Y181C (tyrosine 181 to cysteine), which confer cross-resistance to several nonnucleoside inhibitors, also decrease the potency of U-90152, this drug retains significant activity against these mutant RTs in vitro (IC50s, approximately 8 microgramM).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Althaus I. W., Chou J. J., Gonzales A. J., Deibel M. R., Chou K. C., Kezdy F. J., Romero D. L., Aristoff P. A., Tarpley W. G., Reusser F. Steady-state kinetic studies with the non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitor U-87201E. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6119–6124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin G. C., Fleischmann J., Chung Y., Koyanagi Y., Chen I. S., Golde D. W. Human immunodeficiency virus causes mononuclear phagocyte dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3933–3937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay D., Evans D. B., Deibel M. R., Jr, Vosters A. F., Eckenrode F. M., Einspahr H. M., Hui J. O., Tomasselli A. G., Zurcher-Neely H. A., Heinrikson R. L. Purification and characterization of heterodimeric human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase produced by in vitro processing of p66 with recombinant HIV-1 protease. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14227–14232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deibel M. R., Jr, McQuade T. J., Brunner D. P., Tarpley W. G. Denaturation/refolding of purified recombinant HIV reverse transcriptase yields monomeric enzyme with high enzymatic activity. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 Mar;6(3):329–340. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueweke T. J., Kézdy F. J., Waszak G. A., Deibel M. R., Jr, Tarpley W. G. The binding of a novel bisheteroarylpiperazine mediates inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):27–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank K. B., Noll G. J., Connell E. V., Sim I. S. Kinetic interaction of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase with the antiviral tetrahydroimidazo[4,5,1-jk]-[1,4]-benzodiazepine-2-(1H)-thione compound, R82150. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14232–14236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada S., Koyanagi Y., Yamamoto N. Infection of HTLV-III/LAV in HTLV-I-carrying cells MT-2 and MT-4 and application in a plaque assay. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):563–566. doi: 10.1126/science.2992081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargrave K. D., Proudfoot J. R., Grozinger K. G., Cullen E., Kapadia S. R., Patel U. R., Fuchs V. U., Mauldin S. C., Vitous J., Behnke M. L. Novel non-nucleoside inhibitors of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. 1. Tricyclic pyridobenzo- and dipyridodiazepinones. J Med Chem. 1991 Jul;34(7):2231–2241. doi: 10.1021/jm00111a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Japour A. J., Mayers D. L., Johnson V. A., Kuritzkes D. R., Beckett L. A., Arduino J. M., Lane J., Black R. J., Reichelderfer P. S., D'Aquila R. T. Standardized peripheral blood mononuclear cell culture assay for determination of drug susceptibilities of clinical human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. The RV-43 Study Group, the AIDS Clinical Trials Group Virology Committee Resistance Working Group. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1095–1101. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Dutschman G. E., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Cheng Y. C. In vitro selection and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus-1 resistant to non-nucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merluzzi V. J., Hargrave K. D., Labadia M., Grozinger K., Skoog M., Wu J. C., Shih C. K., Eckner K., Hattox S., Adams J. Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor. Science. 1990 Dec 7;250(4986):1411–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.1701568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou C. Y., Kwok S., Mitchell S. W., Mack D. H., Sninsky J. J., Krebs J. W., Feorino P., Warfield D., Schochetman G. DNA amplification for direct detection of HIV-1 in DNA of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.3336784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauwels R., Andries K., Desmyter J., Schols D., Kukla M. J., Breslin H. J., Raeymaeckers A., Van Gelder J., Woestenborghs R., Heykants J. Potent and selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication in vitro by a novel series of TIBO derivatives. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):470–474. doi: 10.1038/343470a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D. L., Busso M., Tan C. K., Reusser F., Palmer J. R., Poppe S. M., Aristoff P. A., Downey K. M., So A. G., Resnick L. Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors that potently and specifically block human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8806–8810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sardana V. V., Emini E. A., Gotlib L., Graham D. J., Lineberger D. W., Long W. J., Schlabach A. J., Wolfgang J. A., Condra J. H. Functional analysis of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase amino acids involved in resistance to multiple nonnucleoside inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 5;267(25):17526–17530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. K., Evans D. B., Vosters A. F., McQuade T. J., Tarpley W. G. Metal affinity chromatography of recombinant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase containing a human renin cleavable metal binding domain. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 1991 Aug;14(1):69–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Richards C. A., Spector T., Weinhold K. J., Miller W. H., Langlois A. J., Furman P. A. 3'-Azido-3'-deoxythymidine triphosphate as an inhibitor and substrate of purified human immunodeficiency virus reverse transcriptase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Dec;31(12):1972–1977. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.12.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starcich B. R., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., McNeely P. D., Modrow S., Wolf H., Parks E. S., Parks W. P., Josephs S. F., Gallo R. C. Identification and characterization of conserved and variable regions in the envelope gene of HTLV-III/LAV, the retrovirus of AIDS. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan C. K., Castillo C., So A. G., Downey K. M. An auxiliary protein for DNA polymerase-delta from fetal calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):12310–12316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevachari M. B., Battista C., Lane H. C., Psallidopoulos M. C., Zhao B., Cook J., Palmer J. R., Romero D. L., Tarpley W. G., Salzman N. P. Prevention of the spread of HIV-1 infection with nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91213-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Warren T. C., Adams J., Proudfoot J., Skiles J., Raghavan P., Perry C., Potocki I., Farina P. R., Grob P. M. A novel dipyridodiazepinone inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase acts through a nonsubstrate binding site. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 26;30(8):2022–2026. doi: 10.1021/bi00222a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


