Abstract
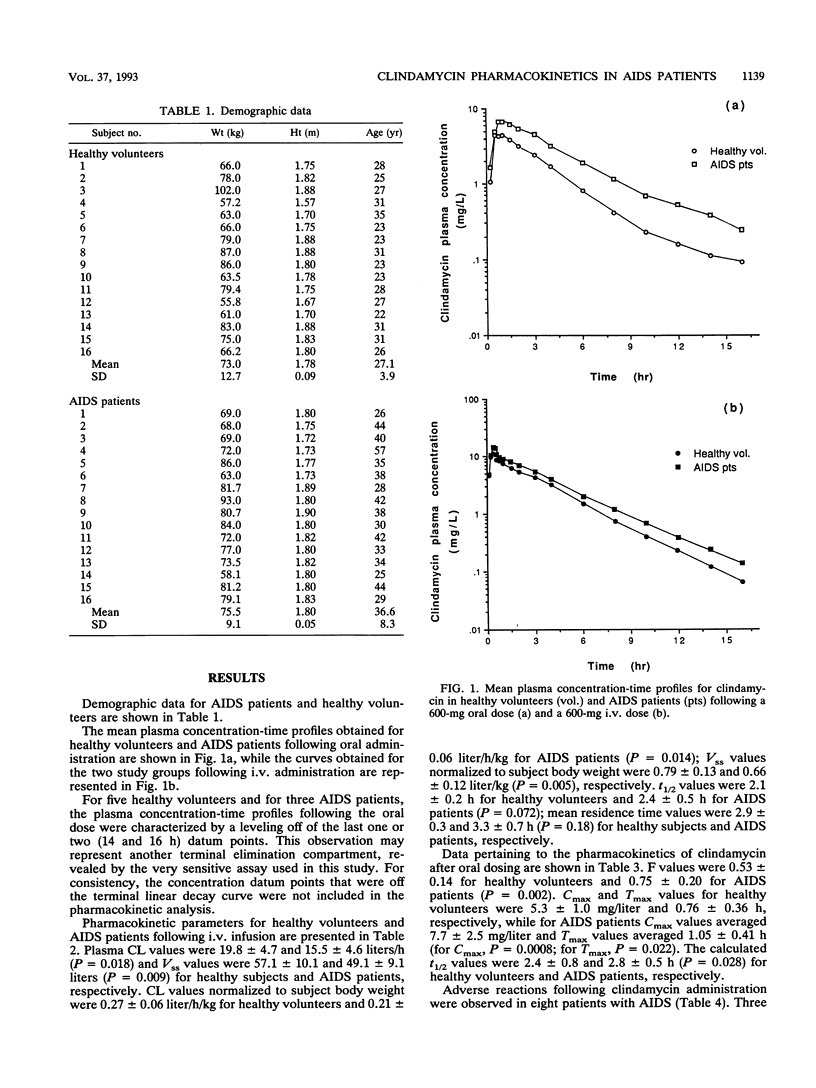
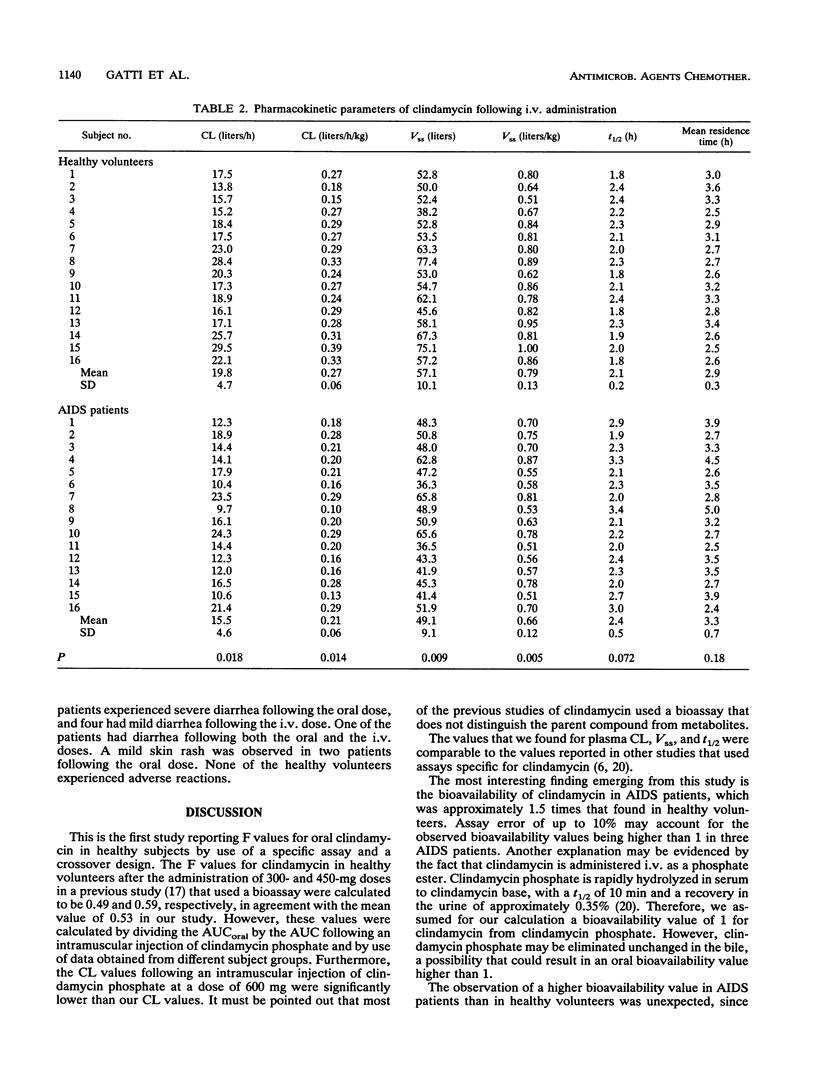
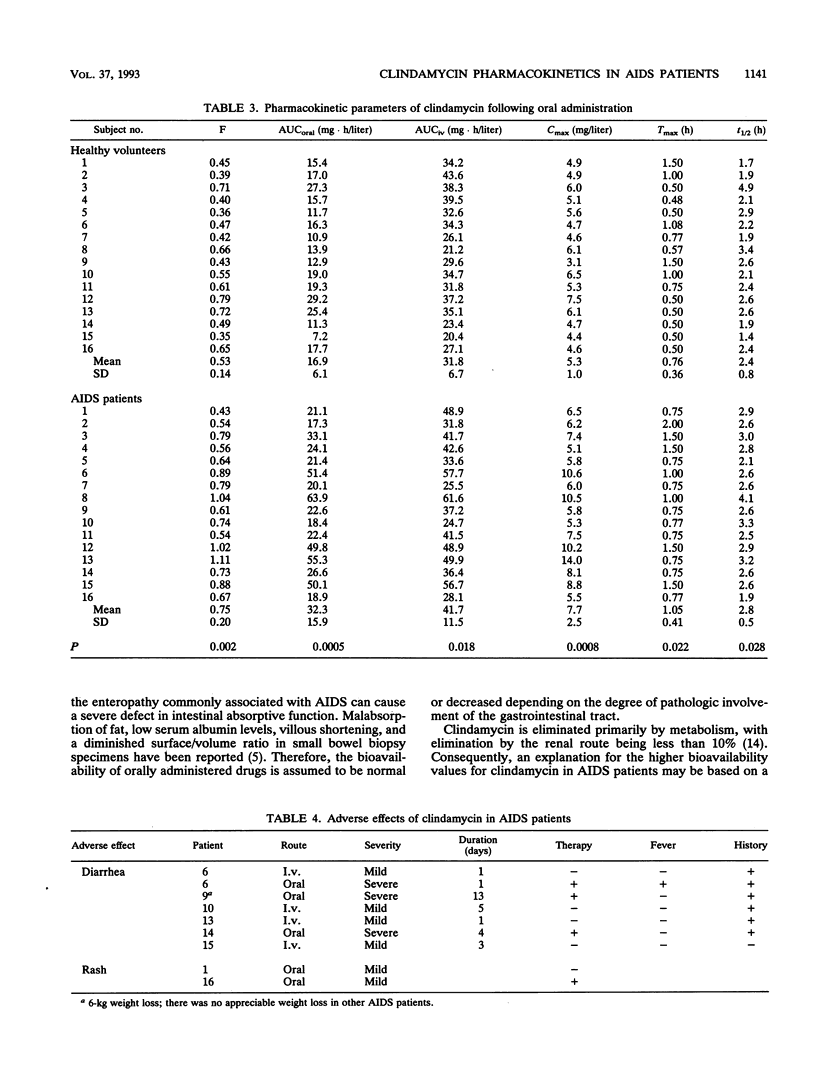
The absolute oral bioavailability and pharmacokinetics of clindamycin administered to 16 healthy volunteers and 16 patients with AIDS were compared. Clindamycin was given intravenously (i.v.) (Cleocin phosphate) at a dose of 600 mg as a 25-min infusion and orally (Cleocin hydrochloride) by use of a crossover design in both study groups. Plasma samples were analyzed by gas-liquid chromatography. Plasma drug clearance and volume of distribution at the steady state following the i.v. dose differed between study groups. The clearances were 0.27 +/- 0.06 liter/h/kg in healthy volunteers and 0.21 +/- 0.06 liter/h/kg in AIDS patients (P = 0.014; Mann-Whitney U test); the volumes of distribution at the steady state were 0.79 +/- 0.13 and 0.66 +/- 0.12 liter/kg in healthy volunteers and AIDS patients, respectively (P = 0.005). The elimination half-life did not differ between the two groups. The bioavailability of clindamycin capsules in AIDS patients was approximately 1.5 times that in healthy volunteers (0.53 +/- 0.14 versus 0.75 +/- 0.20; P = 0.002). Peak concentrations following the oral dose were higher in AIDS patients as well (7.7 +/- 2.5 versus 5.3 +/- 1.0 mg/liter; P = 0.0008). Three AIDS patients experienced severe diarrhea following the oral dose; four patients had mild diarrhea following the i.v. dose. No adverse effects were reported by the healthy volunteers. The pharmacokinetic parameters observed in this study for AIDS patients may be useful for the consideration of clindamycin dosage regimens in patients treated for toxoplasmic encephalitis. These findings suggest that the effect of AIDS on drug disposition deserves further investigation, particularly for orally administered drugs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dannemann B. R., Israelski D. M., Remington J. S. Treatment of toxoplasmic encephalitis with intravenous clindamycin. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Nov;148(11):2477–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dannemann B., McCutchan J. A., Israelski D., Antoniskis D., Leport C., Luft B., Nussbaum J., Clumeck N., Morlat P., Chiu J. Treatment of toxoplasmic encephalitis in patients with AIDS. A randomized trial comparing pyrimethamine plus clindamycin to pyrimethamine plus sulfadiazine. The California Collaborative Treatment Group. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Jan 1;116(1):33–43. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-116-1-33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenpreis E. D., Gulino S. P., Patterson B. K., Craig R. M., Yokoo H., Atkinson A. J., Jr Kinetics of D-xylose absorption in patients with human immunodeficiency virus enteropathy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Jun;49(6):632–640. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaherty J. F., Rodondi L. C., Guglielmo B. J., Fleishaker J. C., Townsend R. J., Gambertoglio J. G. Comparative pharmacokinetics and serum inhibitory activity of clindamycin in different dosing regimens. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Dec;32(12):1825–1829. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.12.1825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C., Salgo M. P., Tanowitz H. B., Wittner M. In vitro assessment of antimicrobial agents against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):14–22. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos H. W. Assessment of therapy for toxoplasma encephalitis. The TE Study Group. Am J Med. 1987 May;82(5):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90151-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofflin J. M., Remington J. S. Clindamycin in a murine model of toxoplasmic encephalitis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):492–496. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kays M. B., White R. L., Gatti G., Gambertoglio J. G. Ex vivo protein binding of clindamycin in sera with normal and elevated alpha 1-acid glycoprotein concentrations. Pharmacotherapy. 1992;12(1):50–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotler D. P., Gaetz H. P., Lange M., Klein E. B., Holt P. R. Enteropathy associated with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Oct;101(4):421–428. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-101-4-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh D. A. Antibacterial activity and pharmacokinetics of clindamycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1981 Jun;7 (Suppl A):3–9. doi: 10.1093/jac/7.suppl_a.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leport C., Bastuji-Garin S., Perronne C., Salmon D., Marche C., Briçaire F., Vilde J. L. An open study of the pyrimethamine-clindamycin combination in AIDS patients with brain toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1989 Sep;160(3):557–558. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.3.557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Remington J. S. AIDS commentary. Toxoplasmic encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Jan;157(1):1–6. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzler C. M., DeHaan R., Schellenberg D., Vandenbosch W. D. Clindamycin dose-bioavailability relationships. J Pharm Sci. 1973 Apr;62(4):591–598. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600620410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. Pneumocystis carinii and Toxoplasma gondii infections in patients with AIDS. Rev Infect Dis. 1986 Nov-Dec;8(6):1001–1011. doi: 10.1093/clinids/8.6.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons R. L., Hossack G., Paddock G. The absorption of antibiotics in adult patients with coeliac disease. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1975 Mar;1(1):39–50. doi: 10.1093/jac/1.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaisance K. I., Drusano G. L., Forrest A., Townsend R. J., Standiford H. C. Pharmacokinetic evaluation of two dosage regimens of clindamycin phosphate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 May;33(5):618–620. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.5.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podzamczer D., Gudiol F. Clindamycin in cerebral toxoplasmosis. Am J Med. 1988 Apr;84(4):800–800. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(88)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revell P., O'Doherty M. J., Tang A., Savidge G. F. Folic acid absorption in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Intern Med. 1991 Sep;230(3):227–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.1991.tb00435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolston K. V., Hoy J. Role of clindamycin in the treatment of central nervous system toxoplasmosis. Am J Med. 1987 Sep;83(3):551–554. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(87)90769-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



