Abstract
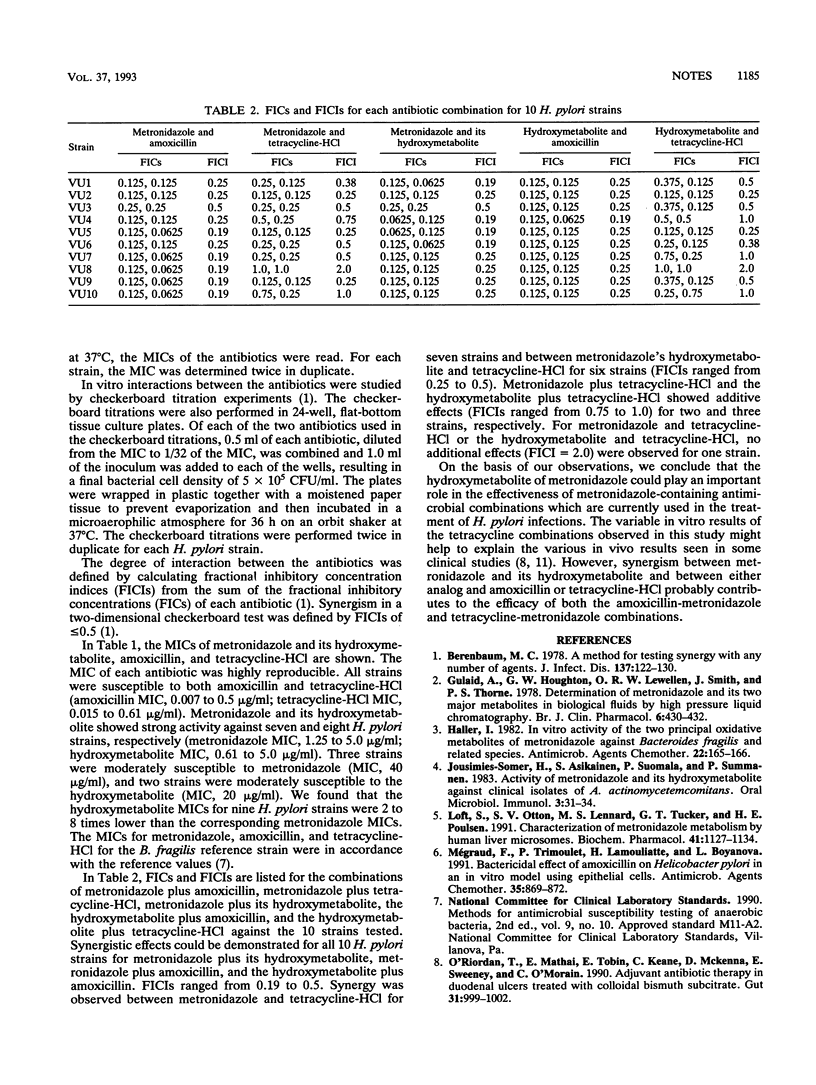
Synergy between metronidazole and its hydroxymetabolite and between each compound and amoxicillin or tetracycline-HCl was determined against Helicobacter pylori. Metronidazole plus its hydroxymetabolite and either compound combined with amoxicillin showed synergism against all 10 strains of H. pylori tested. Metronidazole plus tetracycline-HCl or the hydroxymetabolite plus tetracycline-HCl acted synergistically against seven and six strains, respectively, acted additively against three strains, and had no additional effect against one strain. These results may help to explain the in vivo efficacies of metronidazole combinations in the treatment of H. pylori-associated gastritis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berenbaum M. C. A method for testing for synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 1978 Feb;137(2):122–130. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.2.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulaid A., Houghton G. W., Lewellen O. R., Smith J., Thorne P. S. Determination of metronidazole and its two major metabolites in biological fluids by high pressure liquid chromatography. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;6(5):430–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb04608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller I. In vitro activity of the two principal oxidative metabolites of metronidazole against Bacteroides fragilis and related species. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Jul;22(1):165–166. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jousimies-Somer H., Asikainen S., Suomala P., Summanen P. Activity of metronidazole and its hydroxy metabolite against clinical isolates of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Oral Microbiol Immunol. 1988 Mar;3(1):32–34. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-302x.1988.tb00602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loft S., Otton S. V., Lennard M. S., Tucker G. T., Poulsen H. E. Characterization of metronidazole metabolism by human liver microsomes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1991 Apr 15;41(8):1127–1134. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(91)90650-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megraud F., Trimoulet pascale, Lamouliatte H., Boyanova L. Bactericidal effect of amoxicillin on Helicobacter pylori in an in vitro model using epithelial cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):869–872. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Riordan T., Mathai E., Tobin E., McKenna D., Keane C., Sweeney E., O'Morain C. Adjuvant antibiotic therapy in duodenal ulcers treated with colloidal bismuth subcitrate. Gut. 1990 Sep;31(9):999–1002. doi: 10.1136/gut.31.9.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavicić M. J., van Winkelhoff A. J., de Graaff J. Synergistic effects between amoxicillin, metronidazole, and the hydroxymetabolite of metronidazole against Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 May;35(5):961–966. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.5.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbone B. J., Wyatt J. I., Heatley R. V. Campylobacter pyloridis--a new factor in peptic ulcer disease? Gut. 1986 Jun;27(6):635–641. doi: 10.1136/gut.27.6.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauws E. A., Tytgat G. N. Cure of duodenal ulcer associated with eradication of Helicobacter pylori. Lancet. 1990 May 26;335(8700):1233–1235. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91301-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983 Jun 4;1(8336):1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


