Abstract
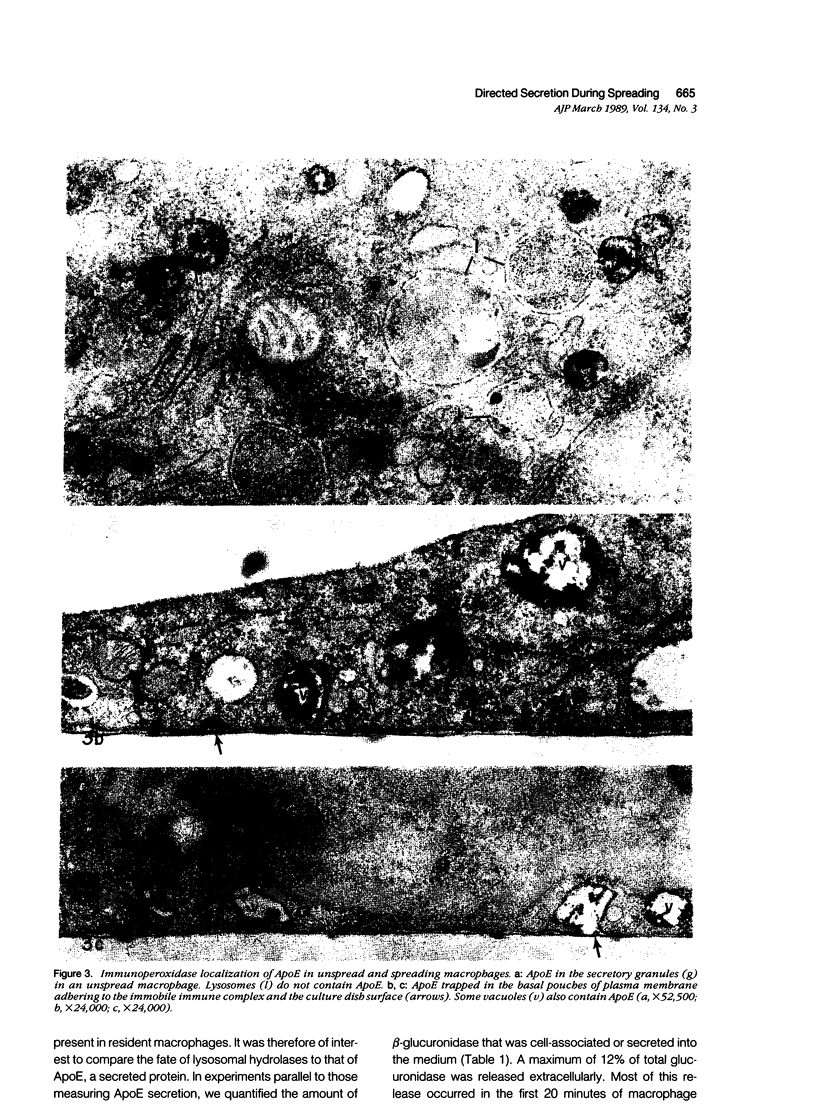
As macrophages spread on an immune complex-coated surface, large, clear basal vacuoles and numerous coated vesicles and tubules form rapidly and are occasionally contiguous with the adherent surface, creating a microcompartment between the immune complex-coated surface and the cell membrane. The present study explored the nature of this basal compartment by examining the distribution of a major secretory product of macrophages, apolipoprotein E (ApoE), and of a lysosomal enzyme, acid phosphatase, by enzyme and immunocytochemistry. Upon contact of the macrophages with the immune complexes, intracellular stores of ApoE were secreted rapidly in the first 10 to 20 minutes to the area of ligand-receptor interaction. ApoE filled the large basal vacuoles and was also found in invaginations on the adherent surface that were sealed to the influx of proteins and peptides from the bulk medium. In contrast, the contents of lysosomes were not redistributed to the basal compartment. By 2 hours most of the ApoE had appeared in the bulk medium, suggesting that the protein could move out of the basal compartment. These data suggest that specific ligand-Fc receptor interactions serve to target secretion by macrophages to selective focal areas of contact, and that there are also mechanisms for retrieval of material from these sites.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman N. R., Beebe J. R. Release of lysosomal enzymes by alveolar mononuclear cells. Nature. 1974 Feb 15;247(5441):475–477. doi: 10.1038/247475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bainton D. F., Takemura R., Stenberg P. E., Werb Z. Rapid fragmentation and reorganization of Golgi membranes during frustrated phagocytosis of immobile immune complexes by macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1989 Jan;134(1):15–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buktenica S., Olenick S. J., Salgia R., Frankfater A. Degradation and regurgitation of extracellular proteins by cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages and baby hamster kidney fibroblasts. Kinetic evidence that the transfer of proteins to lysosomes is not irreversible. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9469–9476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buys S. S., Keogh E. A., Kaplan J. Fusion of intracellular membrane pools with cell surfaces of macrophages stimulated by phorbol esters and calcium ionophores. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):569–576. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90511-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardella C. J., Davies P., Allison A. C. Immune complexes induce selective release of lysosomal hydrolases from macrophages. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):46–48. doi: 10.1038/247046a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles M. H., Glauert A. M. The response of human monocytes to interaction with immobilized immune complexes. J Cell Sci. 1984 Oct;71:141–157. doi: 10.1242/jcs.71.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan P., St Clair R. W. Retroendocytosis of low density lipoprotein. Effect of lysosomal inhibitors on the release of undegraded 125I-low density lipoprotein of altered composition from skin fibroblasts in culture. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1703–1713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Interaction of cells with immune complexes: adherence, release of constituents, and tissue injury. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 2):114s–135s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffstein S. T., Friedman R. S., Weissmann G. Degranulation, membrane addition, and shape change during chemotactic factor-induced aggregation of human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):234–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. B., Jr, Lehmeyer J. E., Guthrie L. A. Generation of superoxide anion and chemiluminescence by human monocytes during phagocytosis and on contact with surface-bound immunoglobulin G. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1551–1556. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keeling P. J., Henson P. M. Lysosomal enzyme release from human monocytes in response to particulate stimuli. J Immunol. 1982 Feb;128(2):563–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo C., Wernette-Hammond M. E., Innerarity T. L. Uptake of canine beta-very low density lipoproteins by mouse peritoneal macrophages is mediated by a low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11194–11201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfer A., Louvard D., Singer S. J. Polarization of the Golgi apparatus and the microtubule-organizing center in cultured fibroblasts at the edge of an experimental wound. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2603–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillai S., Zull J. E. Production of biologically active fragments of parathyroid hormone by isolated Kupffer cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):14919–14923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poo W. J., Conrad L., Janeway C. A., Jr Receptor-directed focusing of lymphokine release by helper T cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):378–380. doi: 10.1038/332378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C. G., Arend W. P. Neutral protease secretion by human monocytes. Effect of surface-bound immune complexes. J Exp Med. 1979 Apr 1;149(4):954–968. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.4.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riezman H. Endocytosis in yeast: several of the yeast secretory mutants are defective in endocytosis. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):1001–1009. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitkovsky M. V., Paul W. E. Immunology. Global or directed exocytosis? Nature. 1988 Mar 24;332(6162):306–307. doi: 10.1038/332306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. A., Yirinec B. D., Silverstein S. C. Phorbol esters and horseradish peroxidase stimulate pinocytosis and redirect the flow of pinocytosed fluid in macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):851–859. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Stenberg P. E., Bainton D. F., Werb Z. Rapid redistribution of clathrin onto macrophage plasma membranes in response to Fc receptor-ligand interaction during frustrated phagocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;102(1):55–69. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura R., Werb Z. Modulation of apoprotein E secretion in response to receptor-mediated endocytosis in resident and inflammatory macrophages. J Exp Med. 1984 Jan 1;159(1):167–178. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E., Michl J., Pfeffer L. M., Silverstein S. C., Tamm I. Interferon suppresses pinocytosis but stimulates phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages: related changes in cytoskeletal organization. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1328–1341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Chin J. R. Apoprotein E is synthesized and secreted by resident and thioglycollate-elicited macrophages but not by pyran copolymer- or bacillus Calmette-Guerin-activated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1272–1293. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. D., Silverstein S. C. Phagocytosing macrophages exclude proteins from the zones of contact with opsonized targets. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):359–361. doi: 10.1038/309359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler H. K., Unanue E. R. Decrease in macrophage antigen catabolism caused by ammonia and chloroquine is associated with inhibition of antigen presentation to T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):175–178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]