Abstract
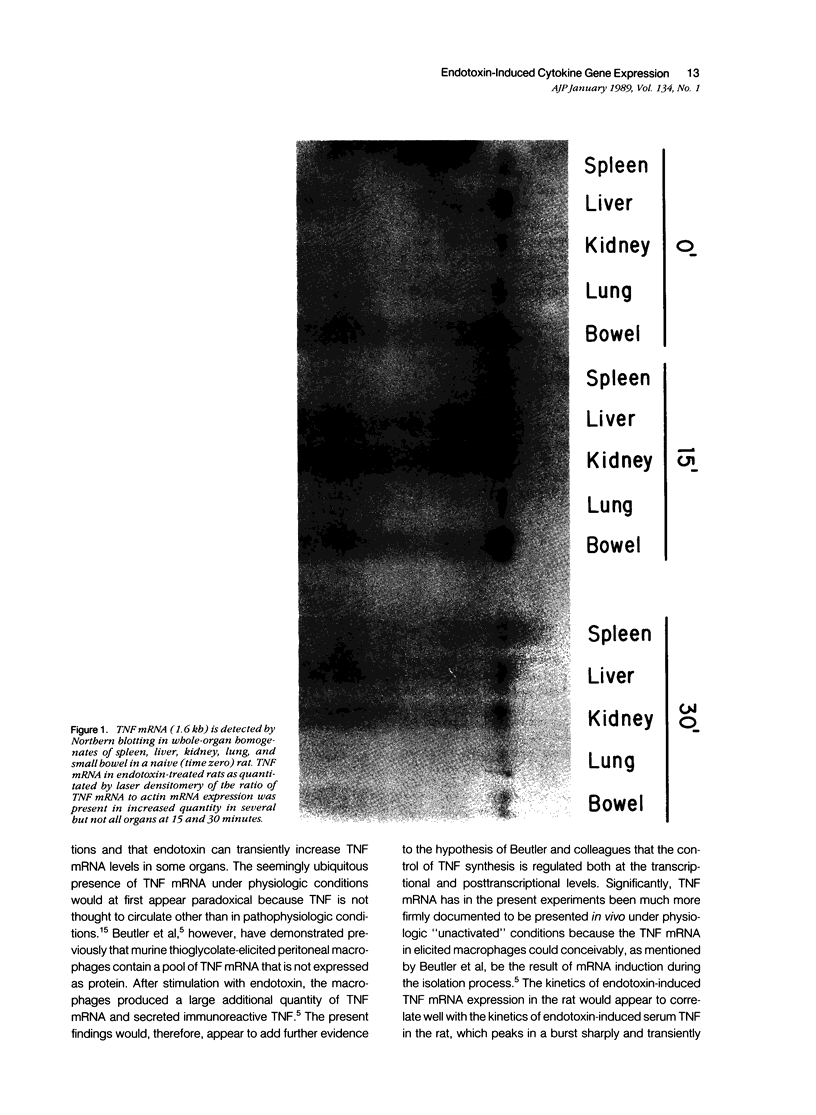
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) mRNA was detected by Northern blotting in whole-organ homogenates of the spleen, liver, kidney, lung, and small bowel in naive and saline-injected control rats, supporting the hypothesis that TNF mRNA is present in vivo in a preformed intracellular pool. TNF mRNA in endotoxin-treated rats as quantitated by densitometry of the ratio of TNF mRNA to actin mRNA in Northern blots was present in increased quantity in the liver, kidney, and lung (1.6-2.9 times over time zero levels) at 15 minutes and increased quantity in the spleen, liver, and kidney (1.3-1.9 times over time zero levels) at 30 minutes. The kinetics of endotoxin-induced TNF gene expression are consistent with the relatively transient peak of serum TNF protein levels reported by previous investigators to occur approximately 1 hour after injection of endotoxin. Because TNF mRNA appeared ubiquitous in the organs of control rats examined and because the endotoxin-induced increase in TNF mRNA was relatively small, endotoxin may induce the expression of the TNF protein in serum not only by increasing TNF mRNA levels but perhaps more importantly by a posttranscriptional mechanism. The presence of a preformed pool of TNF mRNA may teleologically be viewed as a mechanism to increase the rapidity of the host's response to sepsis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchett S. K., Weaver W. M., Westall J. A., Larsen A., Kronheim S., Wilson C. B. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and IL-1 secretion in human mononuclear phagocytes. J Immunol. 1988 May 15;140(10):3473–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cybulsky M. I., Chan M. K., Movat H. Z. Acute inflammation and microthrombosis induced by endotoxin, interleukin-1, and tumor necrosis factor and their implication in gram-negative infection. Lab Invest. 1988 Apr;58(4):365–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issekutz A. C., Bhimji S. Role for endotoxin in the leukocyte infiltration accompanying Escherichia coli inflammation. Infect Immun. 1982 May;36(2):558–566. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.2.558-566.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Tumor necrosis factor. Important Adv Oncol. 1987:105–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remick D. G., Kunkel R. G., Larrick J. W., Kunkel S. L. Acute in vivo effects of human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Lab Invest. 1987 Jun;56(6):583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyderman R., Gewurz H., Mergenhagen S. E. Interactions of the complement system with endotoxic lipopolysaccharide. Generation of a factor chemotactic for polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1968 Aug 1;128(2):259–275. doi: 10.1084/jem.128.2.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovey M. G. The expression of cytokines in the organs of normal individuals: role in homeostasis. A review. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 1988 Apr-Jun;2(2):87–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulich T. R., del Castillo J., Keys M., Granger G. A., Ni R. X. Kinetics and mechanisms of recombinant human interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced changes in circulating numbers of neutrophils and lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3406–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waage A. Production and clearance of tumor necrosis factor in rats exposed to endotoxin and dexamethasone. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1987 Dec;45(3):348–355. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(87)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Meinkoth J. L., Kimmel A. R. Northern and Southern blots. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:572–581. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]