Abstract
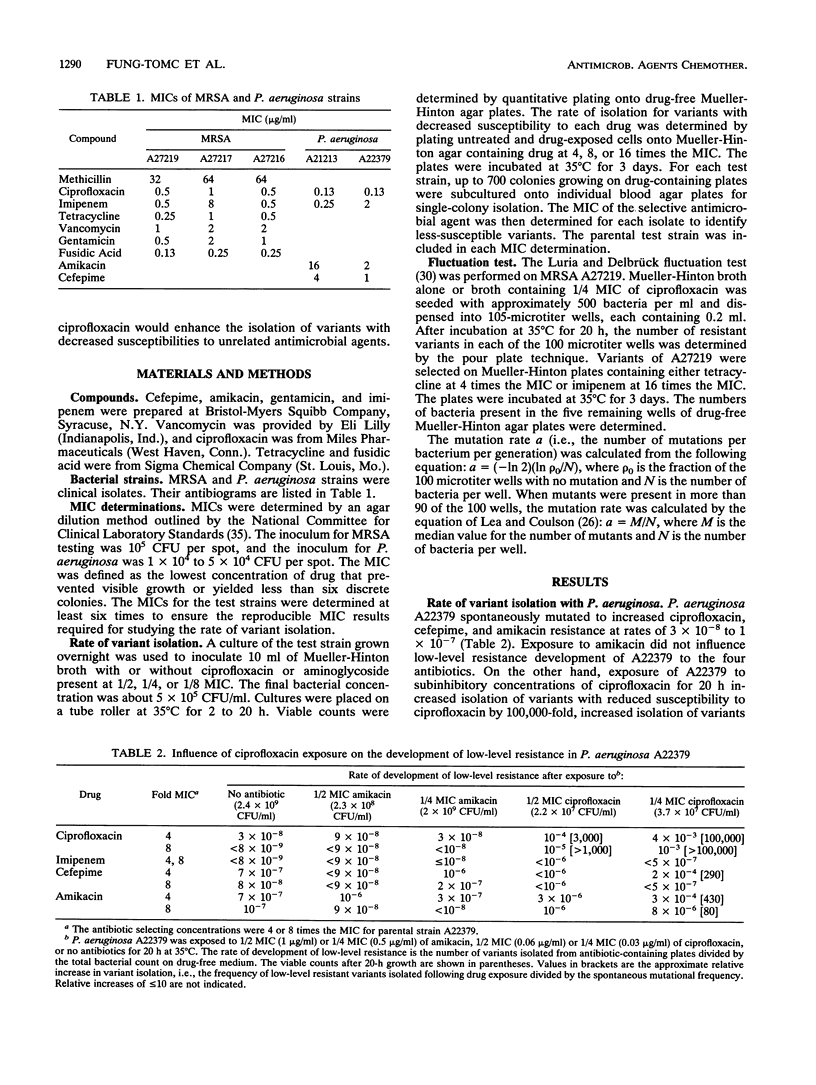
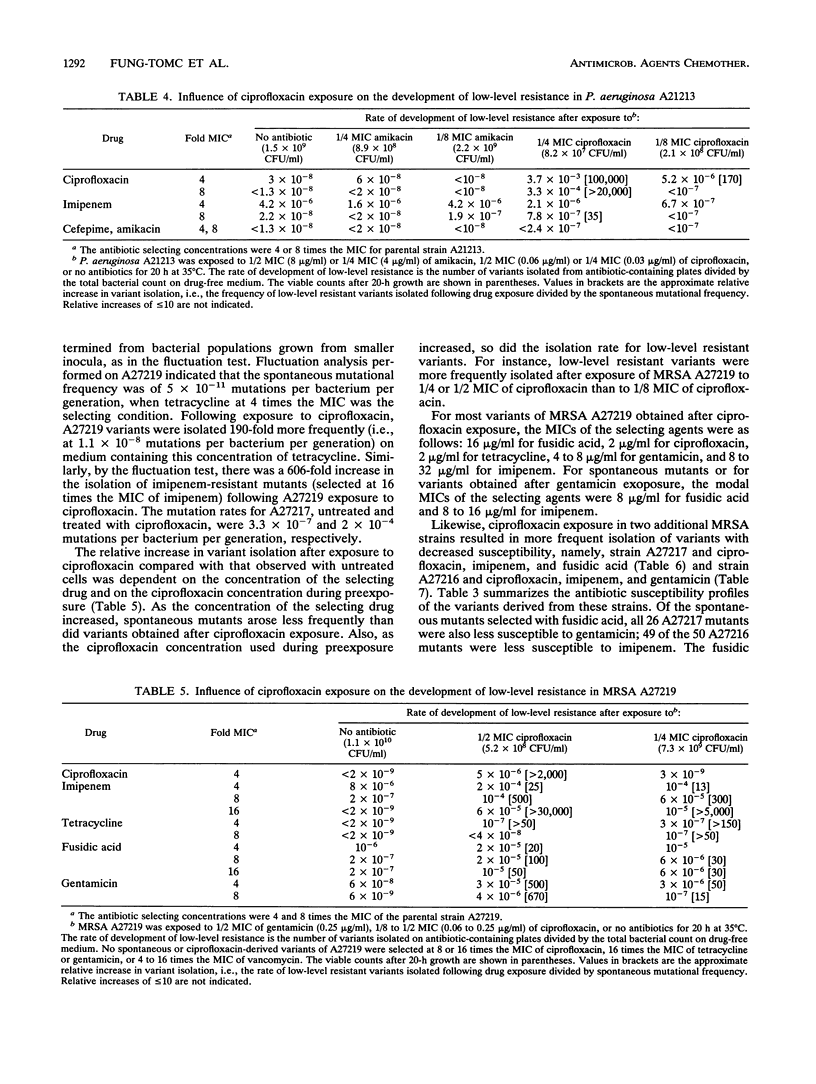
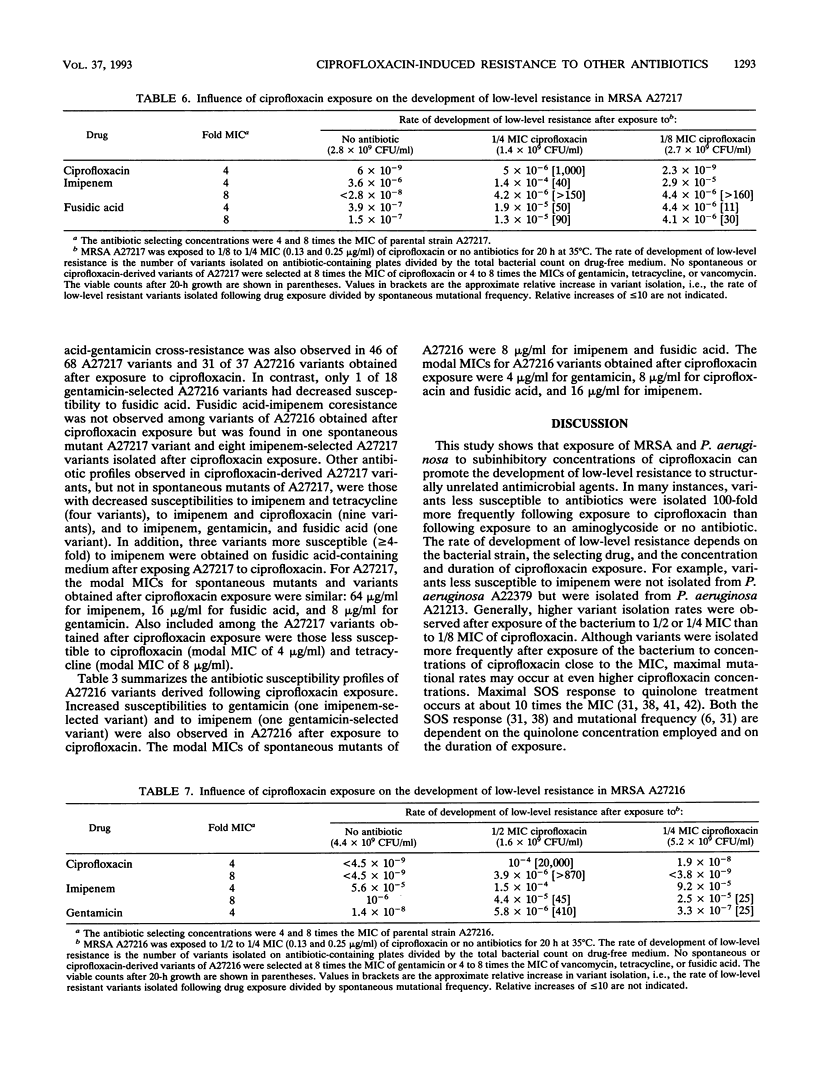
The effects of ciprofloxacin on the rates of development of low-level resistance to other antibiotics were determined in vitro. Three methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and two Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical strains were grown overnight in Mueller-Hinton broth with or without subinhibitory concentrations (1/2, 1/4, and 1/8 MICs) of ciprofloxacin or an aminoglycoside and then quantitatively plated onto medium containing 4 or 8 times the MICs of various antibiotics. The spontaneous mutational frequencies were determined and compared with those of cells not exposed to ciprofloxacin. Exposure of methicillin-resistant S. aureus strains to ciprofloxacin resulted in a > 100-fold increase in the isolation of variants with decreased susceptibilities to ciprofloxacin, tetracycline, imipenem, fusidic acid, and gentamicin, but not vancomycin. Likewise, a > 100-fold increase in the isolation of variants with decreased susceptibilities to ciprofloxacin and imipenem (35-fold) in P. aeruginosa A21213 was observed, and a > 100-fold increase in the isolation of variants with decreased susceptibilities to ciprofloxacin, amikacin, and cefepime in P. aeruginosa A22379 was observed. On the other hand, exposure of these strains to an aminoglycoside did not influence the development of resistance to nonaminoglycoside drugs. These results indicate that exposure to subinhibitory levels of ciprofloxacin can promote the development of low-level resistance to antibiotics with different modes of action.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert G., Pozzetto B., Dorche G. Emergence of quinolone-imipenem cross-resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa after fluoroquinolone therapy. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Mar;29(3):307–312. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.3.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campoli-Richards D. M., Monk J. P., Price A., Benfield P., Todd P. A., Ward A. Ciprofloxacin. A review of its antibacterial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1988 Apr;35(4):373–447. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198835040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Factors influencing the accumulation of ciprofloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1921–1926. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., McMurry L. M., Levy S. B. Endogenous active efflux of norfloxacin in susceptible Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., McMurry L. M., Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Levy S. B. Cross-resistance to fluoroquinolones in multiple-antibiotic-resistant (Mar) Escherichia coli selected by tetracycline or chloramphenicol: decreased drug accumulation associated with membrane changes in addition to OmpF reduction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Aug;33(8):1318–1325. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.8.1318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook T. M., Goss W. A., Deitz W. H. Mechanism of Action of Nalidixic Acid on Escherichia coli V. Possible Mutagenic Effect. J Bacteriol. 1966 Feb;91(2):780–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.2.780-783.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumplin G. C., Odell M. Development of resistance to ofloxacin. Drugs. 1987;34 (Suppl 1):1–8. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198700341-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver J. M., Schollaardt T., Rabin H. R., Thorson C., Bryan L. E. Persistence mechanisms in Pseudomonas aeruginosa from cystic fibrosis patients undergoing ciprofloxacin therapy. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Aug;35(8):1538–1546. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.8.1538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryden M. S., Ludlam H. A., Phillips I. 4-Quinolone resistant staphylococci. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Sep;26(3):448–449. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.3.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Bindschedler M., Wenk M., Frei R., Stalder H., Reber H. Use of ciprofloxacin in the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):236–240. doi: 10.1007/BF02013997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frieden T. R., Mangi R. J. Inappropriate use of oral ciprofloxacin. JAMA. 1990 Sep 19;264(11):1438–1440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu K. P., Grace M. E., Hsiao C. L., Hung P. P. Elimination of antibiotic-resistant plasmids by quinolone antibiotics. Chemotherapy. 1988;34(5):415–418. doi: 10.1159/000238601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda H., Hosaka M., Hirai K., Iyobe S. New norfloxacin resistance gene in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Sep;34(9):1757–1761. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.9.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George R. C., Ball L. C., Norbury P. B. Susceptibility to ciprofloxacin of nosocomial gram-negative bacteria and staphylococci isolated in the UK. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Dec;26 (Suppl F):145–156. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_f.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gransden W. R., Warren C., Phillips I. 4-Quinolone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in the United Kingdom. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jan;34(1):23–27. doi: 10.1099/00222615-34-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann L., Williamson R., Moreau N., Kitzis M. D., Collatz E., Acar J. F., Goldstein F. W. Cross-resistance to nalidixic acid, trimethoprim, and chloramphenicol associated with alterations in outer membrane proteins of Klebsiella, Enterobacter, and Serratia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):501–507. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashmi Z. S., Smith J. M. Outer membrane changes in quinolone resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Sep;28(3):465–470. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.3.465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Mutations producing resistance to norfloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Apr;31(4):582–586. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.4.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Ng E. Y., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of action of and resistance to ciprofloxacin. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):12–20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Tung C., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Genetic and biochemical characterization of norfloxacin resistance in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Apr;29(4):639–644. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. R., Morse S. A. Antibiotic resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae: genetics and mechanisms of resistance. Sex Transm Dis. 1988 Oct-Dec;15(4):217–224. doi: 10.1097/00007435-198810000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Ruble C. A. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Infect Dis. 1991 May;163(5):1080–1086. doi: 10.1093/infdis/163.5.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legakis N. J., Tzouvelekis L. S., Makris A., Kotsifaki H. Outer membrane alterations in multiresistant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa selected by ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Jan;33(1):124–127. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh D. A., Emmanuel F. X., Petch V. J. Ciprofloxacin therapy in complicated urinary tract infections caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other resistant bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Nov;18 (Suppl 500):117–121. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_d.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. E., Marnett L. J., Ames B. N. Spontaneous and mutagen-induced deletions: mechanistic studies in Salmonella tester strain TA102. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4457–4461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S. E., Delbrück M. Mutations of Bacteria from Virus Sensitivity to Virus Resistance. Genetics. 1943 Nov;28(6):491–511. doi: 10.1093/genetics/28.6.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamber S. W., Kolek B., Brookshire K. W., Bonner D. P., Fung-Tomc J. Activity of quinolones in the Ames Salmonella TA102 mutagenicity test and other bacterial genotoxicity assays. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Feb;37(2):213–217. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehtar S., Drabu Y., Blakemore P. Ciprofloxacin in the treatment of infections caused by gentamicin-resistant gram-negative bacteria. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Apr;5(2):248–251. doi: 10.1007/BF02014001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moellering R. C., Jr Interaction between antimicrobial consumption and selection of resistant bacterial strains. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1990;70:18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muder R. R., Brennen C., Goetz A. M., Wagener M. M., Rihs J. D. Association with prior fluoroquinolone therapy of widespread ciprofloxacin resistance among gram-negative isolates in a Veterans Affairs medical center. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Feb;35(2):256–258. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C. Quinolones in perspective. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Oct;26 (Suppl B):1–6. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.suppl_b.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I. Bacterial mutagenicity and the 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Dec;20(6):771–773. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.6.771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips I., Culebras E., Moreno F., Baquero F. Induction of the SOS response by new 4-quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Nov;20(5):631–638. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.5.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddock L. J., Diver J. M., Wise R. Cross-resistance of nalidixic acid resistant Enterobacteriaceae to new quinolones and other antimicrobials. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1986 Aug;5(4):411–415. doi: 10.1007/BF02075696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piddock L. J., Hall M. C., Walters R. N. Phenotypic characterization of quinolone-resistant mutants of Enterobacteriaceae selected from wild type, gyrA type and multiply-resistant (marA) type strains. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Aug;28(2):185–198. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.2.185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power E. G., Phillips I. Induction of the SOS gene (umuC) by 4-quinolone antibacterial drugs. J Med Microbiol. 1992 Feb;36(2):78–82. doi: 10.1099/00222615-36-2-78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raviglione M. C., Boyle J. F., Mariuz P., Pablos-Mendez A., Cortes H., Merlo A. Ciprofloxacin-resistant methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in an acute-care hospital. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2050–2054. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rella M., Haas D. Resistance of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO to nalidixic acid and low levels of beta-lactam antibiotics: mapping of chromosomal genes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Aug;22(2):242–249. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robillard N. J., Scarpa A. L. Genetic and physiological characterization of ciprofloxacin resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):535–539. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rådberg G., Nilsson L. E., Svensson S. Development of quinolone-imipenem cross resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa during exposure to ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2142–2147. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scully B. E., Neu H. C., Parry M. F., Mandell W. Oral ciprofloxacin therapy of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet. 1986 Apr 12;1(8485):819–822. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)90937-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalit I., Stutman H. R., Marks M. I., Chartrand S. A., Hilman B. C. Randomized study of two dosage regimens of ciprofloxacin for treating chronic bronchopulmonary infection in patients with cystic fibrosis. Am J Med. 1987 Apr 27;82(4A):189–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Eng R. H., Bais P., Fan-Havard P., Tecson-Tumang F. Epidemiology of ciprofloxacin resistance among patients with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Oct;26(4):567–572. doi: 10.1093/jac/26.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ubukata K., Itoh-Yamashita N., Konno M. Cloning and expression of the norA gene for fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Sep;33(9):1535–1539. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.9.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisser J., Wiedemann B. Elimination of plasmids by new 4-quinolones. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Nov;28(5):700–702. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.5.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M., Wermundsen I. E. Targeted and untargeted mutagenesis by various inducers of SOS functions in Escherichia coli. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):881–886. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



