Abstract
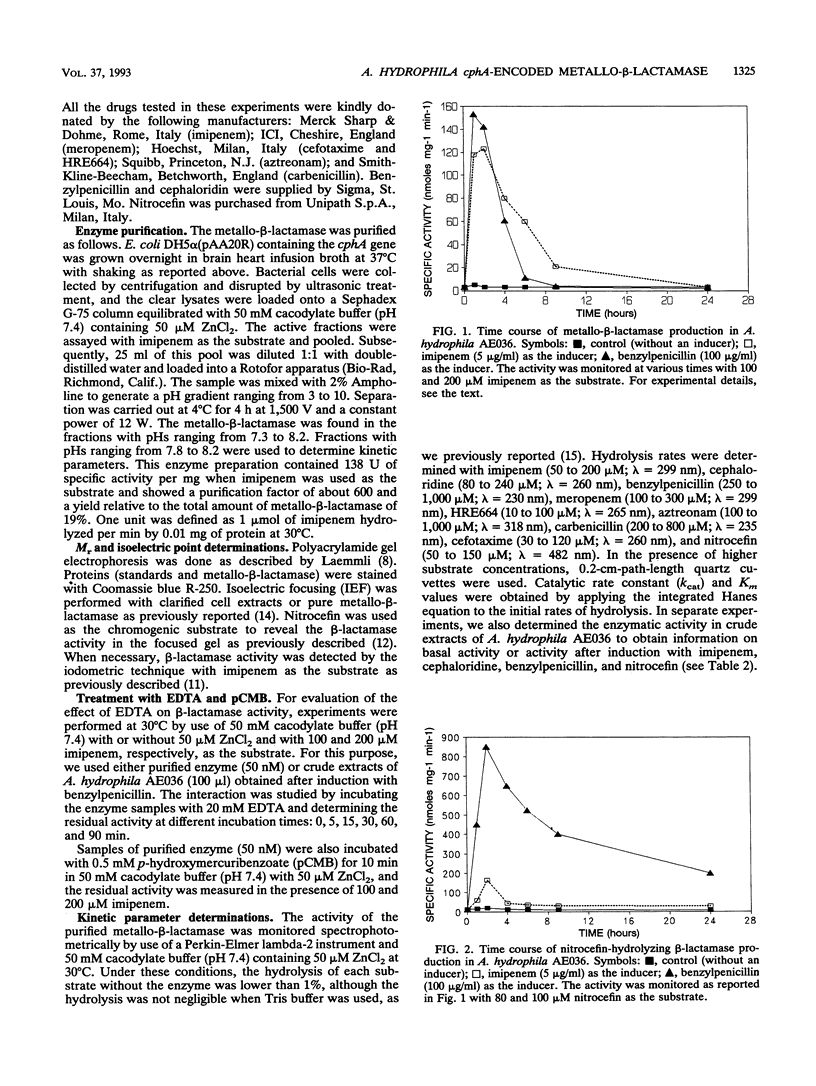
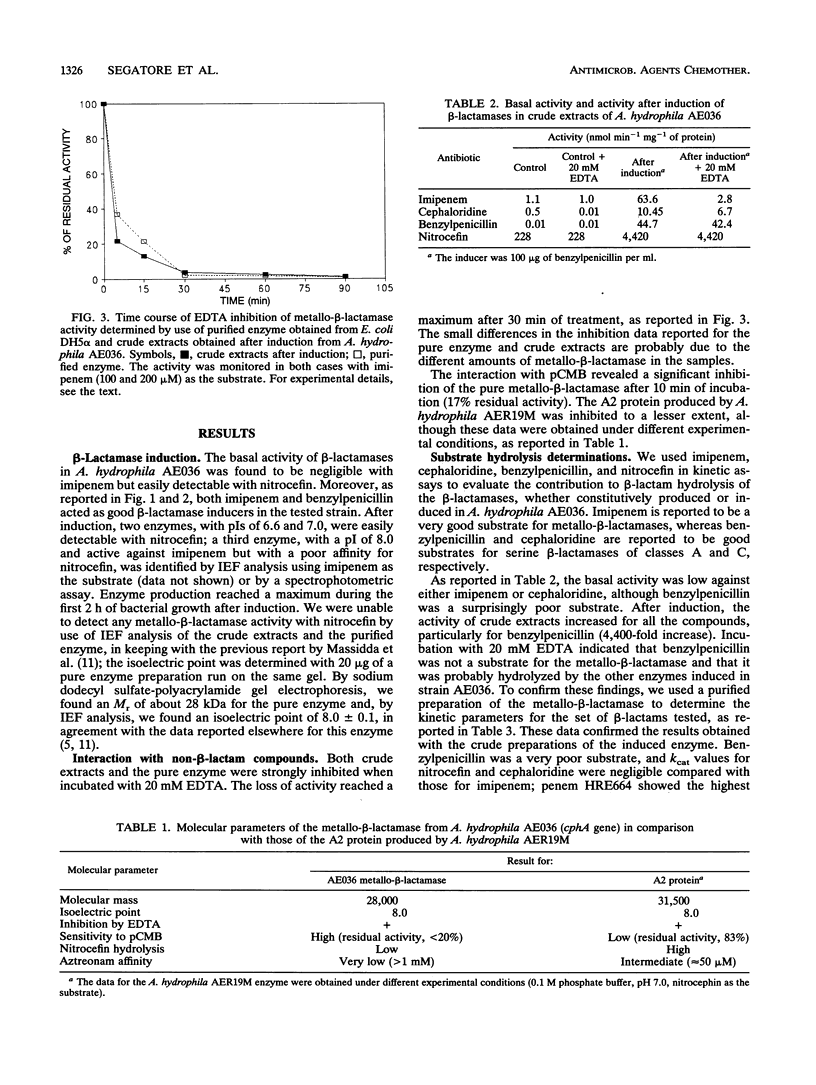
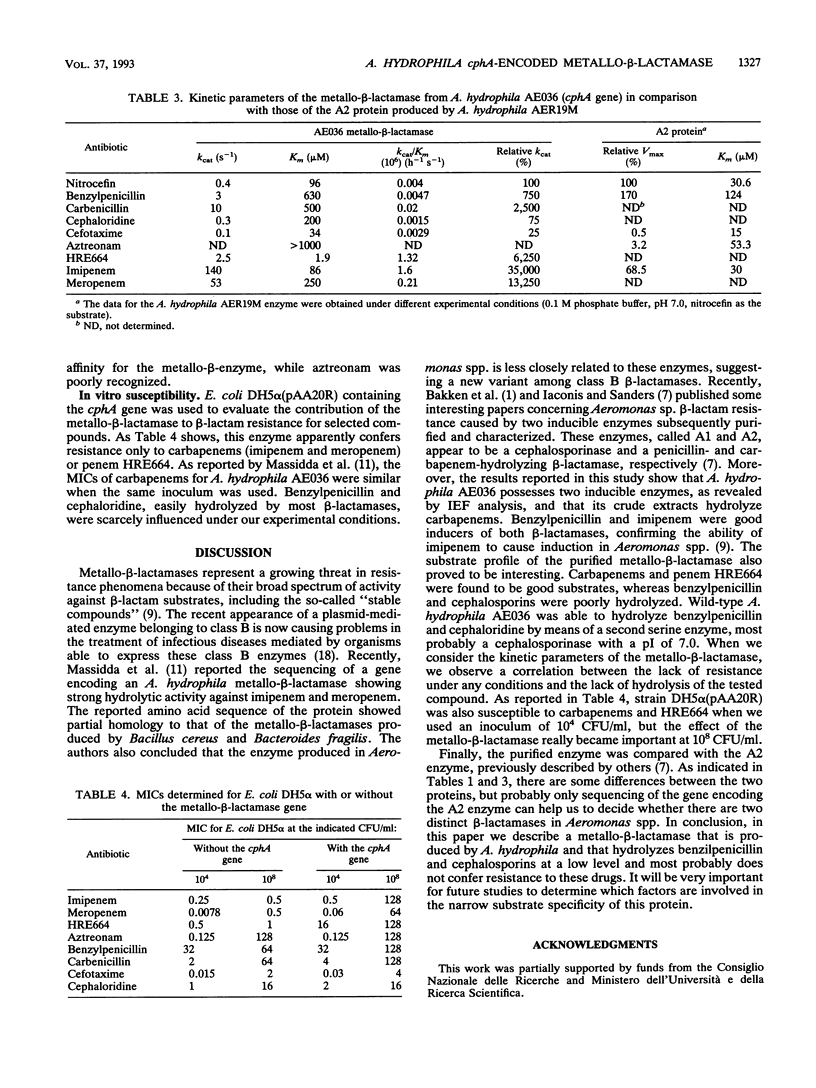
The Aeromonas hydrophila AE036 chromosome contains a cphA gene encoding a metallo-beta-lactamase highly active against carbapenem antibiotics. This enzyme was induced in strain AE036 to the same extent by both benzylpenicillin and imipenem. When the cphA gene was inserted into plasmid pACYC184, used to transform Escherichia coli DH5 alpha, the MICs of imipenem, meropenem, and penem HRE664 for recombinant clone DH5 alpha(pAA20R), expressing the Aeromonas metallo-beta-lactamase, were significantly increased, but those of penicillins and cephalosporins were not. When the metallo-beta-lactamase purified from E. coli DH5 alpha(pAA20R) was assayed with several beta-lactam substrates, it hydrolyzed carbapenems but not penicillins or cephalosporins efficiently. These results demonstrate that this metallo-beta-lactamase possesses an unusual spectrum of activity compared with all the other class B enzymes identified so far, being active on penems and carbapenems only. This enzyme may thus contribute to the development of resistance to penems and carbapenems but not other beta-lactams.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bakken J. S., Sanders C. C., Clark R. B., Hori M. Beta-lactam resistance in Aeromonas spp. caused by inducible beta-lactamases active against penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Sep;32(9):1314–1319. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.9.1314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felici A., Amicosante G., Oratore A., Strom R., Ledent P., Joris B., Fanuel L., Frère J. M. An overview of the kinetic parameters of class B beta-lactamases. Biochem J. 1993 Apr 1;291(Pt 1):151–155. doi: 10.1042/bj2910151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frère J. M. Quantitative relationship between sensitivity to beta-lactam antibiotics and beta-lactamase production in gram-negative bacteria--I. Steady-state treatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 1;38(9):1415–1426. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iaconis J. P., Sanders C. C. Purification and characterization of inducible beta-lactamases in Aeromonas spp. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jan;34(1):44–51. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M. Carbapenemases. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Jun;29(6):609–613. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.6.609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livermore D. M. Interplay of impermeability and chromosomal beta-lactamase activity in imipenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Sep;36(9):2046–2048. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.9.2046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massidda O., Rossolini G. M., Satta G. The Aeromonas hydrophila cphA gene: molecular heterogeneity among class B metallo-beta-lactamases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4611–4617. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4611-4617.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew A., Harris A. M., Marshall M. J., Ross G. W. The use of analytical isoelectric focusing for detection and identification of beta-lactamases. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 May;88(1):169–178. doi: 10.1099/00221287-88-1-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Normark S. Sensitivity of Escherichia coli to various beta-lactams is determined by the interplay of outer membrane permeability and degradation by periplasmic beta-lactamases: a quantitative predictive treatment. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Jul;1(1):29–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb00523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliva B., Marinucci M. C., Amicosante G., Oratore A., Bennett P. M. Citrobacter diversus ULA27 produces two forms of a chromosomal beta-lactamase. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1987 Jul;20(1):23–35. doi: 10.1093/jac/20.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salfi V., Amicosante G., Oratore A. Preliminary experimental data on inhibition of beta-lactamase i from B. cereus by Cu (++) and Zn(++). Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1978 Jul 30;54(14):1298–1303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon K., King A., Phillips I. Beta-lactamases with high activity against imipenem and Sch 34343 from Aeromonas hydrophila. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Jan;17(1):45–50. doi: 10.1093/jac/17.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waley S. G. An explicit model for bacterial resistance: application to beta-lactam antibiotics. Microbiol Sci. 1987 May;4(5):143–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Iyobe S., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. Transferable imipenem resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):147–151. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner V., Sanders C. C., Sanders W. E., Jr, Goering R. V. Role of beta-lactamases and outer membrane proteins in multiple beta-lactam resistance of Enterobacter cloacae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):455–459. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


