Abstract
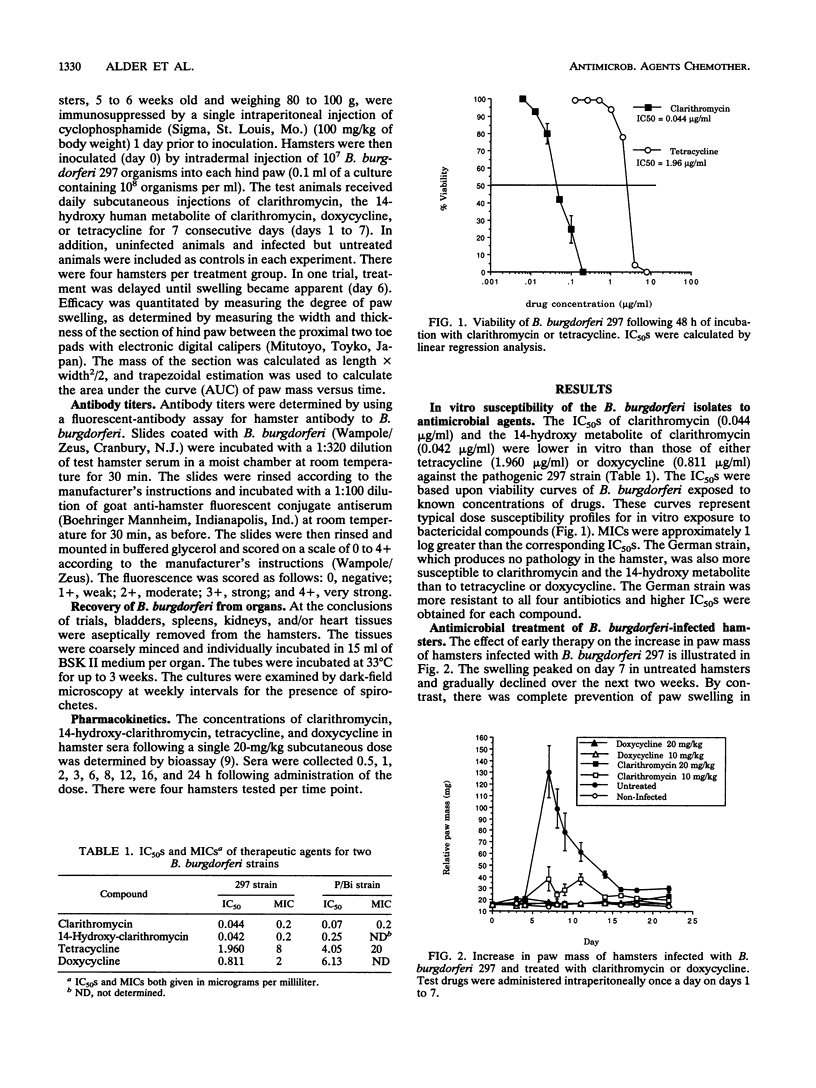
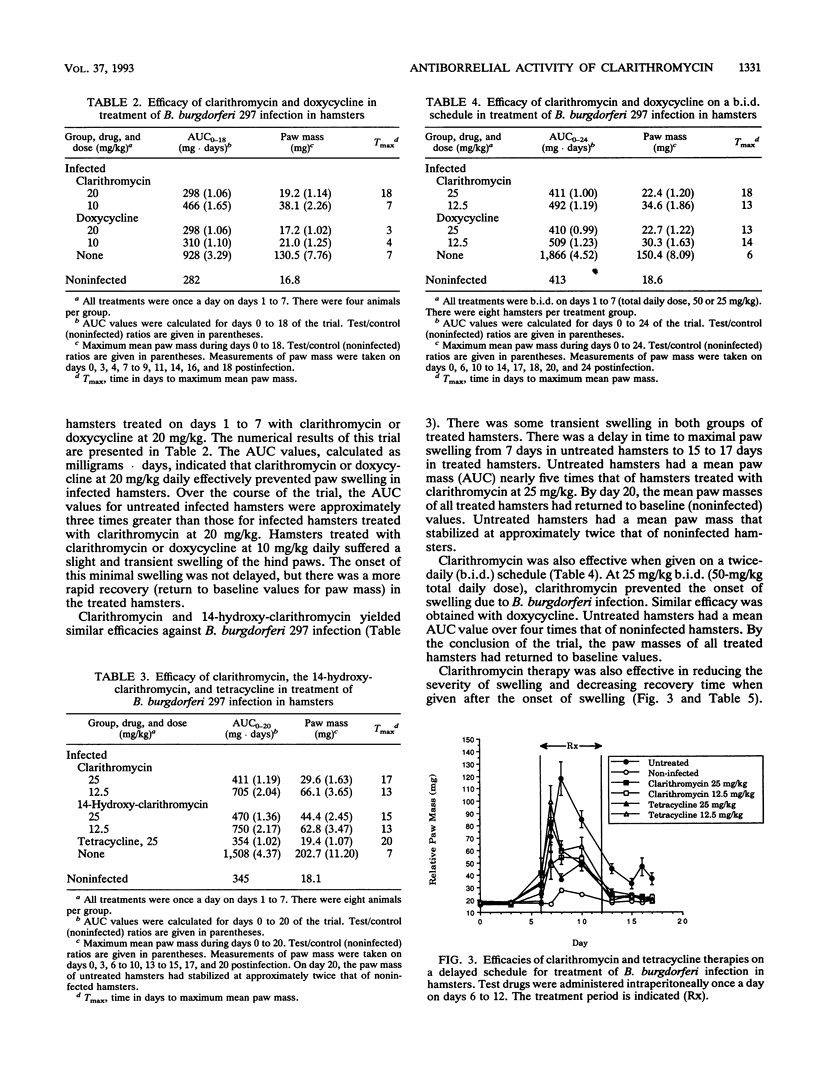
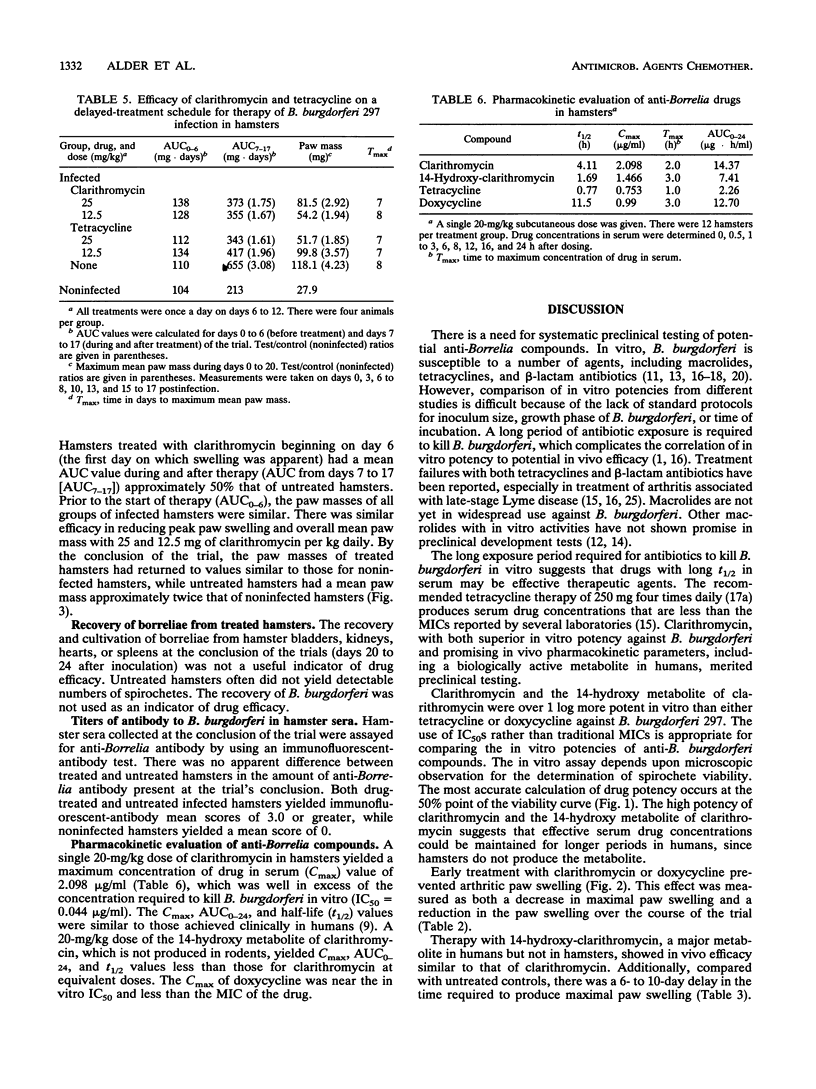
Clarithromycin provided effective therapy against arthritis induced by Borrelia burgdorferi infection in the hamster. In vitro, clarithromycin was at least 1 log more potent than tetracycline against two isolates of B. burgdorferi from human sources, as measured by MICs and 50% inhibitory concentrations. Clarithromycin was effective in preventing the onset of B. burgdorferi-induced arthritis, as determined by several parameters of paw swelling. When administered after the onset of arthritis, clarithromycin therapy reduced the degree of swelling and decreased recovery time. These results suggest that clarithromycin has potential as an effective therapy for Lyme disease.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agger W. A., Callister S. M., Jobe D. A. In vitro susceptibilities of Borrelia burgdorferi to five oral cephalosporins and ceftriaxone. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Aug;36(8):1788–1790. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.8.1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Isolation and cultivation of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):521–525. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger B. W. Treatment of erythema chronicum migrans of Lyme disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:346–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31868.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchstein S. R., Gardner P. Lyme disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1991 Mar;5(1):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Halperin J. J., Pass H., Luft B. J. Ceftriaxone as effective therapy in refractory Lyme disease. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1322–1325. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Halperin J. J., Volkman D. J., Luft B. J. Treatment of late Lyme borreliosis--randomised comparison of ceftriaxone and penicillin. Lancet. 1988 May 28;1(8596):1191–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattwyler R. J., Volkman D. J., Halperin J. J., Luft B. J., Thomas J., Golightly M. G. Specific immune responses in Lyme borreliosis. Characterization of T cell and B cell responses to Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:93–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Steere A. C. Clinical pathologic correlations of Lyme disease by stage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:65–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes P. B., Ramer N., Rode R. A., Freiberg L. Bioassay for A-56268 (TE-031) and identification of its major metabolite, 14-hydroxy-6-O-methyl erythromycin. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Feb;7(1):73–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01962181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldings E. A., Jericho J. Lyme disease. Clin Rheum Dis. 1986 Aug;12(2):343–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C. B., Jurkovich P. J., Collins J. J. Comparative in vitro and in vivo susceptibilities of the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi to cefuroxime and other antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Nov;34(11):2133–2136. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.11.2133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M., Girard D. In-vitro and in-vivo susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi to azithromycin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Jan;25 (Suppl A):33–38. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.suppl_a.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Kodner C., Russell M. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, to four antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Feb;31(2):164–167. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.2.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson S. E., Klein G. C., Schmid G. P., Feeley J. C. Susceptibility of the Lyme disease spirochete to seven antimicrobial agents. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):549–553. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft B. J., Gorevic P. D., Halperin J. J., Volkman D. J., Dattwyler R. J. A perspective on the treatment of Lyme borreliosis. Rev Infect Dis. 1989 Sep-Oct;11 (Suppl 6):S1518–S1525. doi: 10.1093/clinids/11.supplement_6.s1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luger S. W., Krauss E. Serologic tests for Lyme disease. Interlaboratory variability. Arch Intern Med. 1990 Apr;150(4):761–763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mursic V. P., Wilske B., Schierz G., Holmburger M., Süss E. In vitro and in vivo susceptibility of Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;6(4):424–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02013102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preac-Mursic V., Wilske B., Schierz G., Süss E., Gross B. Comparative antimicrobial activity of the new macrolides against Borrelia burgdorferi. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1989 Jul;8(7):651–653. doi: 10.1007/BF01968150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz J. L., Schell R. F., Hejka A., England D. M., Konick L. Induction of lyme arthritis in LSH hamsters. Infect Immun. 1988 Sep;56(9):2336–2342. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.9.2336-2342.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Bartenhagen N. H., Craft J. E., Hutchinson G. J., Newman J. H., Rahn D. W., Sigal L. H., Spieler P. N., Stenn K. S., Malawista S. E. The early clinical manifestations of Lyme disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Jul;99(1):76–82. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-1-76. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Grodzicki R. L., Kornblatt A. N., Craft J. E., Barbour A. G., Burgdorfer W., Schmid G. P., Johnson E., Malawista S. E. The spirochetal etiology of Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 31;308(13):733–740. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303313081301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Bratzke H. J., Neubert U., Wilske B., Duray P. H. Borrelia burgdorferi in a newborn despite oral penicillin for Lyme borreliosis during pregnancy. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1988 Apr;7(4):286–289. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198804000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


