Abstract
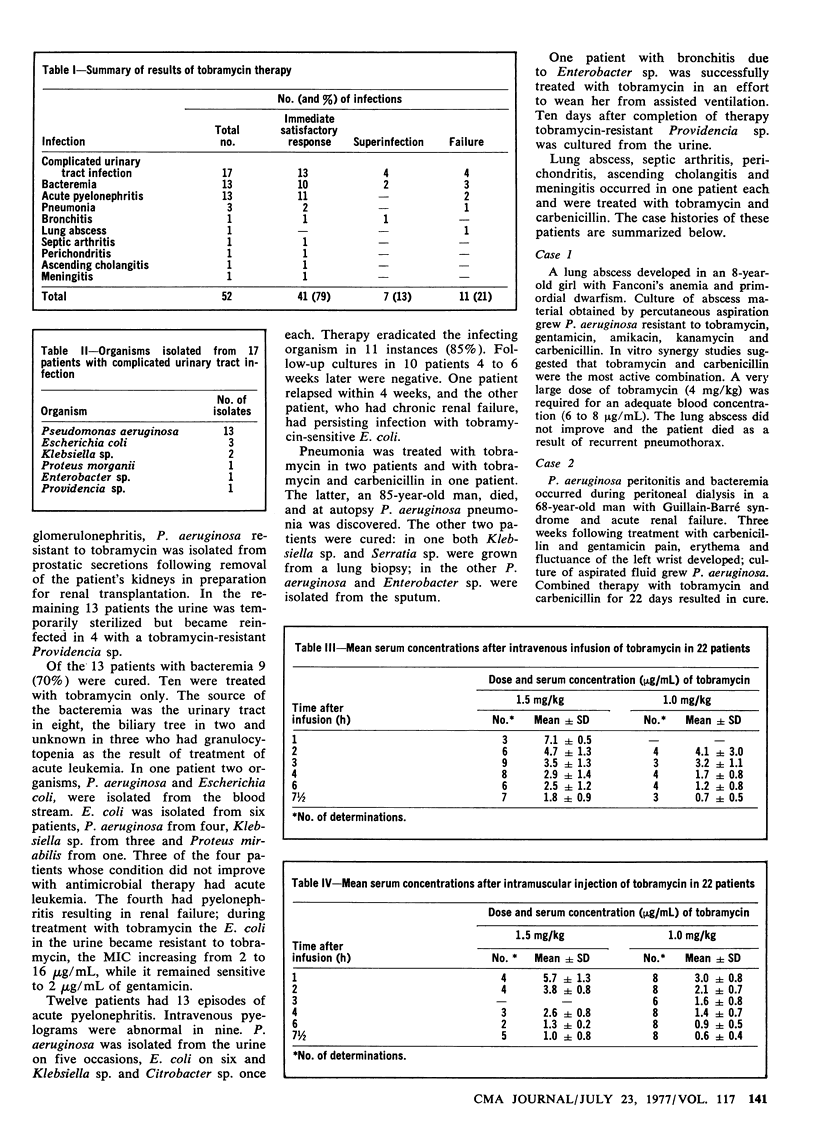
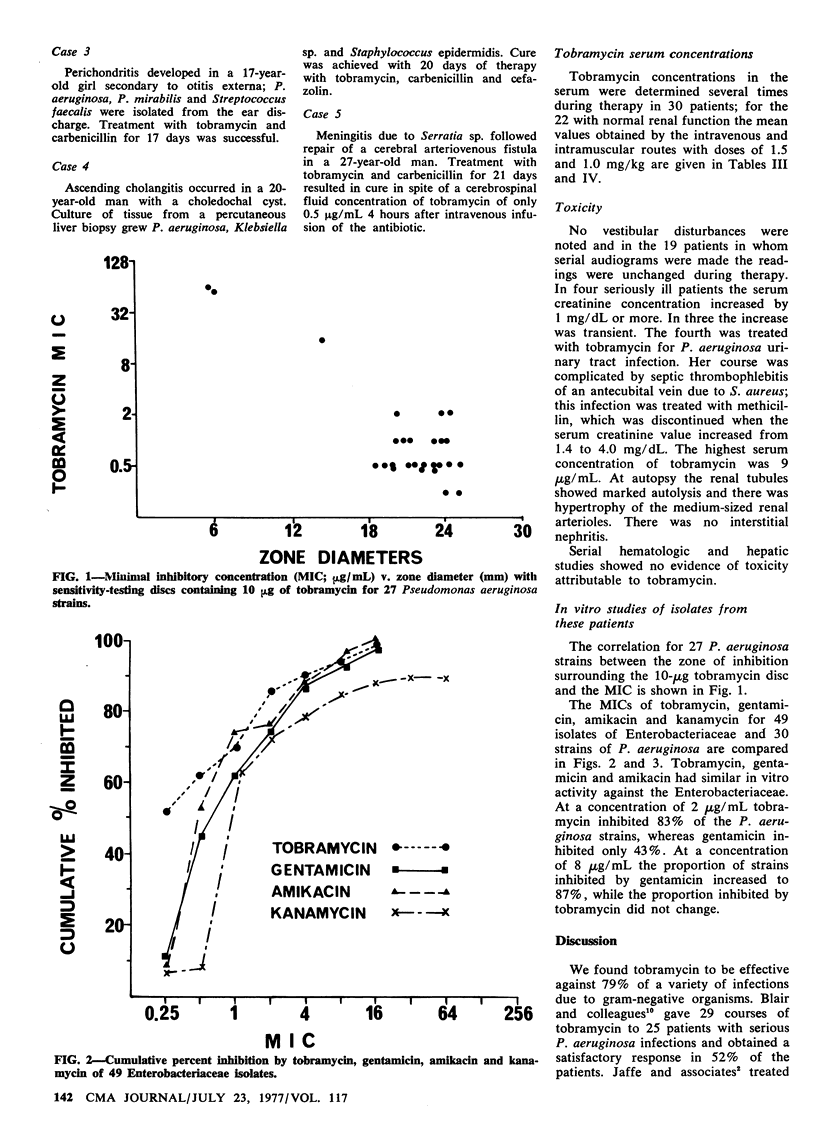
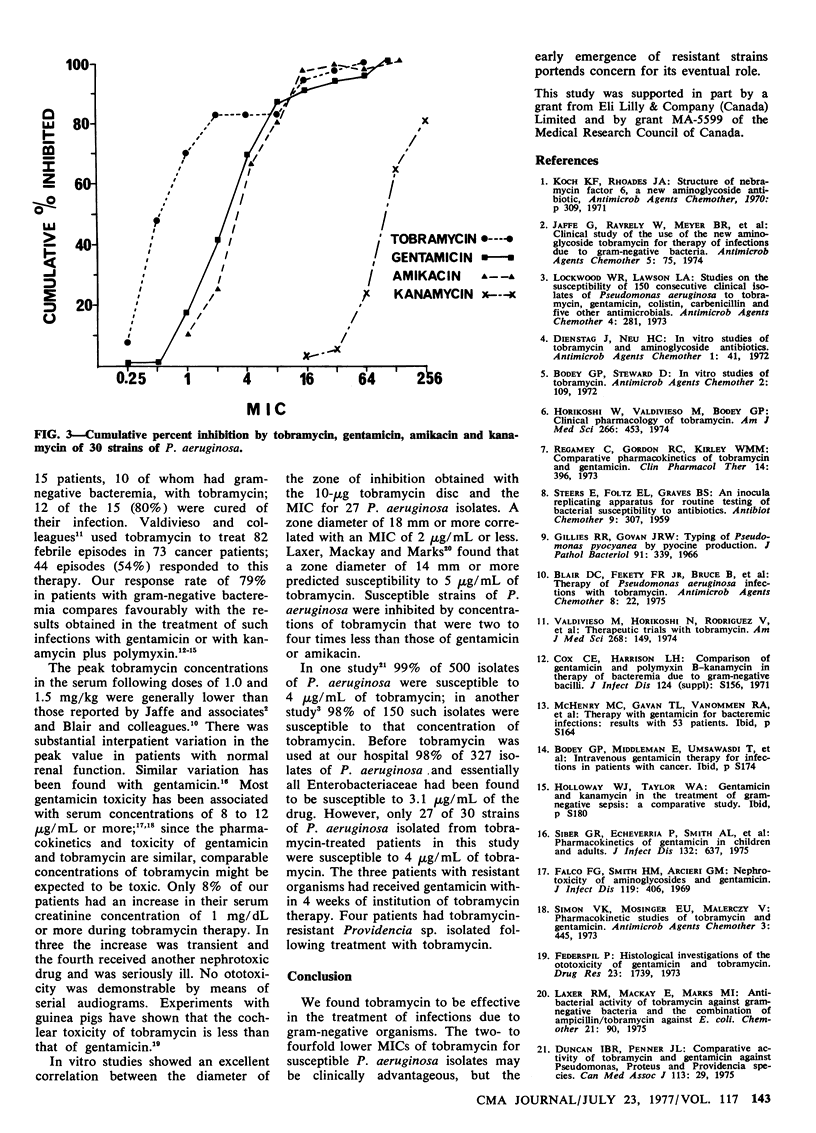
Tobramycin, an aminoglycoside antibiotic, was used to treat 52 infections due to gram-negative organisms in 51 patients. Complicated urinary tract infections, bacteremia and pyelonephritis accounted for 80% of the infections. The rate of immediate satisfactory response was 79%. During therapy with tobramycin, resistant organisms emerged in four patients--two Pseudomonas aeruginosa and two Escherichia coli strains. There were four superinfections with tobramycin-resistant Providencia sp. In four seriously ill patients the serum creatinine concentration increased 1 mg/dL or more; in three the increase was transient. No auditory toxicity was noted in the 19 patients in whom serial audiograms were made. In vitro testing of isolates from these patients showed that tobramycin and gentamicin had equal activity against Enterobacteriaceae. Tobramycin was two to four times more active against susceptible P. aeruginosa.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bodey G. P., Stewart D. In vitro studies of tobramycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Sep;2(3):109–113. doi: 10.1128/aac.2.3.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. E., Harrison L. H. Comparison of gentamicin and polymyxin B-kanamycin in therapy of bacteremia due to gram-negative bacilli. J Infect Dis. 1971 Dec;124 (Suppl):S156–S163. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.supplement_1.s156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducan I. B., Penner J. L. Comparative activity of tobramycin and gentamicin against Pseudomonas, Proteus and Providencia species. Can Med Assoc J. 1975 Jul 12;113(1):29–31. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco F. G., Smith H. M., Arcieri G. M. Nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides and gentamicin. J Infect Dis. 1969 Apr-May;119(4):406–409. doi: 10.1093/infdis/119.4-5.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspil P. [Morphological investigations on the ototoxicity of gentamicin and tobramycin]. Arzneimittelforschung. 1973 Dec;23(12):1739–1745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies R. R., Govan J. R. Typing of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by pyocine production. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(2):339–345. doi: 10.1002/path.1700910207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi N., Valdivieso M., Bodey G. P. Clinical pharmacology of tobramycin. Am J Med Sci. 1973 Dec;266(6):453–458. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197312000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe G., Ravreby W., Meyers B. R., Hirschman S. Z. Clinical study of the use of the new aminoglycoside tobramycin for therapy of infections due to gram-negative bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1974 Jan;5(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/aac.5.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch K. F., Rhoades J. A. Structure of nebramycin factor 6, a new aminoglycosidic antibiotic. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1970;10:309–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laxer R. M., Mackay E., Marks M. I. Antibacterial activity of tobramycin against gram-negative bacteria and the combination of ampicillin/tobramycin against E. coli. Chemotherapy. 1975;21(2):90–98. doi: 10.1159/000221851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood W. R., Lawson L. A. Studies on the susceptibility of 150 consecutive clinical isolates of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to tobramycin, gentamicin, colistin, carbenicillin, and five other antimicrobials. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):281–284. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regamey C., Gordon R. C., Kirby W. M. Comparative pharmacokinetics of tobramycin and gentamicin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1973 May-Jun;14(3):396–403. doi: 10.1002/cpt1973143396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon V. K., Mösinger E. U., Malerczy V. Pharmacokinetic studies of tobramycin and gentamicin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Apr;3(4):445–450. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.4.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valdivieso M., Horikoshi N., Rodriguez V., Bodey G. P. Therapeutic trials with tobramycin. Am J Med Sci. 1974 Sep;268(3):149–156. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197409000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


