Full text
PDF
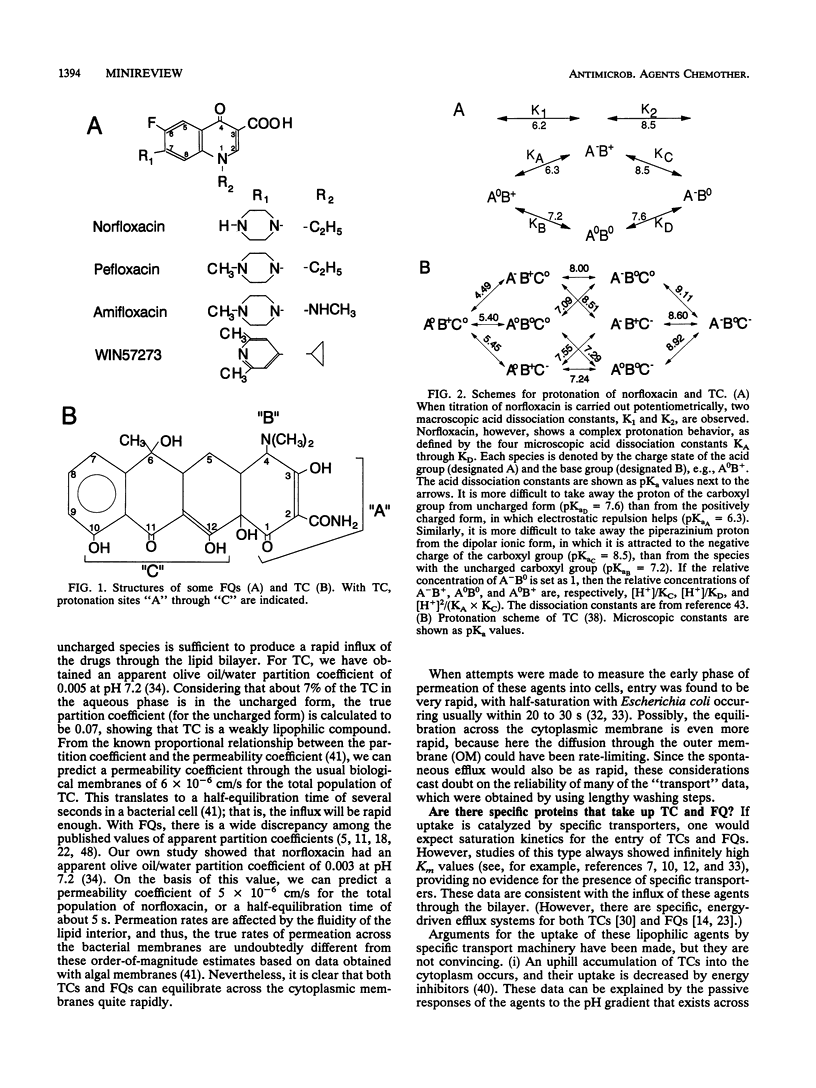

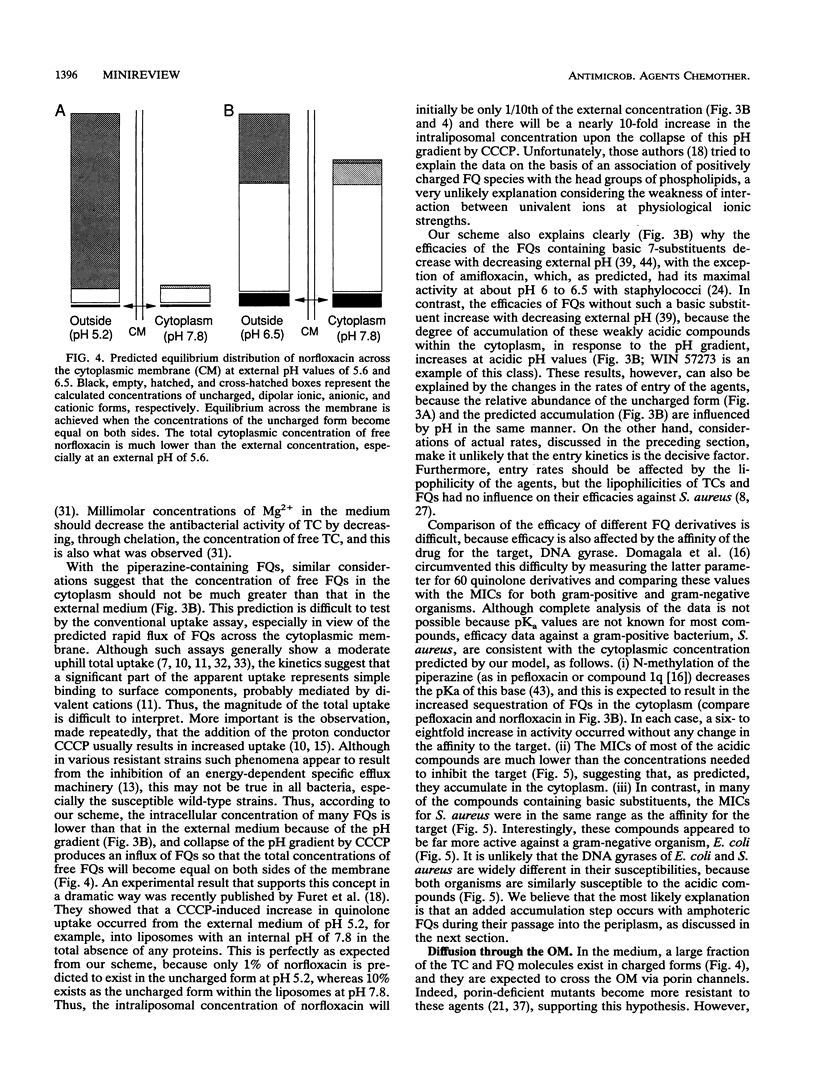
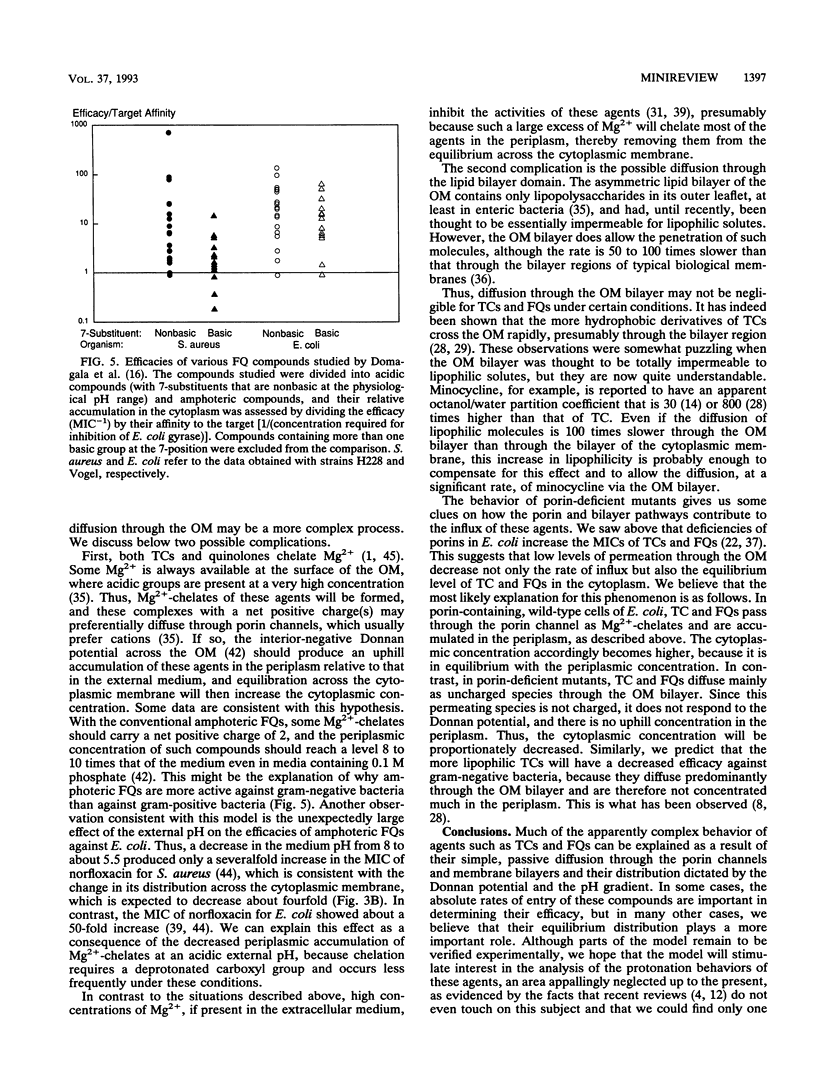


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALBERT A., REES C. W. Avidity of the tetracyclines for the cations of metals. Nature. 1956 Mar 3;177(4505):433–434. doi: 10.1038/177433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argast M., Beck C. F. Tetracycline diffusion through phospholipid bilayers and binding to phospholipids. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Aug;26(2):263–265. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asahina Y., Ishizaki T., Suzue S. Recent advances in structure activity relationships in new quinolones. Prog Drug Res. 1992;38:57–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashby J., Piddock L. J., Wise R. An investigation of the hydrophobicity of the quinolones. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Dec;16(6):805–808. doi: 10.1093/jac/16.6.805-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean R. C., Shepherd W. C., Chan H. Permeability of lipid bilayer membranes to organic solutes. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Sep;52(3):495–508. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedard J., Wong S., Bryan L. E. Accumulation of enoxacin by Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Sep;31(9):1348–1354. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.9.1348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., Robillard N. J. Factors influencing the accumulation of ciprofloxacin in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1921–1926. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. S., Georgopapadakou N. H. Routes of quinolone permeation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Apr;32(4):438–442. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.4.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I., Hawkey P. M., Hinton M. Tetracyclines, molecular and clinical aspects. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1992 Mar;29(3):245–277. doi: 10.1093/jac/29.3.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. P., Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., McMurry L. M., Levy S. B. Endogenous active efflux of norfloxacin in susceptible Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1988 Aug;32(8):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aac.32.8.1187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colaizzi J. L., Klink P. R. pH-Partition behavior of tetracyclines. J Pharm Sci. 1969 Oct;58(10):1184–1189. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600581003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diver J. M., Piddock L. J., Wise R. The accumulation of five quinolone antibacterial agents by Escherichia coli. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1990 Mar;25(3):319–333. doi: 10.1093/jac/25.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domagala J. M., Hanna L. D., Heifetz C. L., Hutt M. P., Mich T. F., Sanchez J. P., Solomon M. New structure-activity relationships of the quinolone antibacterials using the target enzyme. The development and application of a DNA gyrase assay. J Med Chem. 1986 Mar;29(3):394–404. doi: 10.1021/jm00153a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzblau S. G., White K. E. Comparative in vitro activities of 20 fluoroquinolones against Mycobacterium leprae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Feb;34(2):229–231. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furet Y. X., Deshusses J., Pechère J. C. Transport of pefloxacin across the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane in quinolone-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Nov;36(11):2506–2511. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.11.2506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber R. H. Activity of minocycline in Mycobacterium leprae-infected mice. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jul;156(1):236–239. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.1.236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haemers A., Leysen D. C., Bollaert W., Zhang M. Q., Pattyn S. R. Influence of N substitution on antimycobacterial activity of ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):496–497. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Differences in susceptibility to quinolones of outer membrane mutants of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Mar;29(3):535–538. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.3.535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai K., Aoyama H., Suzue S., Irikura T., Iyobe S., Mitsuhashi S. Isolation and characterization of norfloxacin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Aug;30(2):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.30.2.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper D. C., Wolfson J. S., Souza K. S., Ng E. Y., McHugh G. L., Swartz M. N. Mechanisms of quinolone resistance in Escherichia coli: characterization of nfxB and cfxB, two mutant resistance loci decreasing norfloxacin accumulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):283–290. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iravani A., Welty G. S., Newton B. R., Richard G. A. Effects of changes in pH, medium, and inoculum size on the in vitro activity of amifloxacin against urinary isolates of Staphylococcus saprophyticus and Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Apr;27(4):449–451. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.4.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R. Stoichiometry of the H+-ATPase of growing and resting, aerobic Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5534–5538. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klopman G., Macina O. T., Levinson M. E., Rosenkranz H. S. Computer automated structure evaluation of quinolone antibacterial agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1987 Nov;31(11):1831–1840. doi: 10.1128/aac.31.11.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leive L., Telesetsky S., Coleman W. G., Jr, Carr D. Tetracyclines of various hydrophobicities as a probe for permeability of Escherichia coli outer membranes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 May;25(5):539–544. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.5.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L. M., Cullinane J. C., Levy S. B. Transport of the lipophilic analog minocycline differs from that of tetracycline in susceptible and resistant Escherichia coli strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1982 Nov;22(5):791–799. doi: 10.1128/aac.22.5.791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMurry L., Petrucci R. E., Jr, Levy S. B. Active efflux of tetracycline encoded by four genetically different tetracycline resistance determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3974–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau N., Lacroix P., Fournel L. Antibiotic uptake by bacteria as measured by partition in polymer aqueous phase systems. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):94–100. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90430-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer P. G., Piddock L. J. A comparison of methods used for measuring the accumulation of quinolones by Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1991 Nov;28(5):639–653. doi: 10.1093/jac/28.5.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Jarlier V. Permeability of the mycobacterial cell wall. Res Microbiol. 1991 May;142(4):437–443. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90117-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido H., Vaara M. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Mar;49(1):1–32. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.1.1-32.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plésiat P., Nikaido H. Outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria are permeable to steroid probes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 May;6(10):1323–1333. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Schnaitman C. A. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. VII. Evidence that bacteriophage-directed protein 2 functions as a pore. J Bacteriol. 1978 Mar;133(3):1181–1189. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.3.1181-1189.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGLER N. E., BAG S. P., LEYDEN D. E., SUDMEIER J. L., REILLEY C. N. DETERMINATION OF A PROTONATION SCHEME OF TETRACYCLINE USING NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE. Anal Chem. 1965 Jun;37:872–875. doi: 10.1021/ac60226a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. T., Ratcliffe N. T. Einfluss von pH-Wert und Magnesium auf die antibakterielle Aktivität von Chinolonpräparaten. Infection. 1986;14 (Suppl 1):S31–S35. doi: 10.1007/BF01645195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. C., Chopra I. Energetics of tetracycline transport into Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Apr;25(4):446–449. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.4.446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takács-Novák K., Noszál B., Hermecz I., Keresztúri G., Podányi B., Szász G. Protonation equilibria of quinolone antibacterials. J Pharm Sci. 1990 Nov;79(11):1023–1028. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600791116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teoh-Chan C. H., Cowlishaw A., Eley A., Slater G., Greenwood D. Laboratory evaluation of enoxacin: comparison with norfloxacin and nalidixic acid. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jan;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1093/jac/15.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmers K., Sternglanz R. Ionization and divalent cation dissociation constants of nalidixic and oxolinic acids. Bioinorg Chem. 1978 Aug;9(2):145–155. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3061(00)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Inoue M., Mitsuhashi S. In vitro activity of amifloxacin against outer membrane mutants of the family Enterobacteriaceae and frequency of spontaneous resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Nov;33(11):1837–1840. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.11.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A., Ohmori H., Kaneko-Ohdera M., Nomura T., Sawai T. Delta pH-dependent accumulation of tetracycline in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1991 Jan;35(1):53–56. doi: 10.1128/aac.35.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


