Abstract
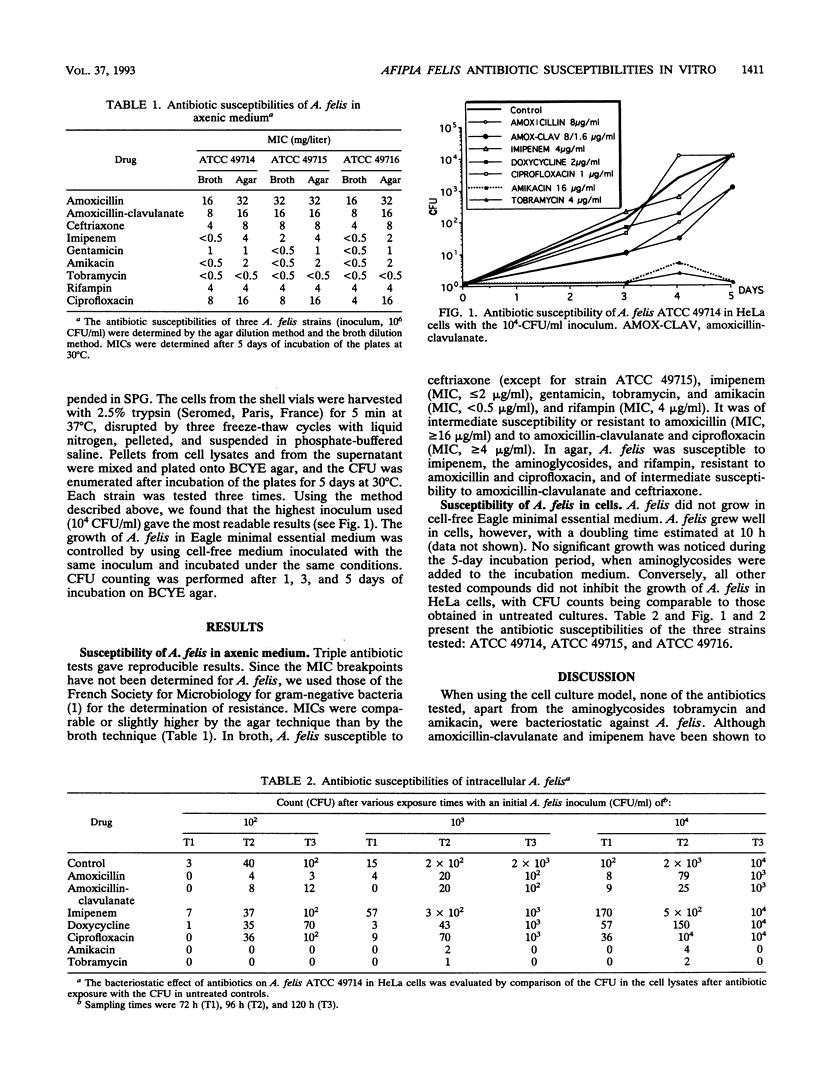
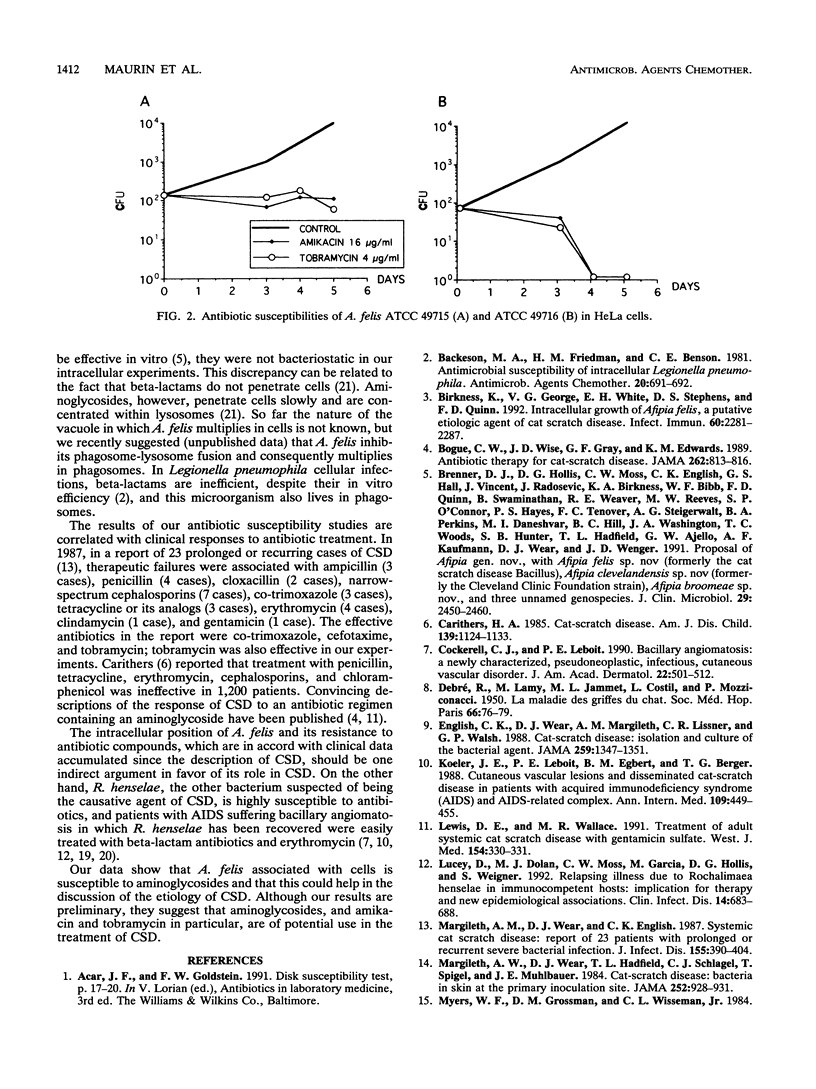
Afipia felis, one of the putative agents of cat scratch disease (CSD), is a facultative intracellular bacterium. Although CSD is considered not to be susceptible to antibiotic therapy, sporadic case reports indicated that aminoglycosides may be effective. We determined the in vitro antibiotic susceptibilities of three A. felis strains in axenic medium and in a cell model. In axenic medium, A. felis was susceptible to imipenem, aminoglycosides, and rifampin when using either the broth dilution technique or the agar technique. When grown in HeLa cells, A. felis was susceptible to amikacin and tobramycin but was resistant to the other compounds tested. Despite its intracellular location, A. felis can apparently be reached by aminoglycosides. Thus, the in vitro data presented here are in accord with the clinical data obtained in patients suffering CSD.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacheson M. A., Friedman H. M., Benson C. E. Antimicrobial susceptibility of intracellular Legionella pneumophila. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Nov;20(5):691–692. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkness K. A., George V. G., White E. H., Stephens D. S., Quinn F. D. Intracellular growth of Afipia felis, a putative etiologic agent of cat scratch disease. Infect Immun. 1992 Jun;60(6):2281–2287. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.6.2281-2287.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogue C. W., Wise J. D., Gray G. F., Edwards K. M. Antibiotic therapy for cat-scratch disease? JAMA. 1989 Aug 11;262(6):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Hollis D. G., Moss C. W., English C. K., Hall G. S., Vincent J., Radosevic J., Birkness K. A., Bibb W. F., Quinn F. D. Proposal of Afipia gen. nov., with Afipia felis sp. nov. (formerly the cat scratch disease bacillus), Afipia clevelandensis sp. nov. (formerly the Cleveland Clinic Foundation strain), Afipia broomeae sp. nov., and three unnamed genospecies. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Nov;29(11):2450–2460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.11.2450-2460.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers H. A. Cat-scratch disease. An overview based on a study of 1,200 patients. Am J Dis Child. 1985 Nov;139(11):1124–1133. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1985.02140130062031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerell C. J., LeBoit P. E. Bacillary angiomatosis: a newly characterized, pseudoneoplastic, infectious, cutaneous vascular disorder. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1990 Mar;22(3):501–512. doi: 10.1016/0190-9622(90)70071-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English C. K., Wear D. J., Margileth A. M., Lissner C. R., Walsh G. P. Cat-scratch disease. Isolation and culture of the bacterial agent. JAMA. 1988 Mar 4;259(9):1347–1352. doi: 10.1001/jama.259.9.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koehler J. E., LeBoit P. E., Egbert B. M., Berger T. G. Cutaneous vascular lesions and disseminated cat-scratch disease in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Sep 15;109(6):449–455. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-6-449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. E., Wallace M. R. Treatment of adult systemic cat scratch disease with gentamicin sulfate. West J Med. 1991 Mar;154(3):330–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucey D., Dolan M. J., Moss C. W., Garcia M., Hollis D. G., Wegner S., Morgan G., Almeida R., Leong D., Greisen K. S. Relapsing illness due to Rochalimaea henselae in immunocompetent hosts: implication for therapy and new epidemiological associations. Clin Infect Dis. 1992 Mar;14(3):683–688. doi: 10.1093/clinids/14.3.683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margileth A. M., Wear D. J., English C. K. Systemic cat scratch disease: report of 23 patients with prolonged or recurrent severe bacterial infection. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):390–402. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margileth A. W., Wear D. J., Hadfield T. L., Schlagel C. J., Spigel G. T., Muhlbauer J. E. Cat-scratch disease. Bacteria in skin at the primary inoculation site. JAMA. 1984 Aug 17;252(7):928–931. doi: 10.1001/jama.252.7.928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers W. F., Grossman D. M., Wisseman C. L., Jr Antibiotic susceptibility patterns in Rochalimaea quintana, the agent of trench fever. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jun;25(6):690–693. doi: 10.1128/aac.25.6.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins B. A., Swaminathan B., Jackson L. A., Brenner D. J., Wenger J. D., Regnery R. L., Wear D. J. Case 22-1992--pathogenesis of cat scratch disease. N Engl J Med. 1992 Nov 26;327(22):1599–1601. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199211263272215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnery R. L., Olson J. G., Perkins B. A., Bibb W. Serological response to "Rochalimaea henselae" antigen in suspected cat-scratch disease. Lancet. 1992 Jun 13;339(8807):1443–1445. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(92)92032-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudikoff D., Phelps R. G., Gordon R. E., Battone E. J. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related bacillary vascular proliferation (epithelioid angiomatosis): rapid response to erythromycin therapy. Arch Dermatol. 1989 May;125(5):706–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Bonfiglio T. A., Steigbigel R. T., Pereira M. An atypical subcutaneous infection associated with acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Nov;80(5):714–718. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/80.5.714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulkens P. M. Intracellular distribution and activity of antibiotics. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1991 Feb;10(2):100–106. doi: 10.1007/BF01964420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wear D. J., Margileth A. M., Hadfield T. L., Fischer G. W., Schlagel C. J., King F. M. Cat scratch disease: a bacterial infection. Science. 1983 Sep 30;221(4618):1403–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.6612349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



