Abstract
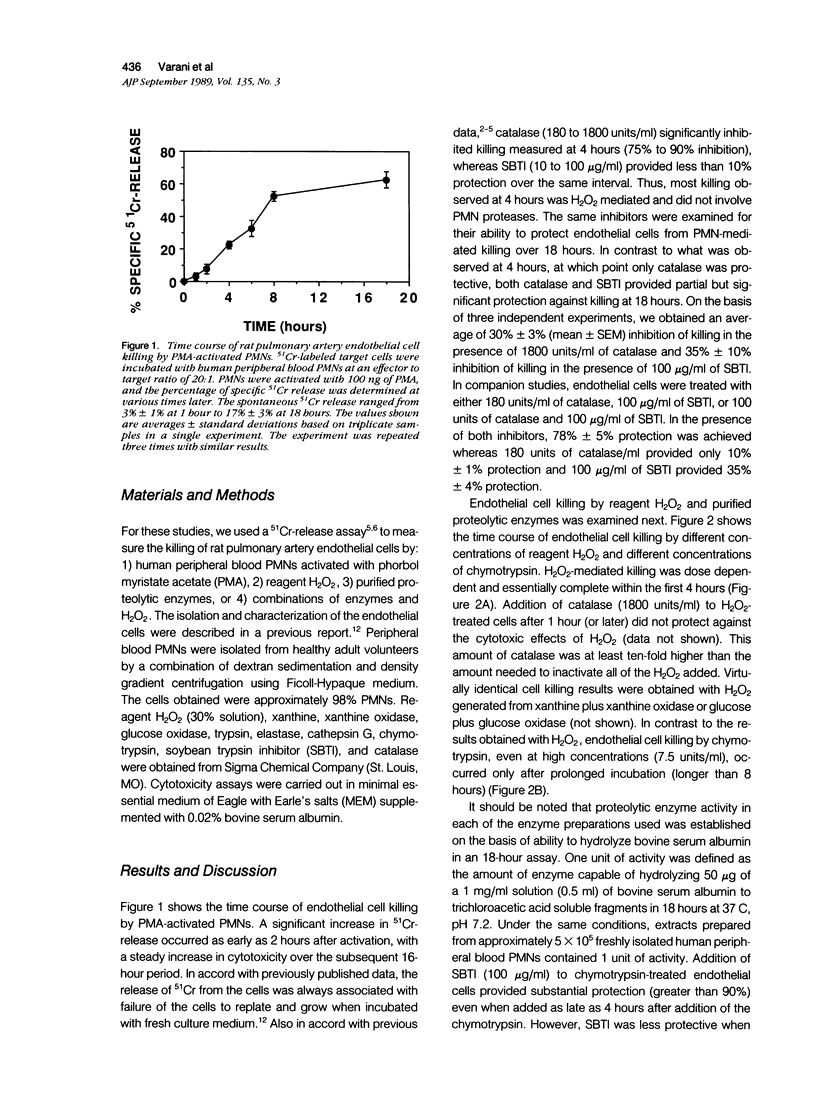
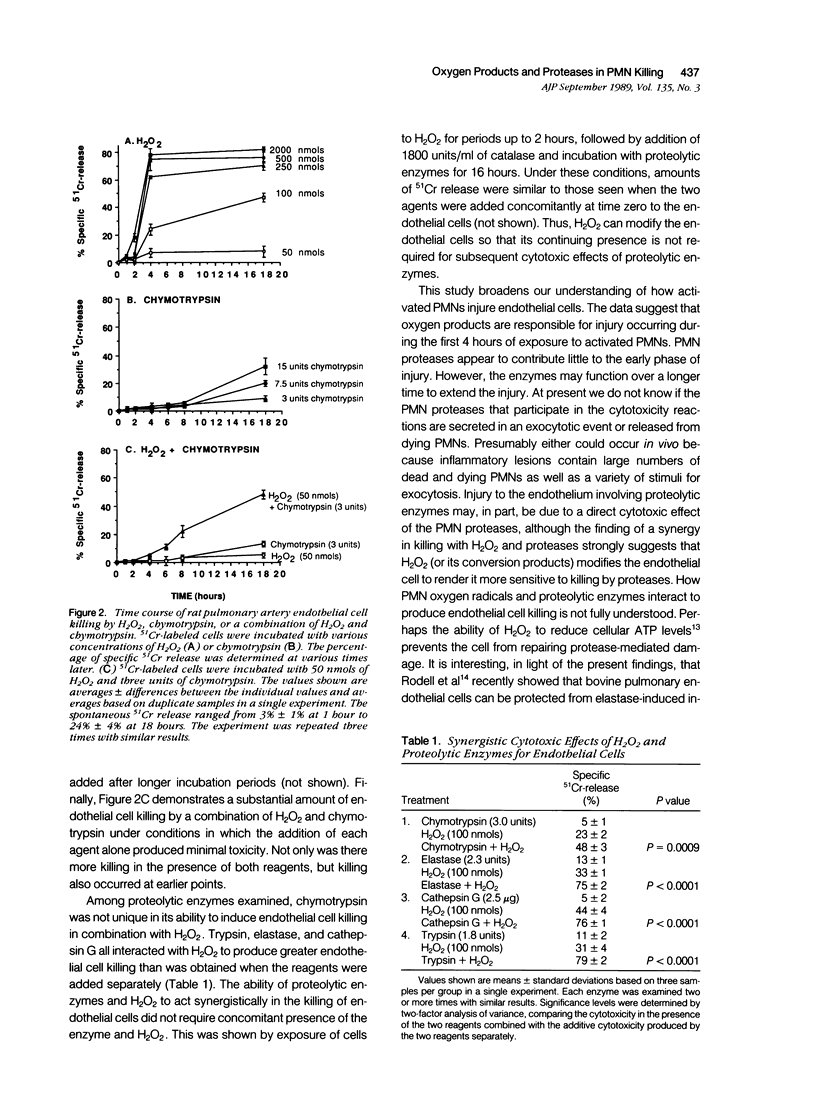
Killing of rat pulmonary artery endothelial cells by activated polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs), as measured at 4 hours, is catalase sensitive, iron dependent, and unaffected by addition of protease inhibitors. If the time course for exposure of endothelial cells to activated PMNs is extended to 18 hours, progressive injury occurs. Endothelial cell injury resulting at 18 hours is partially inhibited by catalase and partially inhibited by soybean trypsin inhibitor. Together, these two inhibitors function synergistically to protect the cells from injury. Exposure of endothelial cells to reagent H2O2 and purified proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase, and cathepsin G) mimics the effects of activated PMNs: H2O2 alone is cytotoxic with maximal killing achieved by 4 hours; proteolytic enzymes produce cytotoxicity only at high concentrations and only after prolonged incubation (longer than 8 hours); and, in combination, H2O2 and proteolytic enzymes act synergistically. These data provide compelling evidence that PMN-mediated injury of endothelial cells involves interaction between oxygen products and proteases.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fligiel S. E., Lee E. C., McCoy J. P., Johnson K. J., Varani J. Protein degradation following treatment with hydrogen peroxide. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):418–425. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I. Action of streptococcal haemolysins and proteolytic enzymes on Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Br J Exp Pathol. 1959 Oct;40:417–423. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBURG I., RAM M. Action of antibodies and plasmin on Ehrlich ascites tumour cells. Nature. 1960 Jan 30;185:328–330. doi: 10.1038/185328b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon D. E., Varani J., Phan S. H., Ward J. H., Kaplan J., Till G. O., Simon R. H., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Source of iron in neutrophil-mediated killing of endothelial cells. Lab Invest. 1987 Jul;57(1):37–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald R. A., Moy W. W. Effect of oxygen-derived free radicals on hyaluronic acid. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Apr;23(4):455–463. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Killen P. D., Harker L. A., Striker G. E., Wright D. G. Neutrophil-mediated endothelial injury in vitro mechanisms of cell detachment. J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;68(6):1394–1403. doi: 10.1172/JCI110390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlan J. M., Schwartz B. R., Reidy M. A., Schwartz S. M., Ochs H. D., Harker L. A. Activated neutrophils disrupt endothelial monolayer integrity by an oxygen radical-independent mechanism. Lab Invest. 1985 Feb;52(2):141–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. J., 2nd Neutrophils kill pulmonary endothelial cells by a hydrogen-peroxide-dependent pathway. An in vitro model of neutrophil-mediated lung injury. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1984 Aug;130(2):209–213. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1984.130.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontremoli S., Melloni E., Michetti M., Sacco O., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Damiani G., Horecker B. L. Cytolytic effects of neutrophils: role for a membrane-bound neutral proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1685–1689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodell T. C., Cheronis J. C., Ohnemus C. L., Piermattei D. J., Repine J. E. Xanthine oxidase mediates elastase-induced injury to isolated lungs and endothelium. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Nov;63(5):2159–2163. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.5.2159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks T., Moldow C. F., Craddock P. R., Bowers T. K., Jacob H. S. Oxygen radicals mediate endothelial cell damage by complement-stimulated granulocytes. An in vitro model of immune vascular damage. J Clin Invest. 1978 May;61(5):1161–1167. doi: 10.1172/JCI109031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedly L. A., Tonnesen M. G., Sandhaus R. A., Haslett C., Guthrie L. A., Johnston R. B., Jr, Henson P. M., Worthen G. S. Neutrophil-mediated injury to endothelial cells. Enhancement by endotoxin and essential role of neutrophil elastase. J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;77(4):1233–1243. doi: 10.1172/JCI112426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spragg R. G., Hinshaw D. B., Hyslop P. A., Schraufstätter I. U., Cochrane C. G. Alterations in adenosine triphosphate and energy charge in cultured endothelial and P388D1 cells after oxidant injury. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1471–1476. doi: 10.1172/JCI112126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Bendelow M. J., Sealey D. E., Kunkel S. L., Gannon D. E., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Tumor necrosis factor enhances susceptibility of vascular endothelial cells to neutrophil-mediated killing. Lab Invest. 1988 Aug;59(2):292–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Fligiel S. E., Till G. O., Kunkel R. G., Ryan U. S., Ward P. A. Pulmonary endothelial cell killing by human neutrophils. Possible involvement of hydroxyl radical. Lab Invest. 1985 Dec;53(6):656–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 9;320(6):365–376. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902093200606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Young J., LoBuglio A. F., Slivka A., Nimeh N. F. Role of hydrogen peroxide in neutrophil-mediated destruction of cultured endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):714–721. doi: 10.1172/JCI110307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



