Abstract
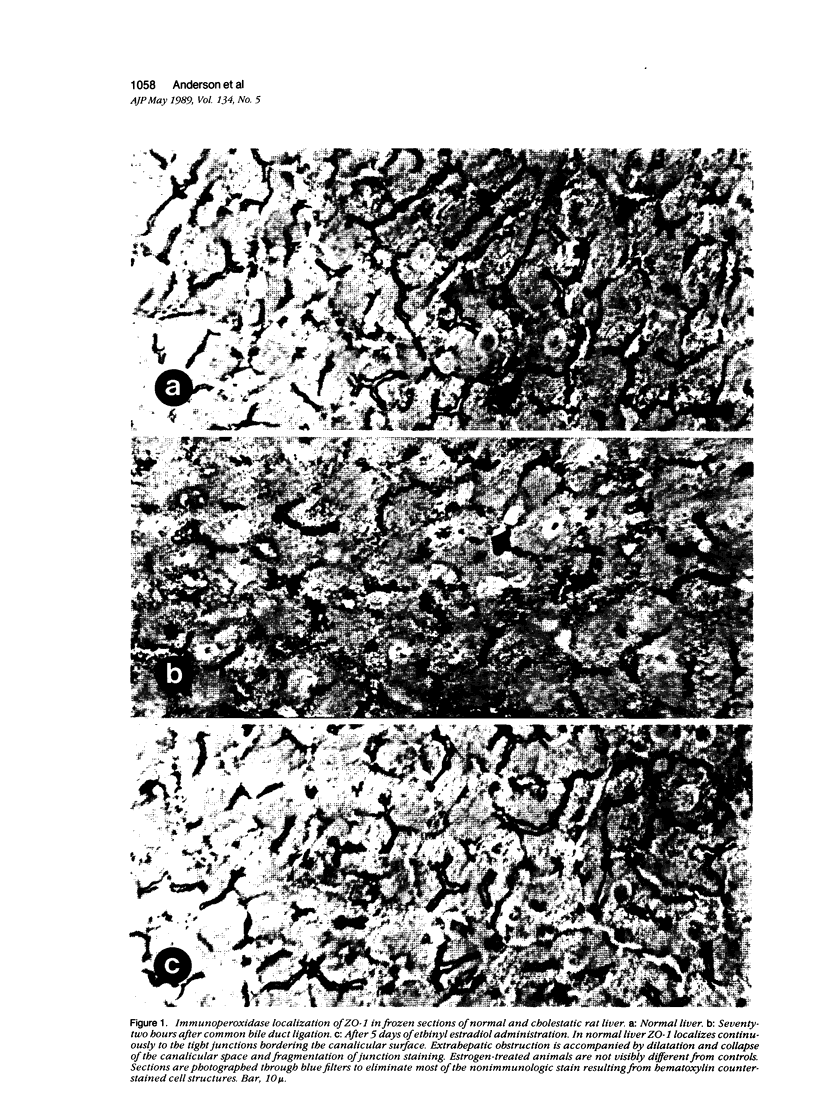
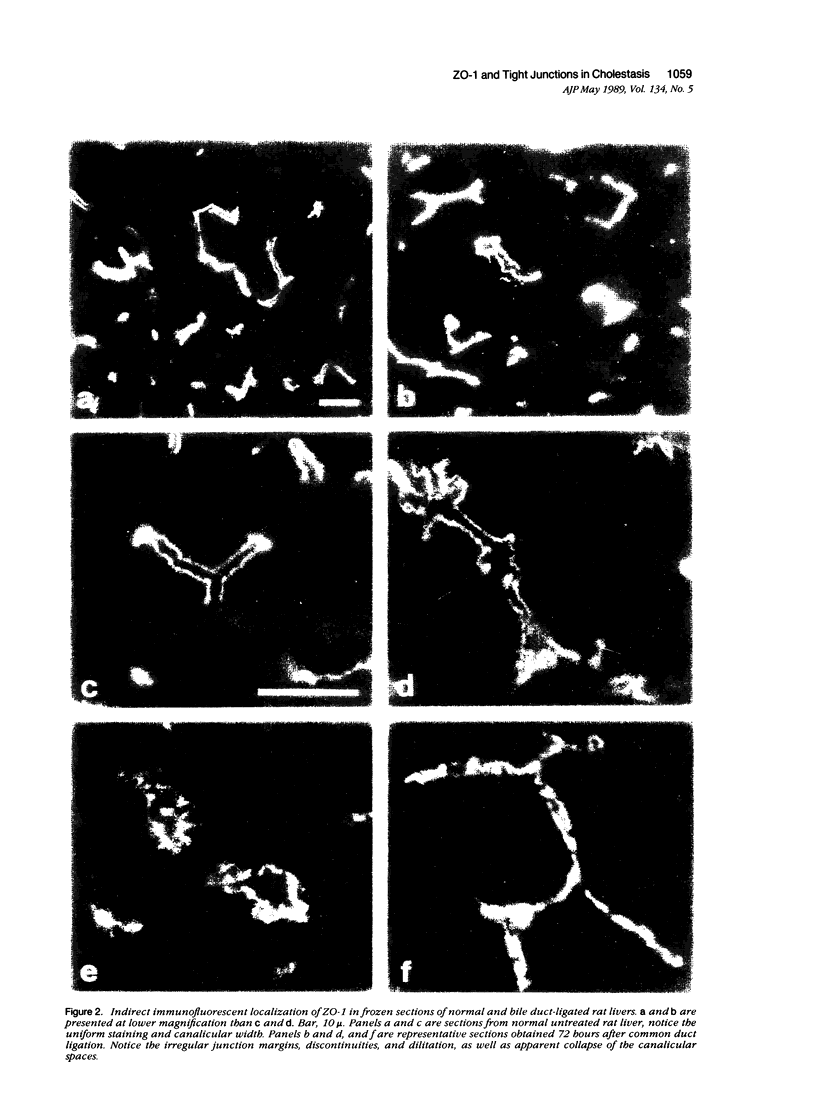
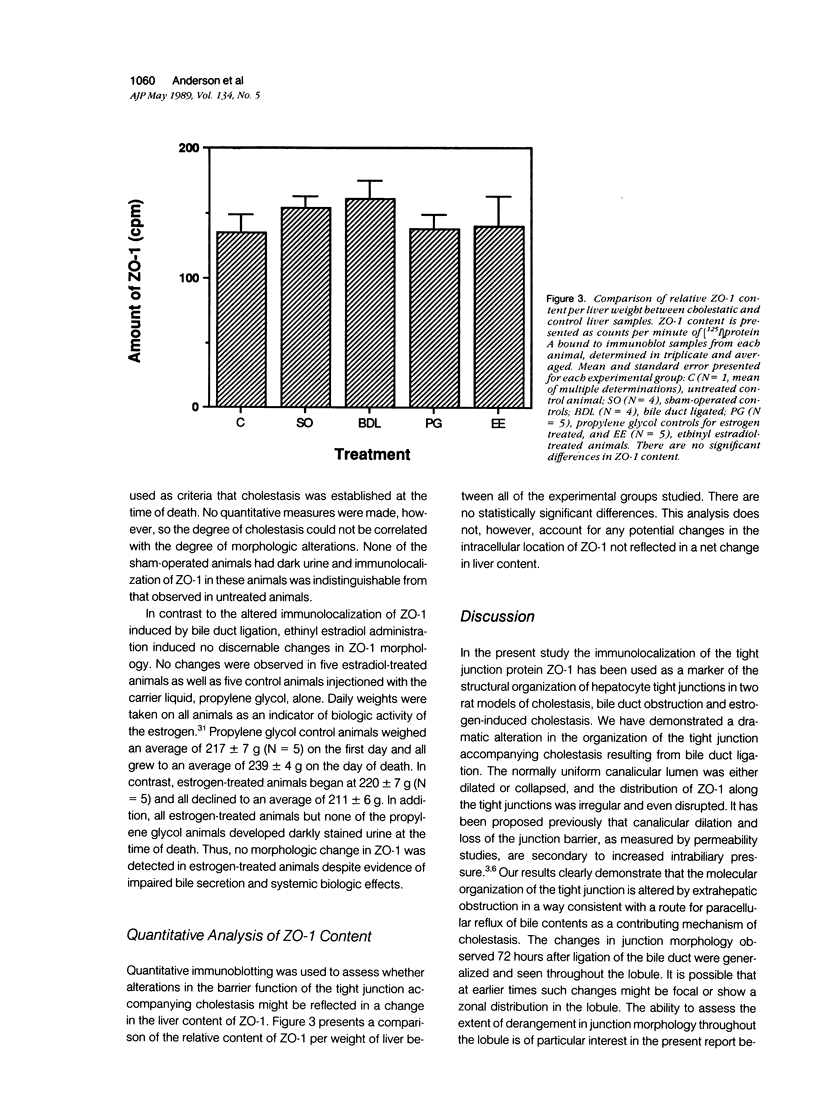
Structural alterations in hepatocyte tight junctions accompanying cholestasis were investigated using immunolocalization of ZO-1, the first known protein component of the tight junction. Disruption in the paracellular barrier function of the tight junction has been proposed to allow reflux of bile into the blood. Cholestasis was induced in 210 to 235 g male Sprague-Dawley rats either by five consecutive daily subcutaneous injections of 17-alpha-ethinyl estradiol (0.5 mg/kg/d in propylene glycol) or ligation of the common bile duct for 72 hours. The structural organization of the tight junction was assessed in each model by indirect immunofluorescent and immunoperoxidase staining for ZO-1 on frozen sections of liver and compared with controls. In control, sham-operated, and estradiol-injected animals, ZO-1 localizes in a uniform continuous manner along the margins of the canaliculi. In contrast, bile duct ligation results in the appearance of numerous discontinuities in ZO-1 staining accompanied by dilation or collapse of the lumenal space. Tissue content of the ZO-1 protein, as determined by quantitative immunoblotting, was unaffected in either cholestatic model compared with controls. These findings indicate that the molecular organization of the tight junction can be assessed from immunostaining patterns of ZO-1 in frozen sections of cholestatic livers. Under these experimental conditions, the organization of the tight junction at the level of the ZO-1 protein is altered by bile duct obstruction but not by ethinyl estradiol.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Stevenson B. R., Jesaitis L. A., Goodenough D. A., Mooseker M. S. Characterization of ZO-1, a protein component of the tight junction from mouse liver and Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1141–1149. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer J. L. Tight junctions in normal and cholestatic liver: does the paracellular pathway have functional significance? Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):614–617. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citi S., Sabanay H., Jakes R., Geiger B., Kendrick-Jones J. Cingulin, a new peripheral component of tight junctions. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):272–276. doi: 10.1038/333272a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claude P., Goodenough D. A. Fracture faces of zonulae occludentes from "tight" and "leaky" epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):390–400. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. A., Kern F., Jr, Showalter R., Sutherland E., Sinensky M., Simon F. R. Alterations of hepatic Na+,K+-atpase and bile flow by estrogen: effects on liver surface membrane lipid structure and function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4130–4134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., Desmet V. J. Morphologic changes of the junctional complex of the hepatocytes in rat liver after bile duct ligation. Br J Exp Pathol. 1978 Apr;59(2):220–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vos R., Desmet V. Morphology of liver cell tight junctions in ethinyl estradiol induced cholestasis. Pathol Res Pract. 1981 May;171(3-4):381–388. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(81)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond J. M. Twenty-first Bowditch lecture. The epithelial junction: bridge, gate, and fence. Physiologist. 1977 Feb;20(1):10–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easter D. W., Wade J. B., Boyer J. L. Structural integrity of hepatocyte tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):745–749. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Hepatocyte bile secretion: current views and controversies. Hepatology. 1981 Jul-Aug;1(4):352–359. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Gilula N. B. Variations in tight and gap junctions in mammalian tissues. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jun;53(3):758–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.3.758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMPTON J. C. Electron microscopic study of extrahepatic biliary obstruction in the mouse. Lab Invest. 1961 May-Jun;10:502–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeschke H., Trummer E., Krell H. Increase in biliary permeability subsequent to intrahepatic cholestasis by estradiol valerate in rats. Gastroenterology. 1987 Sep;93(3):533–538. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90916-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarde S., Elias E., Wade J. B., Boyer J. L. Structural heterogeneity of hepatocyte "tight" junctions: a quantitative analysis. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):193–203. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Layden T. J., Elias E., Boyer J. L. Bile formation in the rat: the role of the paracellular shunt pathway. J Clin Invest. 1978 Dec;62(6):1375–1385. doi: 10.1172/JCI109258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Dharmsathaphorn K. Occluding junction structure-function relationships in a cultured epithelial monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2124–2133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz J., Aoki A., Merlo M., Forssmann W. G. Morphological alterations and functional changes of interhepatocellular junctions induced by bile duct ligation. Cell Tissue Res. 1977 Aug 26;182(3):299–310. doi: 10.1007/BF00219766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley R. H. Mechanisms of bile formation and cholestasis: clinical significance of recent experimental work. Am J Gastroenterol. 1986 Sep;81(9):731–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oelberg D. G., Lester R. Cellular mechanisms of cholestasis. Annu Rev Med. 1986;37:297–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.37.020186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips M. J., Poucell S., Oda M. Mechanisms of cholestasis. Lab Invest. 1986 Jun;54(6):593–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaa G. L., Priestly B. G. Intrahepatic cholestasis induced by drugs and chemicals. Pharmacol Rev. 1976 Sep;28(3):207–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes H., Ribalta J., González M. C., Segovia N., Oberhauser E. Sulfobromophthalein clearance tests before and after ethinyl estradiol administration, in women and men with familial history of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gastroenterology. 1981 Aug;81(2):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robenek H., Herwig J., Themann H. The morphologic characteristics of intercellular junctions between normal human liver cells and cells from patients with extrahepatic cholestasis. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):93–114. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosario J., Sutherland E., Zaccaro L., Simon F. R. Ethinylestradiol administration selectively alters liver sinusoidal membrane lipid fluidity and protein composition. Biochemistry. 1988 May 31;27(11):3939–3946. doi: 10.1021/bi00411a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. J., Simon F. R. Estrogen-induced cholestasis: clues to pathogenesis and treatment. Hepatology. 1983 Jul-Aug;3(4):607–613. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840030422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M., Elledge S., Sweetser D., Young R. A., Davis R. W. Lambda gt 11: gene isolation with antibody probes and other applications. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:107–128. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54073-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Anderson J. M., Bullivant S. The epithelial tight junction: structure, function and preliminary biochemical characterization. Mol Cell Biochem. 1988 Oct;83(2):129–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00226141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson B. R., Siliciano J. D., Mooseker M. S., Goodenough D. A. Identification of ZO-1: a high molecular weight polypeptide associated with the tight junction (zonula occludens) in a variety of epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]