Abstract
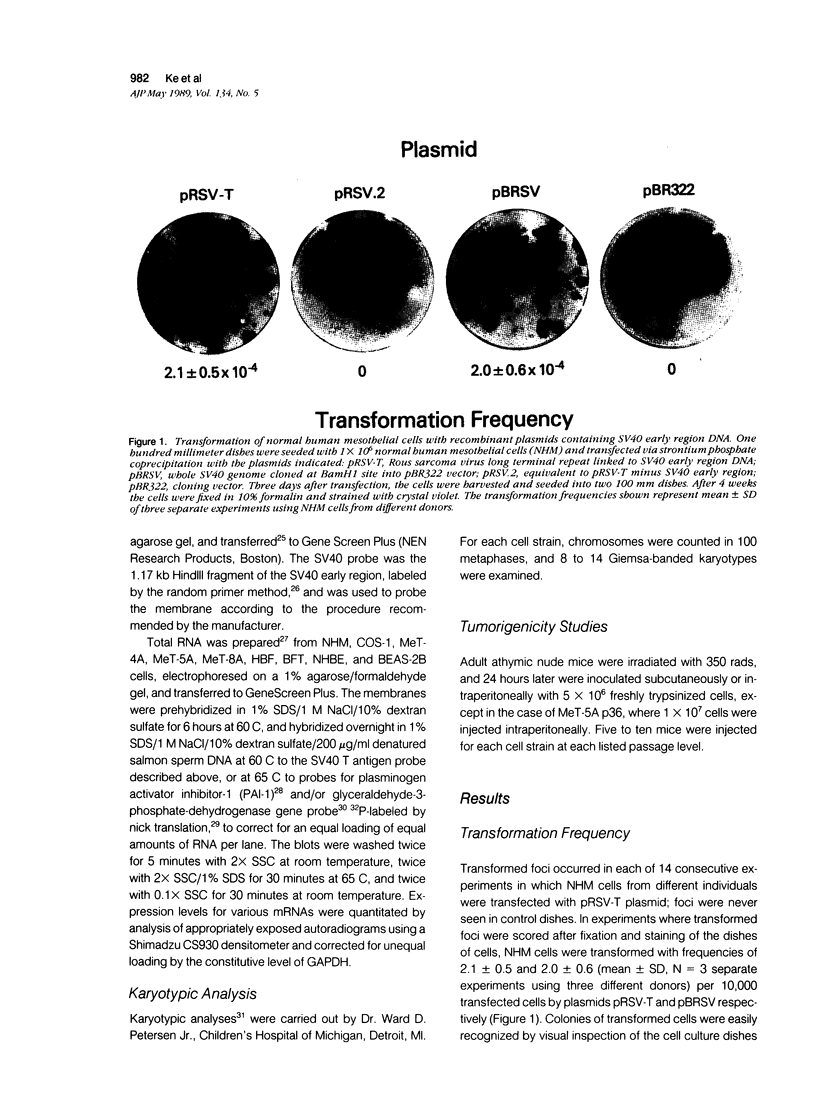
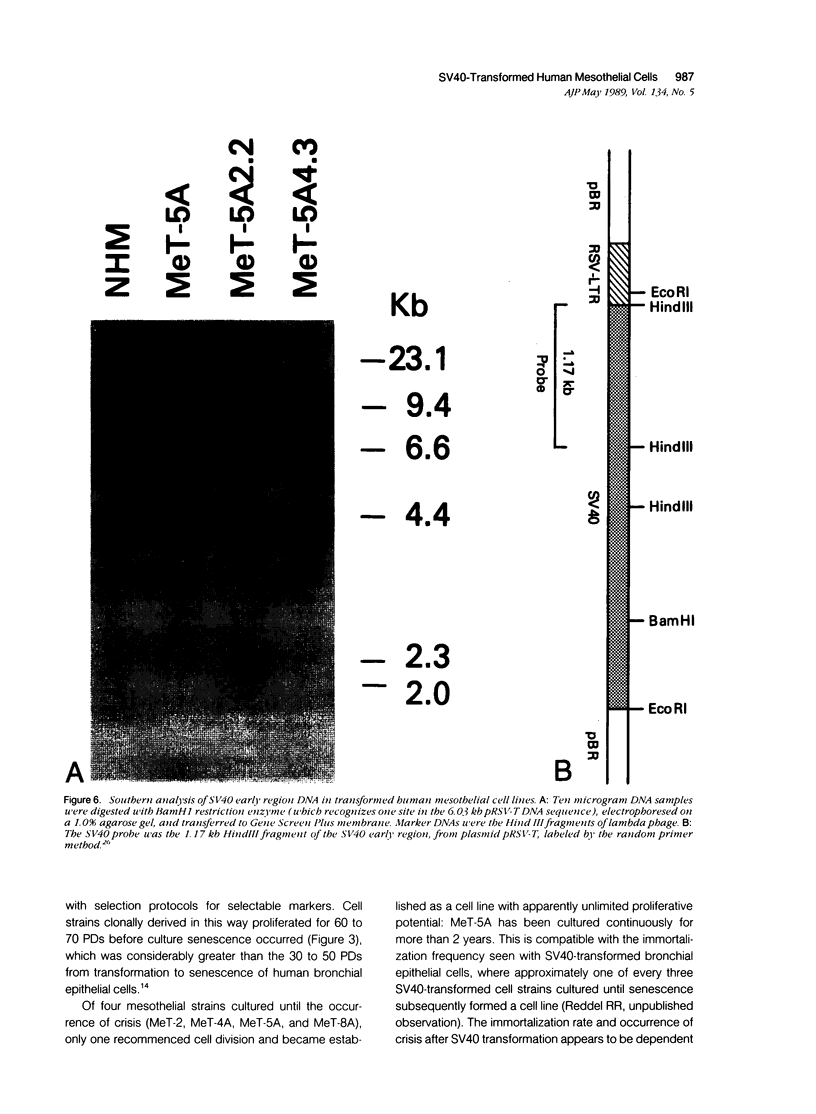
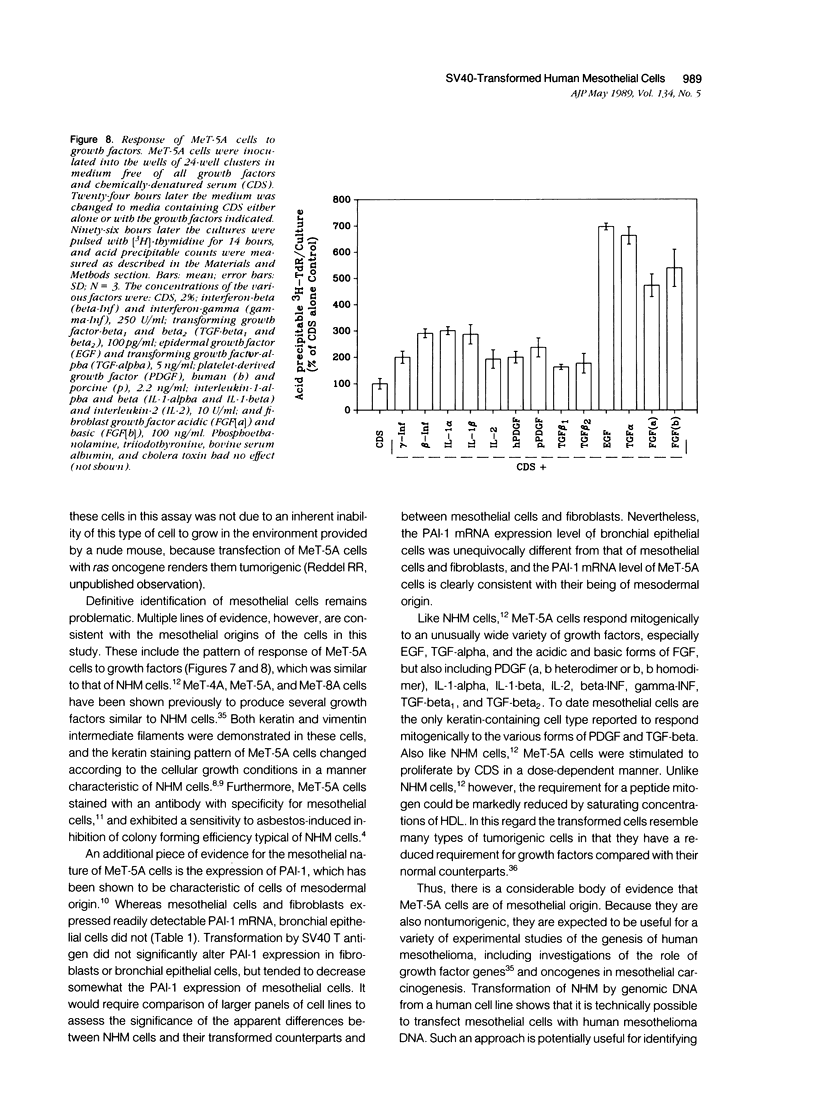
Normal human mesothelial (NHM) cells were transfected with a plasmid containing SV40 early region DNA. Individual colonies of transformed cells from several donors were subcultured for periods of 5 to 6 months and 60 to 70 population doublings (PDs) before senescence, in contrast to a culture lifespan of approximately 1 month and 15 PDs for NHM cells. One such culture, designated MeT-5A, escaped senescence and has been passaged continuously for more than 2 years. These cells had a single integrated copy of SV40 early region DNA in their genome, expressed SV40 large T antigen, and exhibited features of mesothelial cells including sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of asbestos fibers. One year after injection subcutaneously or intraperitoneally in athymic nude mice, these cells remain nontumorigenic, and therefore are a potential model system for in vitro fiber carcinogenesis studies.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brash D. E., Reddel R. R., Quanrud M., Yang K., Farrell M. P., Harris C. C. Strontium phosphate transfection of human cells in primary culture: stable expression of the simian virus 40 large-T-antigen gene in primary human bronchial epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2031–2034. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S. E. In vitro transformation of human epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;823(3):161–194. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(86)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connell N. D., Rheinwald J. G. Regulation of the cytoskeleton in mesothelial cells: reversible loss of keratin and increase in vimentin during rapid growth in culture. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):245–253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90155-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., Mossman B. T. The pathogenesis of asbestos-associated diseases. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 17;306(24):1446–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206173062403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiPaolo J. A. Relative difficulties in transforming human and animal cells in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Jan;70(1):3–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Lechner J. F., Reddel R. R., Roberts A. B., Robbins K. C., Gabrielson E. W., Harris C. C. Comparison of production of transforming growth factor-beta and platelet-derived growth factor by normal human mesothelial cells and mesothelioma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Dec 1;47(23):6180–6184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Zeheb R., Yang A. Y., Rafferty U. M., Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L., Dano K., Lebo R. V., Gelehrter T. D. cDNA cloning of human plasminogen activator-inhibitor from endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1986 Dec;78(6):1673–1680. doi: 10.1172/JCI112761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holley R. W. Control of growth of mammalian cells in cell culture. Nature. 1975 Dec 11;258(5535):487–490. doi: 10.1038/258487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huschtscha L. I., Holliday R. Limited and unlimited growth of SV40-transformed cells from human diploid MRC-5 fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:77–99. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurand M. C., Bernaudin J. F., Renier A., Kaplan H., Bignon J. Rat pleural mesothelial cells in culture. In Vitro. 1981 Feb;17(2):98–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02618065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaurand M. C., Kaplan H., Thiollet J., Pinchon M. C., Bernaudin J. F., Bignon J. Phagocytosis of chrysotile fibers by pleural mesothelial cells in culture. Am J Pathol. 1979 Mar;94(3):529–538. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaRocca P. J., Rheinwald J. G. Coexpression of simple epithelial keratins and vimentin by human mesothelium and mesothelioma in vivo and in culture. Cancer Res. 1984 Jul;44(7):2991–2999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laveck M. A., Somers A. N., Moore L. L., Gerwin B. I., Lechner J. F. Dissimilar peptide growth factors can induce normal human mesothelial cell multiplication. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;24(11):1077–1084. doi: 10.1007/BF02620808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechner J. F., Tokiwa T., LaVeck M., Benedict W. F., Banks-Schlegel S., Yeager H., Jr, Banerjee A., Harris C. C. Asbestos-associated chromosomal changes in human mesothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson W. D., Jr, Simpson W. F., Hukku B. Cell culture characterization: monitoring for cell identification. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:164–178. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddel R. R., Ke Y., Gerwin B. I., McMenamin M. G., Lechner J. F., Su R. T., Brash D. E., Park J. B., Rhim J. S., Harris C. C. Transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells by infection with SV40 or adenovirus-12 SV40 hybrid virus, or transfection via strontium phosphate coprecipitation with a plasmid containing SV40 early region genes. Cancer Res. 1988 Apr 1;48(7):1904–1909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid L. C. Cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:152–164. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rendall R. E. Physical and chemical characteristics of UICC reference samples. IARC Sci Publ. 1980;(30):87–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Jorgensen J. L., Hahn W. C., Terpstra A. J., O'Connell T. M., Plummer K. K. Mesosecrin: a secreted glycoprotein produced in abundance by human mesothelial, endothelial, and kidney epithelial cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):263–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack G. H., Jr Human cell transformation by simian virus 40--a review. In Vitro. 1981 Jan;17(1):1–19. doi: 10.1007/BF02618025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahel R. A., O'Hara C. J., Waibel R., Martin A. Monoclonal antibodies against mesothelial membrane antigen discriminate between malignant mesothelioma and lung adenocarcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):218–223. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Oostwaard T. M., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells in a growth-factor-defined medium: induction by a neuroblastoma-derived transforming growth factor independently of the EGF receptor. J Cell Physiol. 1985 May;123(2):151–160. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







