Abstract
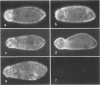
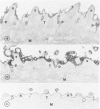
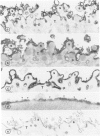
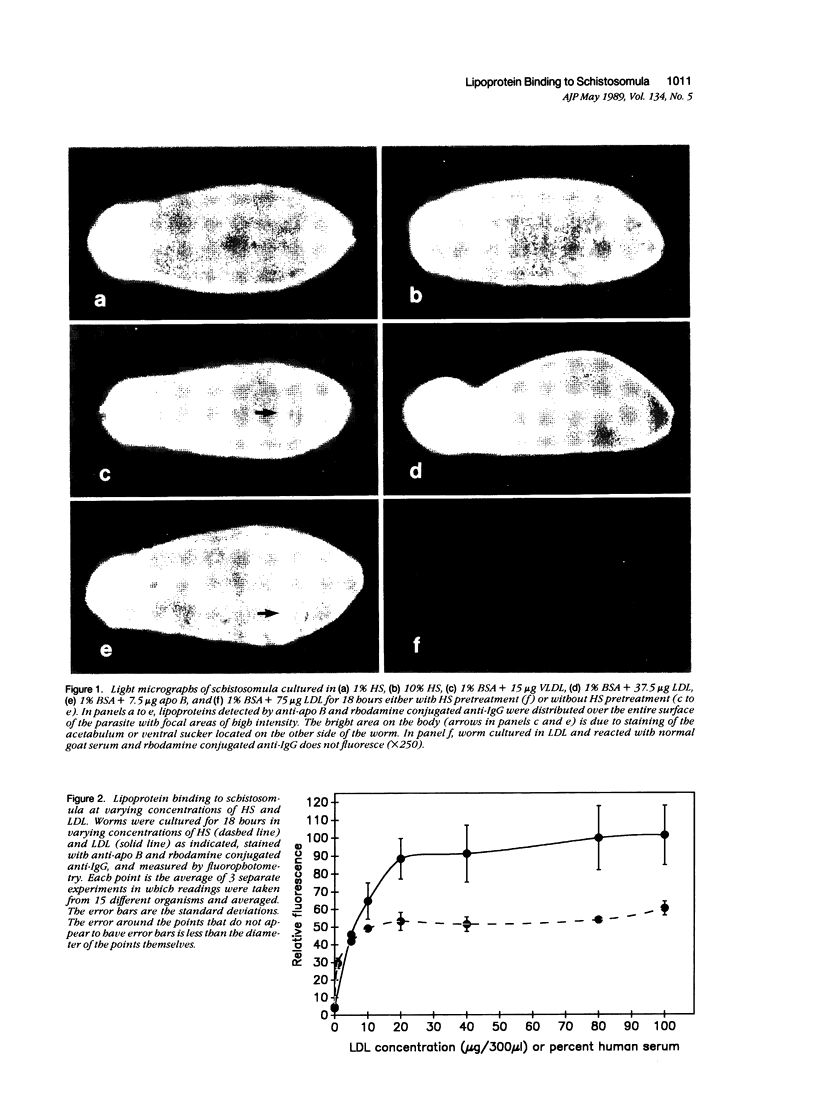
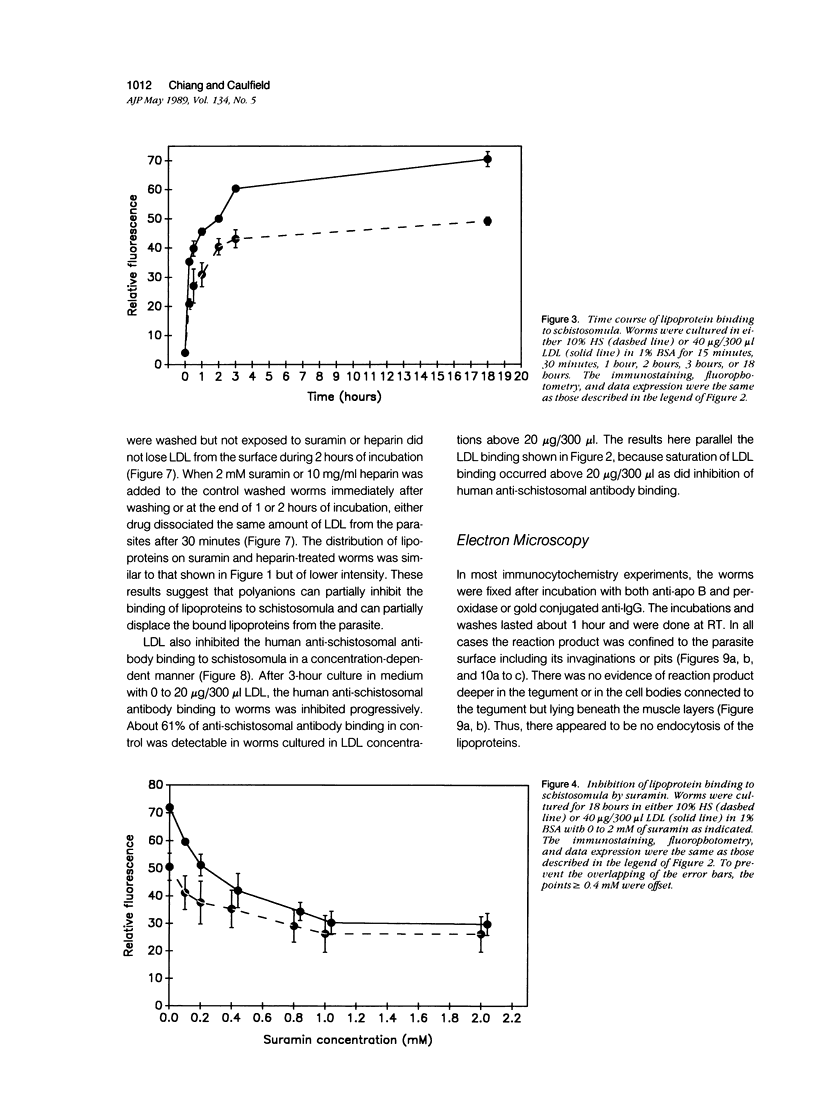
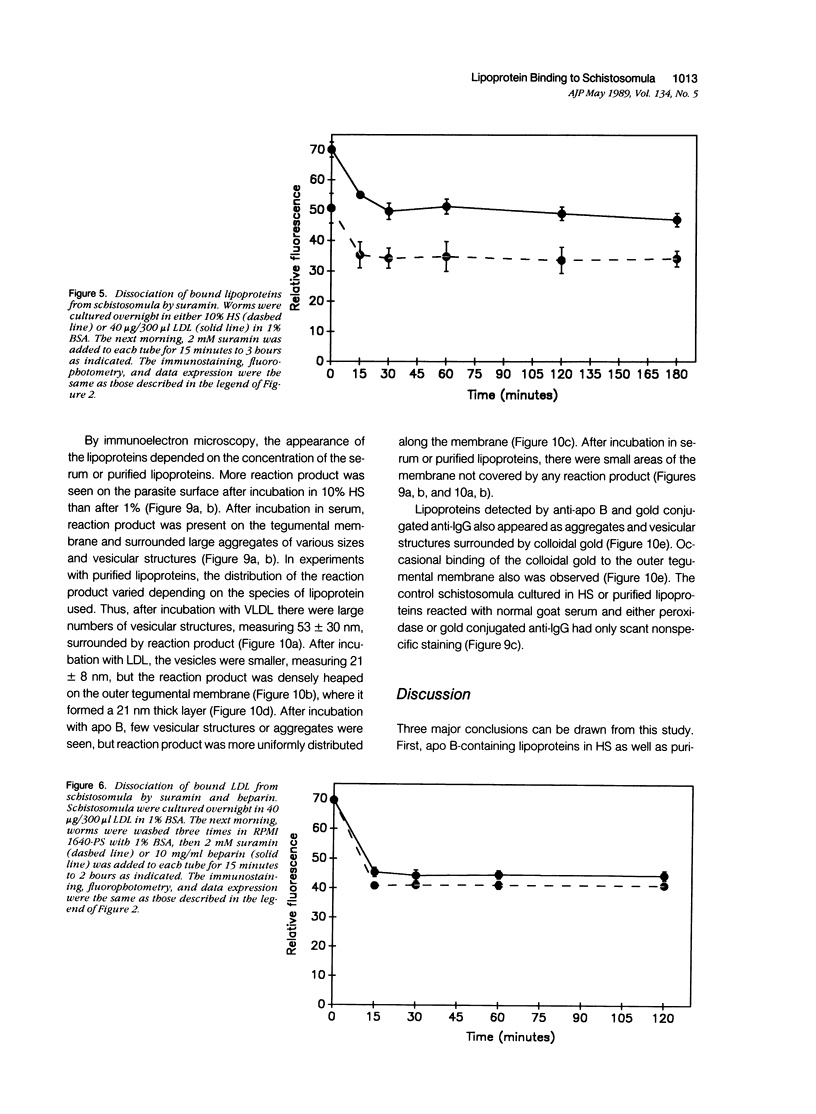
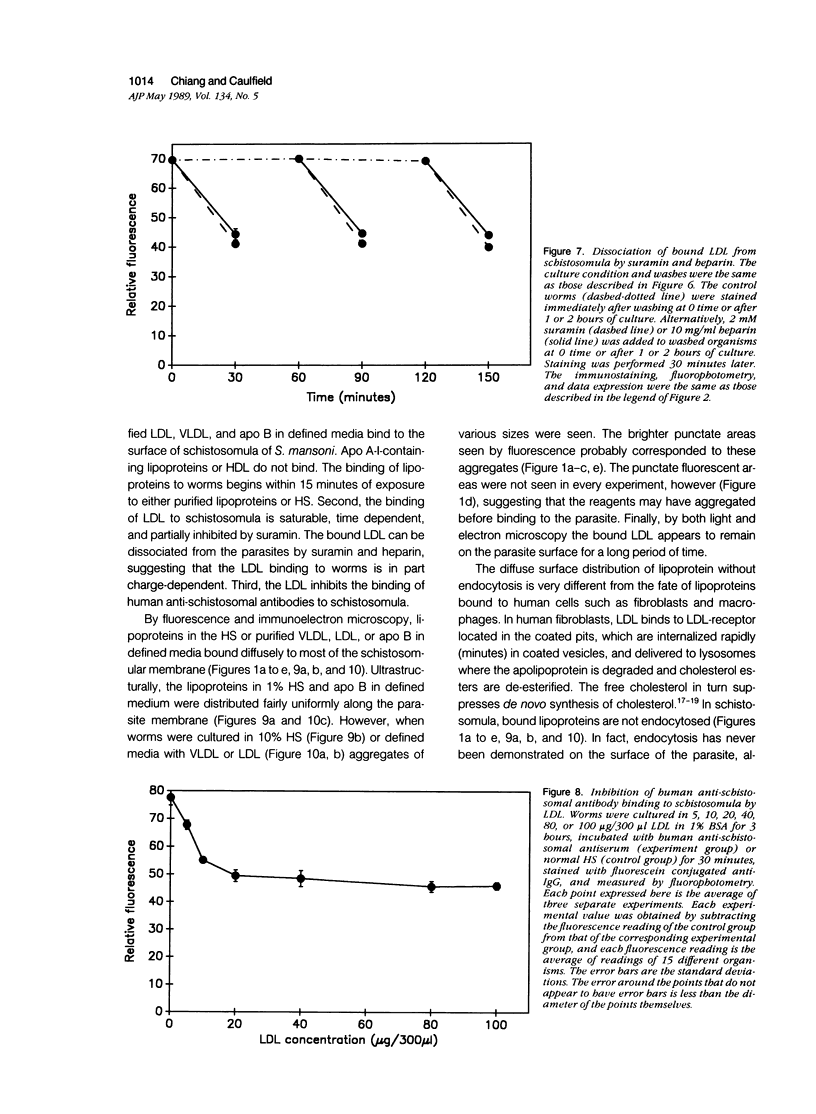
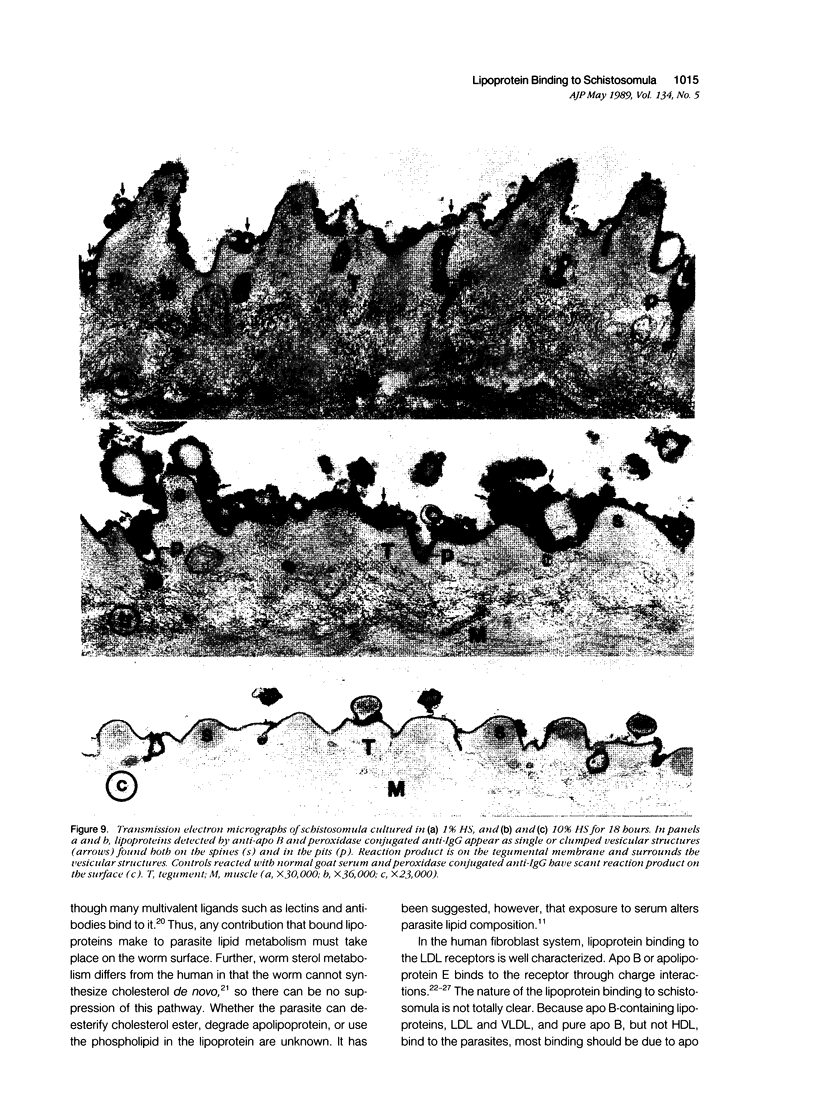
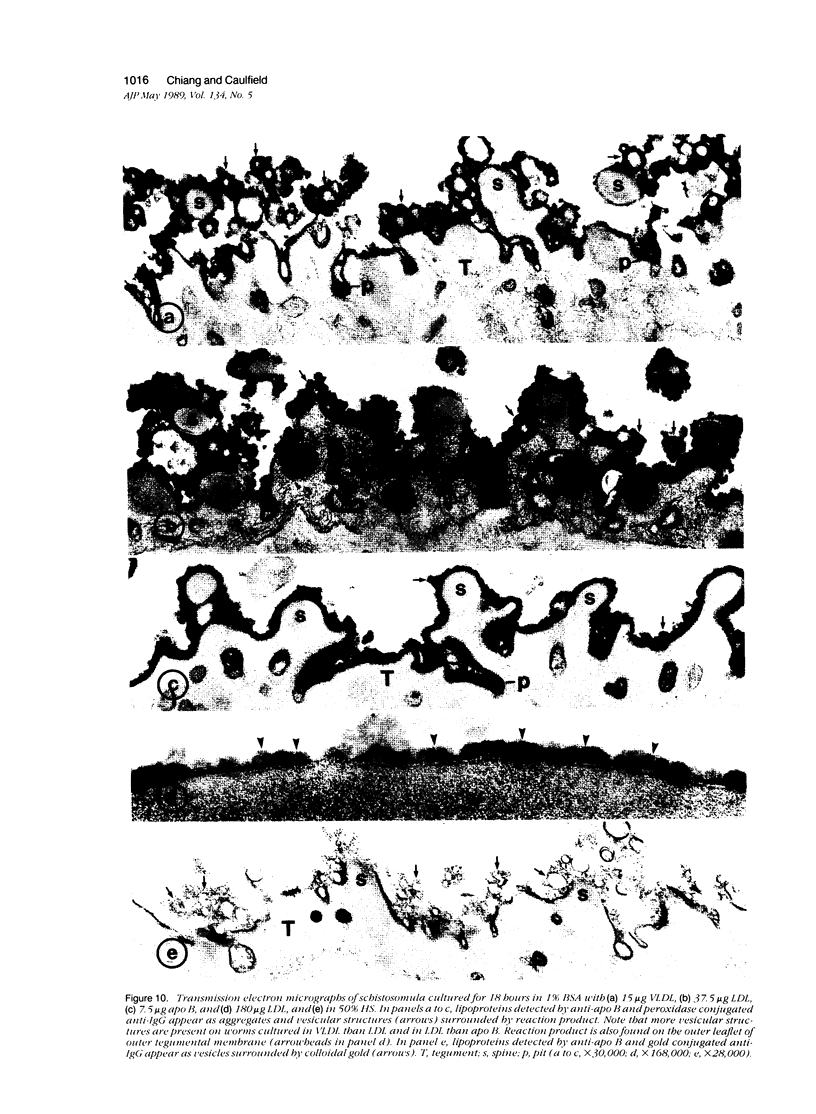
Host molecules such as serum lipoproteins, blood group glycolipids, and histocompatibility antigens may bind to schistosomes and thereby prevent immune recognition of the parasite. This study examines the kinetics of lipoprotein binding, the ability of polyanions to inhibit lipoprotein binding, the binding of anti-schistosomal antibodies to worms that have previously bound low-density lipoprotein (LDL), and the distribution of lipoproteins bound to the parasites. Lipoproteins in human serum (HS) and purified LDL, very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), and apolipoprotein B (apo B) in defined media were demonstrated on the surface of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by fluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy using a polyclonal goat anti-human apolipoprotein B antibody (anti-apo B). By fluorophotometric microscopy, lipoprotein binding began within 15 minutes and was largely completed within 3 hours of exposure. Lipoprotein binding saturated at 10% HS or 20 micrograms protein/300 microliters of purified LDL. Suramin inhibited LDL binding by 59% in a dose-dependent fashion. In the absence of LDL in the medium, 2 mM suramin dissociated 41% of bound LDL from the worm surface within 15 minutes and 10 mg/ml heparin dissociated 36%. The binding of human anti-schistosomal antibodies to schistosomula was inhibited by bound LDL. By fluorescence microscopy, serum or purified lipoproteins were distributed over the entire surface of the parasite with focal areas of high intensity. Ultrastructurally, reaction product was seen on the outer leaflet of the outer tegumental membrane and in aggregates and surrounding vesicular structures varying in diameter from 13 to 83 nm. These studies demonstrate that lipoproteins bind to the surface of schistosomula. The binding of lipoproteins is partially inhibited by polyanions, reduces the binding of human anti-schistosomal antibodies, and may help the parasite escape the immune response.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogitsh B. J. Schistosoma mansoni: suramin and trypan blue in vitro and the ultrastructure of feeding schistosomules. Exp Parasitol. 1985 Oct;60(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(85)90018-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Deuel T. F., Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L. Inhibition of the binding of low-density lipoprotein to its cell surface receptor in human fibroblasts by positively charged proteins. J Supramol Struct. 1978;8(3):223–234. doi: 10.1002/jss.400080302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A. Schistosoma mansoni: adsorption of human blood group A and B antigens by schistosomula. J Parasitol. 1974 Apr;60(2):260–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. A., Sell K. W. Surface antigens on Schistosoma mansoni. II. Adsorption of a Forssman-like host antigen by schistosomula. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Dec;12(4):525–540. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter B. D., Damian R. T. Murine alloantigen acquisition by schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: further evidence for the presence of K, D, and I region gene products on the tegumental surface. Parasite Immunol. 1982 Nov;4(6):383–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1982.tb00450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitter B. D., McCormick S. L., Damian R. T. Murine alloantigen acquisition by Schistosoma mansoni: presence of H-2K determinants on adult worms and failure of allogeneic lymphocytes to recognize acquired MHC gene products on schistosomula. J Parasitol. 1982 Aug;68(4):513–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldring O. L., Clegg J. A., Smithers S. R., Terry R. J. Acquisition of human blood group antigens by Schistosoma mansoni. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(1):181–187. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Coated pits, coated vesicles, and receptor-mediated endocytosis. Nature. 1979 Jun 21;279(5715):679–685. doi: 10.1038/279679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Basu S. K., Brunschede G. Y., Brown M. S. Release of low density lipoprotein from its cell surface receptor by sulfated glycosaminoglycans. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90258-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis: concepts emerging from the LDL receptor system. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. The low-density lipoprotein pathway and its relation to atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innerarity T. L., Weisgraber K. H., Rall S. C., Jr, Mahley R. W. Functional domains of apolipoprotein E and apolipoprotein B. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1987;715:51–59. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J. K., Stein M. J., David J. R., Sher A. Schistosoma mansoni: rapid isolation and purification of schistosomula of different developmental stages by centrifugation on discontinuous density gradients of Percoll. Exp Parasitol. 1982 Feb;53(1):39–44. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(82)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lint T. F., Behrends C. L., Gewurz H. Serum lipoproteins and C567-INH activity. J Immunol. 1977 Sep;119(3):883–888. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L., Pitas R. E., Weisgraber K. H., Brown J. H., Gross E. Inhibition of lipoprotein binding to cell surface receptors of fibroblasts following selective modification of arginyl residues in arginine-rich and B apoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7279–7287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer F., Meyer H., Bueding E. Lipid metabolism in the parasitic and free-living flatworms, Schistosoma mansoni and Dugesia dorotocephala. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Jul 14;210(2):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90170-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podack E. R., Kolb W. P., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The C5b-6 complex: formation, isolation, and inhibition of its activity by lipoprotein and the S-protein of human serum. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):1841–1848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramalho-Pinto F. J., Gazzinelli G., Howells R. E., Mota-Santos T. A., Figueiredo E. A., Pellegrino J. Schistosoma mansoni: defined system for stepwise transformation of cercaria to schistosomule in vitro. Exp Parasitol. 1974 Dec;36(3):360–372. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(74)90076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek F. D., Campos E. G., Afonso L. C. Evidence for the occurrence of LDL receptors in extracts of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Mar;28(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90062-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek F. D., McLaren D. J. Schistosoma mansoni: modulation of schistosomular lipid composition by serum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1981 Aug;3(4):239–252. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(81)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek F. D., McLaren D. J., Smithers S. R. Serum-induced expression of a surface protein in schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: a possible receptor for lipid uptake. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1983 Dec;9(4):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(83)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumjanek F. D., Pereira M. A., Silveira A. M. The interaction of human serum with the surface membrane of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jan;14(1):63–73. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90106-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W. Protein domains of the low density lipoprotein receptor. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1987;715:39–44. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1987.tb09901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelson J. C., Caulfield J. P., David J. R. Schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni clear concanavalin A from their surface by sloughing. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):355–362. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider W. J., Beisiegel U., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Purification of the low density lipoprotein receptor, an acidic glycoprotein of 164,000 molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2664–2673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Hall B. F., Vadas M. A. Acquisition of murine major histocompatibility complex gene products by schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. J Exp Med. 1978 Jul 1;148(1):46–57. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher A., Sacks D. L., Simpson A. J., Singer A. Dichotomy in the tissue origin of schistosome acquired class I and class II major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):952–957. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson A. J., Singer D., McCutchan T. F., Sacks D. L., Sher A. Evidence that schistosome MHC antigens are not synthesized by the parasite but are acquired from the host as intact glycoproteins. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):962–965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Herz J. Topological mapping of complement component C9 by recombinant DNA techniques suggests a novel mechanism for its insertion into target membranes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1951–1957. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02457.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavares C. A., Cordeiro M. N., Mota-Santos T. A., Gazzinelli G. Artificially transformed schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni: mechanism of acquisition of protection against antibody-mediated killing. Parasitology. 1980 Feb;80(1):95–104. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000000548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavares C. A., Soares R. C., Coelho P. M., Gazzinelli G. Schistosoma mansoni: evidence for a role of serum factors in protecting artificially transformed schistosomula against antibody-mediated killing in vitro. Parasitology. 1978 Oct;77(2):225–243. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000049404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschopp J., Jongeneel C. V. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte mediated cytolysis. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 19;27(8):2641–2646. doi: 10.1021/bi00408a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisgraber K. H., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Role of lysine residues of plasma lipoproteins in high affinity binding to cell surface receptors on human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):9053–9062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]