Abstract
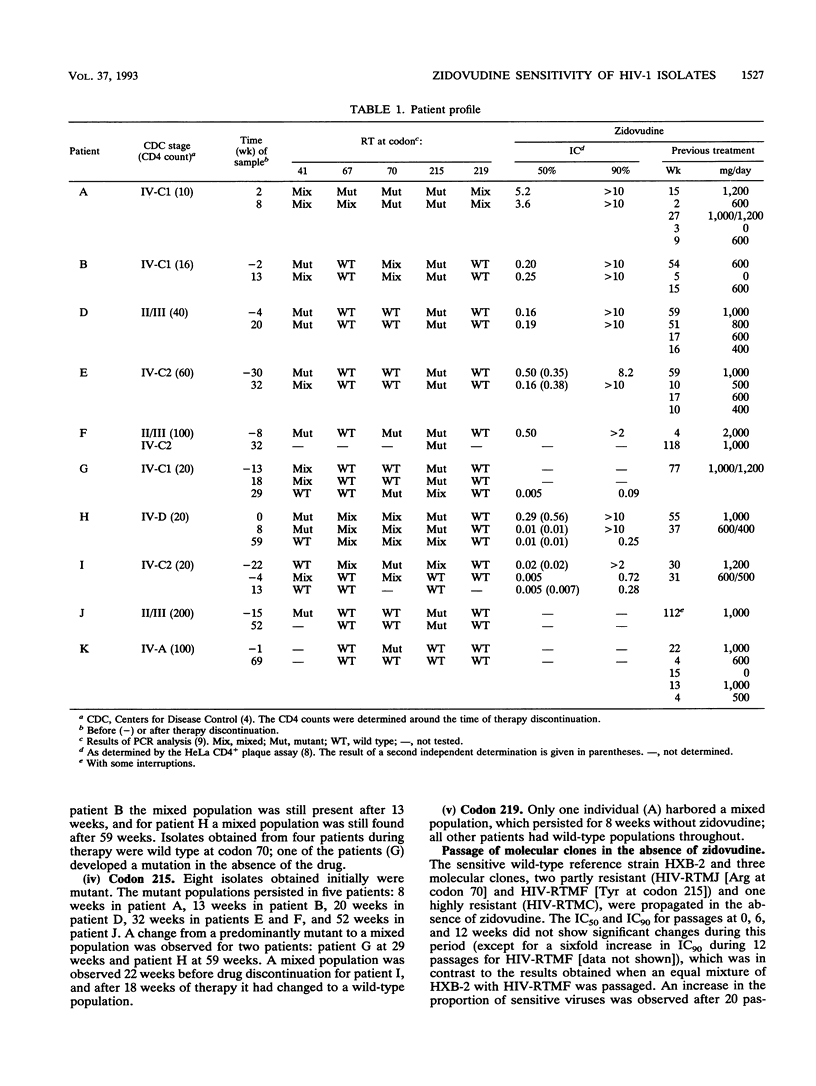
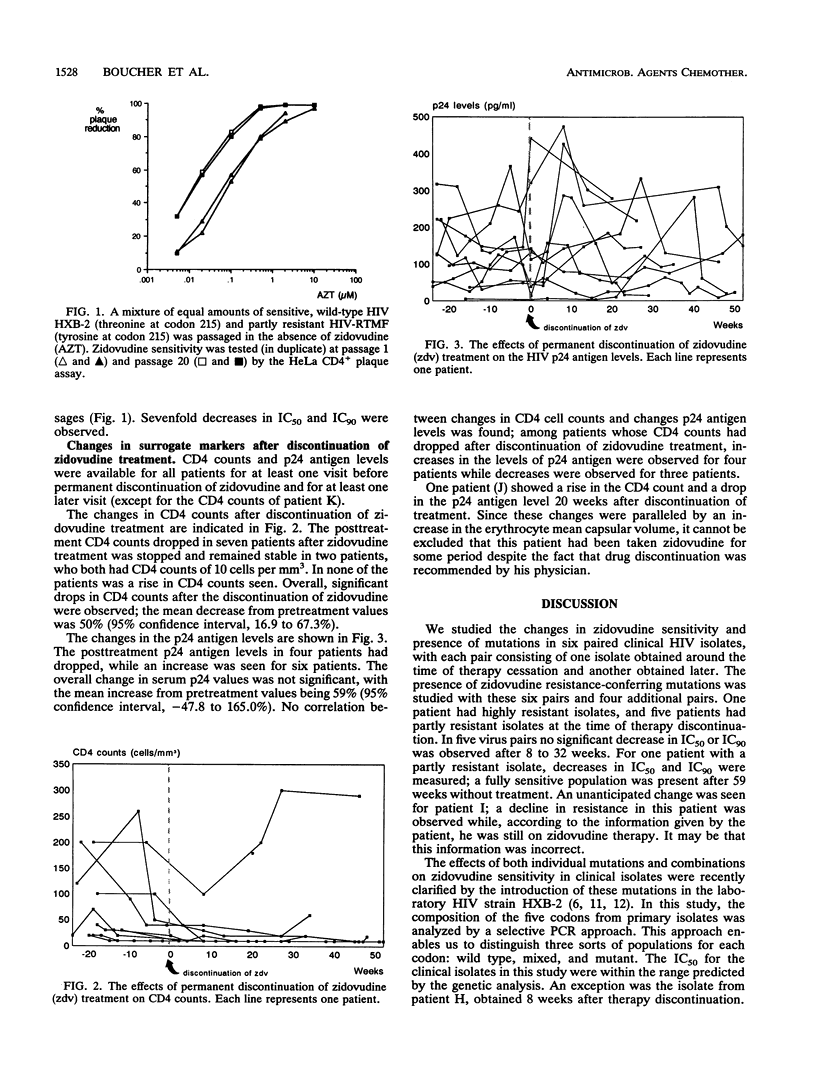
Zidovudine treatment of individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) results in HIV-1 isolates with a reduced zidovudine sensitivity in vitro. This reduction is due to mutations causing amino acid substitutions at five codons (41, 67, 70, 215, and 219) on the reverse transcriptase enzyme of HIV. HIV-1 isolates were obtained 8 to 69 weeks after therapy discontinuation from 10 patients at different stages of disease. Zidovudine sensitivity was determined by the HeLa CD4+ plaque assay. The presence of the resistance-conferring mutations was determined by using a selective polymerase chain reaction. Sensitivity could be determined for six isolate pairs: one showed a decline in the 50% inhibitory zidovudine concentration after therapy discontinuation; four pairs did not show a change. The majority of changes in the five codons in isolates from all 10 patients were the result of a relative increase in the wild-type sequence. Complete changes from mutant to the wild type were seen for only two codons in isolates from two patients. This study of isolates from a small group of individuals at different stages of disease, who had been taking zidovudine for 1 to 2 years, shows that a period of 1 year without zidovudine may be required to achieve a change from a mutant or mixed virus population to a wild-type virus population.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert J., Wahlberg J., Lundeberg J., Cox S., Sandström E., Wahren B., Uhlén M. Persistence of azidothymidine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA genotypes in posttreatment sera. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5627–5630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5627-5630.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., O'Sullivan E., Mulder J. W., Ramautarsing C., Kellam P., Darby G., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Ordered appearance of zidovudine resistance mutations during treatment of 18 human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):105–110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., Tersmette M., Lange J. M., Kellam P., de Goede R. E., Mulder J. W., Darby G., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Zidovudine sensitivity of human immunodeficiency viruses from high-risk, symptom-free individuals during therapy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., de Wolf F., Paul D. A., Epstein L. G., Lange J. M., Krone W. J., Speelman H., Wolters E. C., Van der Noordaa J., Oleske J. M. Expression of human immunodeficiency virus antigen (HIV-Ag) in serum and cerebrospinal fluid during acute and chronic infection. Lancet. 1986 Jul 26;2(8500):177–180. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92485-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S., McGavin K., Birch C., Lucas R. Reversion from zidovudine resistance to sensitivity on cessation of treatment. Lancet. 1991 Sep 28;338(8770):830–831. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)90727-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Chesebro B., Richman D. D. Susceptibilities of zidovudine-susceptible and -resistant human immunodeficiency virus isolates to antiviral agents determined by using a quantitative plaque reduction assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Coates K. E., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus selected by passage in cell culture. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5232–5236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5232-5236.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kellam P., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine resistance predicted by direct detection of mutations in DNA from HIV-infected lymphocytes. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):137–144. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Guatelli J. C., Grimes J., Tsiatis A., Gingeras T. Detection of mutations associated with zidovudine resistance in human immunodeficiency virus by use of the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1075–1081. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


