Abstract
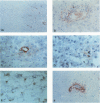
Cryostat sections of central nervous system (CNS) tissues of patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) and other CNS diseases were stained with antibodies to fibronectin, a macrophage fibronectin receptor component, fibrin/fibrinogen, and albumin using immunoperoxidase. In active, but not inactive, MS plaques vessel fibronectin was increased (to approximately 57% of Factor VIII+ vessels) over uninvolved MS and normal control white matter (P less than 0.001 for both). Fibronectin was primarily localized to vessel walls and amount of staining correlated with degree of inflammation. Active plaques and necrotic lesions also had extracellular fibronectin and fibrin/ogen. These molecules and the fibronectin receptor were found on macrophages. Albumin was more widely and diffusely distributed in lesions than fibronectin. Thus, in addition to extravasation from damaged vessels, fibronectin may be deposited on or synthesized by endothelial cells and macrophages in the CNS. Fibronectin could facilitate monocyte adhesion to endothelial cell luminal surfaces, promote migration of mononuclear cells, and enhance myelin phagocytosis in MS lesions.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi K., Yamauchi K., Bernaudin J. F., Fouret P., Ferrans V. J., Crystal R. G. Evaluation of fibronectin gene expression by in situ hybridization. Differential expression of the fibronectin gene among populations of human alveolar macrophages. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):193–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams C. W., Poston R. N., Buk S. J., Sidhu Y. S., Vipond H. Inflammatory vasculitis in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci. 1985 Jul;69(3):269–283. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(85)90139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Fiers W., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. J., Goodwin J. L. Fibronectin receptors of phagocytes. Characterization of the Arg-Gly-Asp binding proteins of human monocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):777–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cammer W., Brosnan C. F., Basile C., Bloom B. R., Norton W. T. Complement potentiates the degradation of myelin proteins by plasmin: implications for a mechanism of inflammatory demyelination. Brain Res. 1986 Jan 29;364(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90990-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciano P. S., Colvin R. B., Dvorak A. M., McDonagh J., Dvorak H. F. Macrophage migration in fibrin gel matrices. Lab Invest. 1986 Jan;54(1):62–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Dvorak H. F., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin in delayed-type hypersensitivity skin reactions: associations with vessel permeability and endothelial cell activation. J Immunol. 1981 Feb;126(2):787–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Quinn J. H., Winn H. J., Lanigan J. M., Dellepella P., Colvin R. B. Fibronectin is produced by blood vessels in response to injury. J Exp Med. 1982 Aug 1;156(2):646–651. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.2.646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cofano F., Comoglio P. M., Landolfo S., Tarone G. Mouse immune interferon enhances fibronectin production of elicited macrophages. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3102–3106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czop J. K., Kadish J. L., Zepf D. M., Austen K. F. Identification with monoclonal antibodies of different regions of human plasma fibronectin, including that which interacts with human monocyte fibronectin receptors. Immunology. 1985 Mar;54(3):407–417. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejana E., Colella S., Conforti G., Abbadini M., Gaboli M., Marchisio P. C. Fibronectin and vitronectin regulate the organization of their respective Arg-Gly-Asp adhesion receptors in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):1215–1223. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty G. J., Murdoch S., Hogg N. The function of human intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in the generation of an immune response. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):35–39. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) interaction with intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) is one of at least three mechanisms for lymphocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):321–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorak H. F., Senger D. R., Dvorak A. M., Harvey V. S., McDonagh J. Regulation of extravascular coagulation by microvascular permeability. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1059–1061. doi: 10.1126/science.3975602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziarski R. Modulation of polyclonal activation by plasma fibronectin and fibronectin fragments. Immunology. 1987 Jun;61(2):111–116. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgington T. S., Curtiss L. K., Plow E. F. A linkage between the hemostatic and immune systems embodied in the fibrinolytic release of lymphocyte suppressive peptides. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):471–477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feigin I. The effect of saponification on the mucopolysaccharides of the ground substance of the human brain: the relation to focal edema and multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Mar;40(2):102–111. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198103000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch H. E., Blanco C. E., Parks M. E. Fibrinolytic activity of plaques and white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 May;40(3):271–280. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198105000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsburgh C. R., Jr, Clark R. A., Kirkpatrick C. H. Lymphokines and platelets promote human monocyte adherence to fibrinogen and fibronectin in vitro. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Jan;41(1):14–24. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.1.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosein B., Bianco C. Monocyte receptors for fibronectin characterized by a monoclonal antibody that interferes with receptor activity. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):157–170. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes C. C., Male D. K., Lantos P. L. Adhesion of lymphocytes to cerebral microvascular cells: effects of interferon-gamma, tumour necrosis factor and interleukin-1. Immunology. 1988 Aug;64(4):677–681. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones F. S., Burgoon M. P., Hoffman S., Crossin K. L., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. A cDNA clone for cytotactin contains sequences similar to epidermal growth factor-like repeats and segments of fibronectin and fibrinogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2186–2190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S., Maruta K., Burkart V., Gillis S., Kolb H. IL-1 and IFN-gamma increase vascular permeability. Immunology. 1988 Jun;64(2):301–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon D. K., Geczy C. L. Recombinant IFN-gamma synergizes with lipopolysaccharide to induce macrophage membrane procoagulants. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1536–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Raine C. S. Immunogold localization and analysis of IgG during immune-mediated demyelination. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):641–648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Tacke R., Scherer H., Teplow D., Früh K., Schachner M. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):701–703. doi: 10.1038/334701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachman R. L., Hajjar K. A., Silverstein R. L., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces endothelial cell synthesis of plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1595–1600. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Hotchi M. Ultrastructural cytochemical studies on the cell coat of macrophages and the localization of fibronectin in granuloma formation. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1987 Nov;37(11):1707–1718. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1987.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer-Marks N., Ziff M. Migration of lymphocytes through endothelial cell monolayers: augmentation by interferon-gamma. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jul;114(2):307–323. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90324-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson P. Y., Koh C. S., Kwaan H. C. Role of the clotting system in the pathogenesis of neuroimmunologic disease. Fed Proc. 1987 Jan;46(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pober J. S. Warner-Lambert/Parke-Davis award lecture. Cytokine-mediated activation of vascular endothelium. Physiology and pathology. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):426–433. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price J., Hynes R. O. Astrocytes in culture synthesize and secrete a variant form of fibronectin. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2205–2211. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02205.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Scheinberg L. C. On the immunopathology of plaque development and repair in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Dec;20(2-3):189–201. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90160-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahuddin T. S., Kalimo H., Johansson B. B., Olsson Y. Observations on exsudation of fibronectin, fibrinogen and albumin in the brain after carotid infusion of hyperosmolar solutions. An immunohistochemical study in the rat indicating longlasting changes in the brain microenvironment and multifocal nerve cell injuries. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;76(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00687674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schluesener H. J., Sobel R. A., Linington C., Weiner H. L. A monoclonal antibody against a myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein induces relapses and demyelination in central nervous system autoimmune disease. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4016–4021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Ames M. B. Major histocompatibility complex molecule expression in the human central nervous system: immunohistochemical analysis of 40 patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1988 Jan;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198801000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Blanchette B. W., Bhan A. K., Colvin R. B. The immunopathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. I. Quantitative analysis of inflammatory cells in situ. J Immunol. 1984 May;132(5):2393–2401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Collins A. B., Colvin R. B., Bhan A. K. The in situ cellular immune response in acute herpes simplex encephalitis. Am J Pathol. 1986 Nov;125(2):332–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Hafler D. A., Castro E. E., Morimoto C., Weiner H. L. The 2H4 (CD45R) antigen is selectively decreased in multiple sclerosis lesions. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;140(7):2210–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobel R. A., Schneeberger E. E., Colvin R. B. The immunopathology of acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. V. A light microscopic and ultrastructural immunohistochemical analysis of fibronectin and fibrinogen. Am J Pathol. 1988 Jun;131(3):547–558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokrab T. E., Johansson B. B., Kalimo H., Olsson Y. A transient hypertensive opening of the blood-brain barrier can lead to brain damage. Extravasation of serum proteins and cellular changes in rats subjected to aortic compression. Acta Neuropathol. 1988;75(6):557–565. doi: 10.1007/BF00686200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D., Nawroth P., Handley D., Kisiel W. An endothelial cell-dependent pathway of coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada Y., Huang C., Hemler M. E. Fibronectin receptor structures in the VLA family of heterodimers. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):607–609. doi: 10.1038/326607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., Schwarzbauer J. E., Hynes R. O. A single rat fibronectin gene generates three different mRNAs by alternative splicing of a complex exon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5140–5144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter J., DeJong L. J., Smith M. E. Opsonization with antimyelin antibody increases the uptake and intracellular metabolism of myelin in inflammatory macrophages. J Neurochem. 1986 Sep;47(3):779–789. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb00679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]