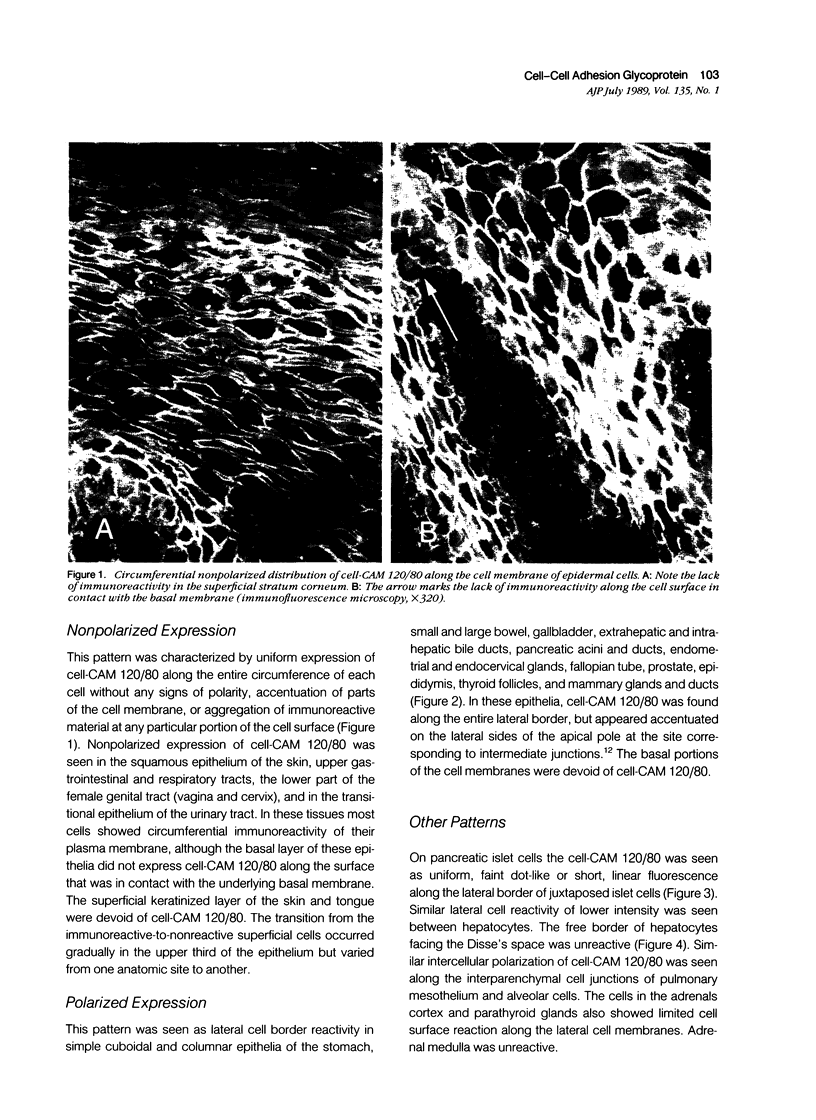
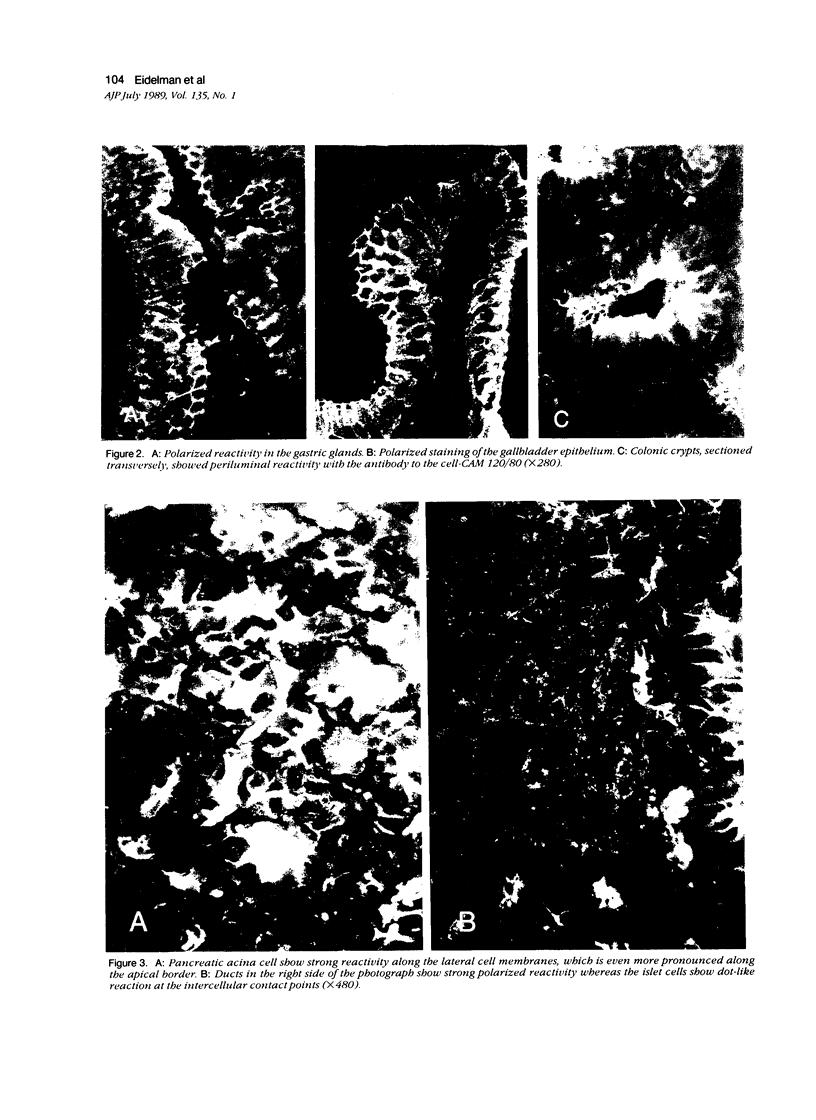
Abstract
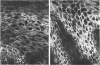
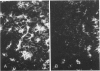
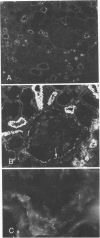
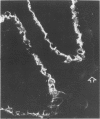
Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies raised to the 80 kd glycoprotein component of the cell to cell adhesion molecule cell-CAM 120/80 were used to map its distribution immunohistochemically in normal human tissues and in benign and malignant tumors. Cell-CAM 120/80 was found in all normal epithelial tissues, but was not expressed on neural, lymphoid, smooth, striated and cardiac muscle, connective tissue, or the germ cells in either sex. The expression of this adhesion molecule was polarized in ductal and glandular epithelia and evenly circumferential in squamous and transitional epithelia. Some organs, such as the kidney, liver and endocrine glands, showed unique organ to tissue specific patterns. Maturation-dependent loss of cell-CAM 120/80 was noticed in superficial layers of squamous epithelium and the placenta. Benign epithelial tumors expressed cell-CAM 120/80 in a manner comparable with their tissue of origin. Malignant tumors expressed cell-CAM 120/80 either in a manner similar to the tissue of their origin or assumed a less polarized phenotype. Overall, the immunoreactivity in many malignant tumors appeared weaker and the polarization was less pronounced. Thus, cell-CAM 120/80 is a universal marker of human epithelial cells, but its mode of expression differs in various anatomic sites, and may be influenced by maturation or malignant transformation of cells.
Full text
PDF

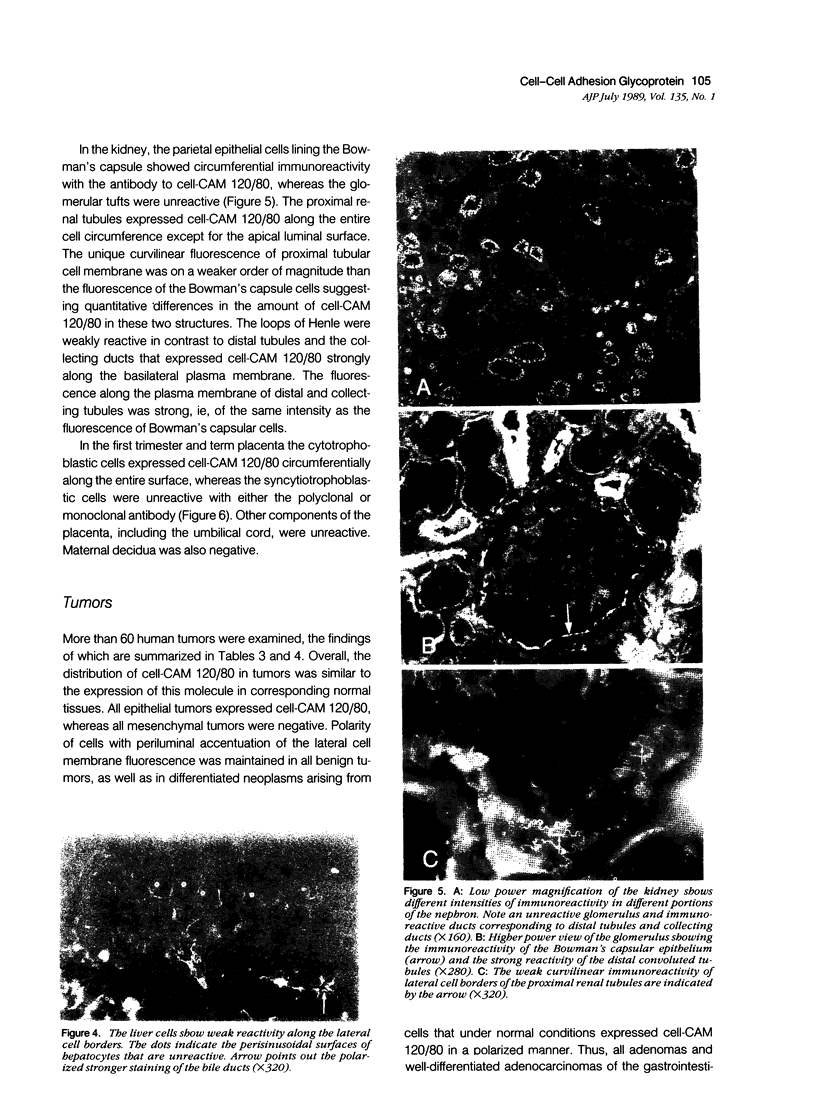


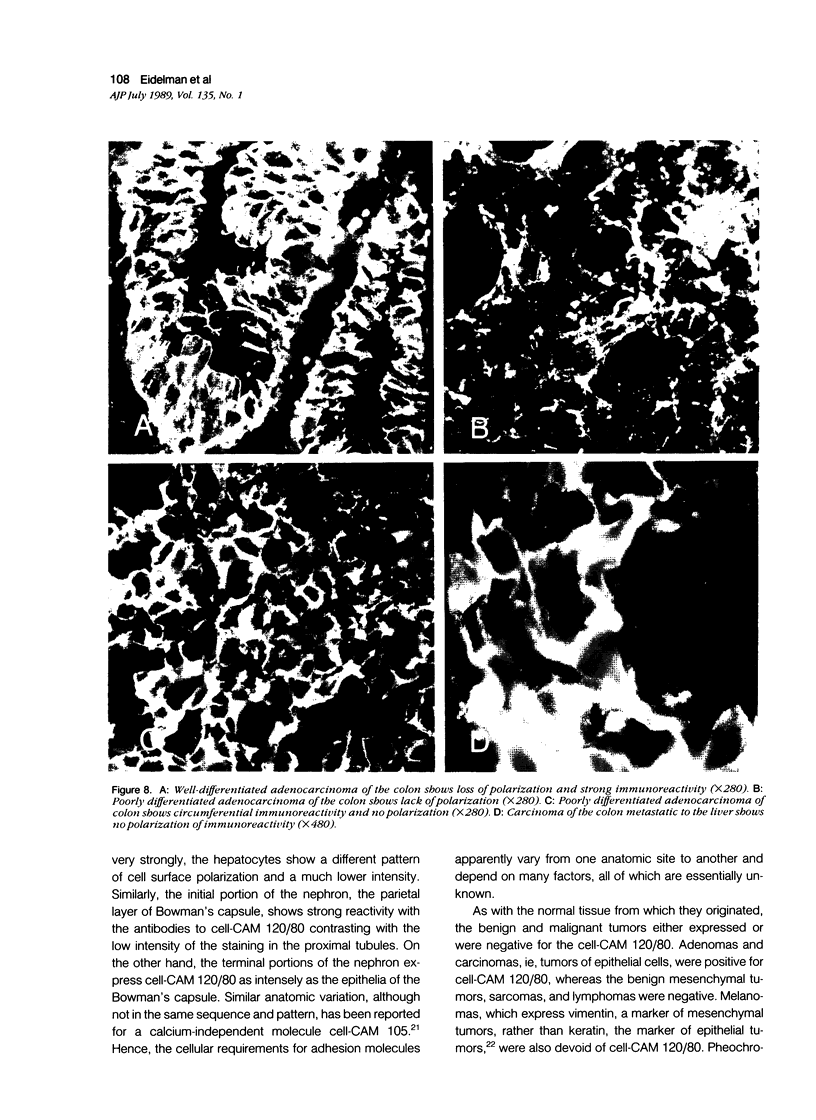


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boller K., Vestweber D., Kemler R. Cell-adhesion molecule uvomorulin is localized in the intermediate junctions of adult intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):327–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damjanov I., Andrews P. W. Ultrastructural differentiation of a clonal human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Cancer Res. 1983 May;43(5):2190–2198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damjanov I., Damjanov A., Damsky C. H. Developmentally regulated expression of the cell-cell adhesion glycoprotein cell-CAM 120/80 in peri-implantation mouse embryos and extraembryonic membranes. Dev Biol. 1986 Jul;116(1):194–202. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damsky C. H., Richa J., Solter D., Knudsen K., Buck C. A. Identification and purification of a cell surface glycoprotein mediating intercellular adhesion in embryonic and adult tissue. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):455–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90379-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Cell adhesion molecules in the regulation of animal form and tissue pattern. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:81–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Expression of cell adhesion molecules during embryogenesis and regeneration. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Nov;161(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Murray B. A., Mege R. M., Cunningham B. A., Gallin W. J. Cellular expression of liver and neural cell adhesion molecules after transfection with their cDNAs results in specific cell-cell binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8502–8506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin W. J., Sorkin B. C., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the liver cell adhesion molecule, L-CAM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2808–2812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyafil F., Morello D., Babinet C., Jacob F. A cell surface glycoprotein involved in the compaction of embryonal carcinoma cells and cleavage stage embryos. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):927–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90456-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imhof B. A., Vollmers H. P., Goodman S. L., Birchmeier W. Cell-cell interaction and polarity of epithelial cells: specific perturbation using a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):667–675. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90099-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mansouri A., Spurr N., Goodfellow P. N., Kemler R. Characterization and chromosomal localization of the gene encoding the human cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin. Differentiation. 1988 Jun;38(1):67–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1988.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Virtanen I., Talerman A. Intermediate filament proteins in human testis and testicular germ-cell tumors. Am J Pathol. 1985 Sep;120(3):402–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagafuchi A., Shirayoshi Y., Okazaki K., Yasuda K., Takeichi M. Transformation of cell adhesion properties by exogenously introduced E-cadherin cDNA. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):341–343. doi: 10.1038/329341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nose A., Takeichi M. A novel cadherin cell adhesion molecule: its expression patterns associated with implantation and organogenesis of mouse embryos. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2649–2658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odin P., Asplund M., Busch C., Obrink B. Immunohistochemical localization of cellCAM 105 in rat tissues: appearance in epithelia, platelets, and granulocytes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1988 Jul;36(7):729–739. doi: 10.1177/36.7.3290331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richa J., Damsky C. H., Buck C. A., Knowles B. B., Solter D. Cell surface glycoproteins mediate compaction, trophoblast attachment, and endoderm formation during early mouse development. Dev Biol. 1985 Apr;108(2):513–521. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringwald M., Schuh R., Vestweber D., Eistetter H., Lottspeich F., Engel J., Dölz R., Jähnig F., Epplen J., Mayer S. The structure of cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin. Insights into the molecular mechanism of Ca2+-dependent cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3647–3653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02697.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh R., Vestweber D., Riede I., Ringwald M., Rosenberg U. B., Jäckle H., Kemler R. Molecular cloning of the mouse cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin: cDNA contains a B1-related sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Delouvée A., Gallin W. J., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Ontogenetic expression of cell adhesion molecules: L-CAM is found in epithelia derived from the three primary germ layers. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vestweber D., Kemler R. Rabbit antiserum against a purified surface glycoprotein decompacts mouse preimplantation embryos and reacts with specific adult tissues. Exp Cell Res. 1984 May;152(1):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90241-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida-Noro C., Suzuki N., Takeichi M. Molecular nature of the calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion system in mouse teratocarcinoma and embryonic cells studied with a monoclonal antibody. Dev Biol. 1984 Jan;101(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90112-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida C., Takeichi M. Teratocarcinoma cell adhesion: identification of a cell-surface protein involved in calcium-dependent cell aggregation. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90339-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]