Abstract
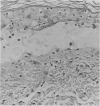
Three cases are described in which Stevens-Johnson syndrome progressed in the course of a few days to toxic epidermal necrolysis. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, allopurinol in combination with hydrochlorothiazide, phenytoin and possibly ampicillin were implicated in the causation of the disease.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amon R. B., Dimond R. L. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Rapid differentiation between staphylococcal- and drug-induced disease. Arch Dermatol. 1975 Nov;111(11):1433–1437. doi: 10.1001/archderm.111.11.1433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott J. P., Kent J., Lyell A., Gemmell C. G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis produced by an extracellular product of Staphylococcus aureus. Br J Dermatol. 1971 Aug;85(2):145–149. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1971.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAILEY G., ROSENBAUM J. M., ANDERSON B. TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS. JAMA. 1965 Mar 22;191:979–982. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080120013003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchine J. R., Macaraeg P. V., Jr, Lasagna L., Azarnoff D. L., Brunk S. F., Hvidberg E. F., Owen J. A., Jr Drugs as etiologic factors in the Stevens-Johnson syndrome. Am J Med. 1968 Mar;44(3):390–405. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(68)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björnberg A. Fifteen cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell). Acta Derm Venereol. 1973;53(2):149–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böttiger L. E., Strandberg I., Westerholm B. Drug-induced febrile mucocutaneous syndrome with a survey of the literature. Acta Med Scand. 1975 Sep;198(3):229–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M., Fritsch P., Epstein E. H. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. Clinical features, pathogenesis, and recent microbiological and biochemical developments. Arch Dermatol. 1977 Feb;113(2):207–219. doi: 10.1001/archderm.113.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellman M. H., Fretzin D. F., Olson W. Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with allopurinol administration. Arch Dermatol. 1975 Aug;111(8):986–990. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor G. L. Toxic epidermal necrolysis, azotemia, and death after allopurinol therapy. JAMA. 1970 Apr 20;212(3):478–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koblenzer P. J. Acute epidermal necrolysis (Ritter von Rittershain-Lyell). A clinicopathologic study. Arch Dermatol. 1967 Jun;95(6):608–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYELL A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: an eruption resembling scalding of the skin. Br J Dermatol. 1956 Nov;68(11):355–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1956.tb12766.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyell A. A review of toxic epidermal necrolysis in Britain. Br J Dermatol. 1967 Dec;79(12):662–671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1967.tb11434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyell A., Dick H. M., Alexander J. O. Outbreak of toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with staphylococci. Lancet. 1969 Apr 19;1(7599):787–789. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyell A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Lancet. 1969 Jun 7;1(7606):1155–1155. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91676-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melish M. E., Glasgow L. A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1970 May 14;282(20):1114–1119. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197005142822002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen J. E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. A review of 75 cases in children. Arch Dermatol. 1975 Sep;111(9):1135–1139. doi: 10.1001/archderm.111.9.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M. J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. A report of 42 cases. Br J Dermatol. 1967 Dec;79(12):672–677. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1967.tb11435.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stratigos J. D., Bartsokas S. K., Capetanakis J. Further experiences of toxic epidermal necrolysis incriminating allopurinol, pyrazolone and derivatives. Br J Dermatol. 1972 Jun;86(6):564–567. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1972.tb05070.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trentham D. E., Silverman H. A., Townes A. S. Letter: Cause of adult toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1975 Apr 17;292(16):870–870. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197504172921618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]