Abstract
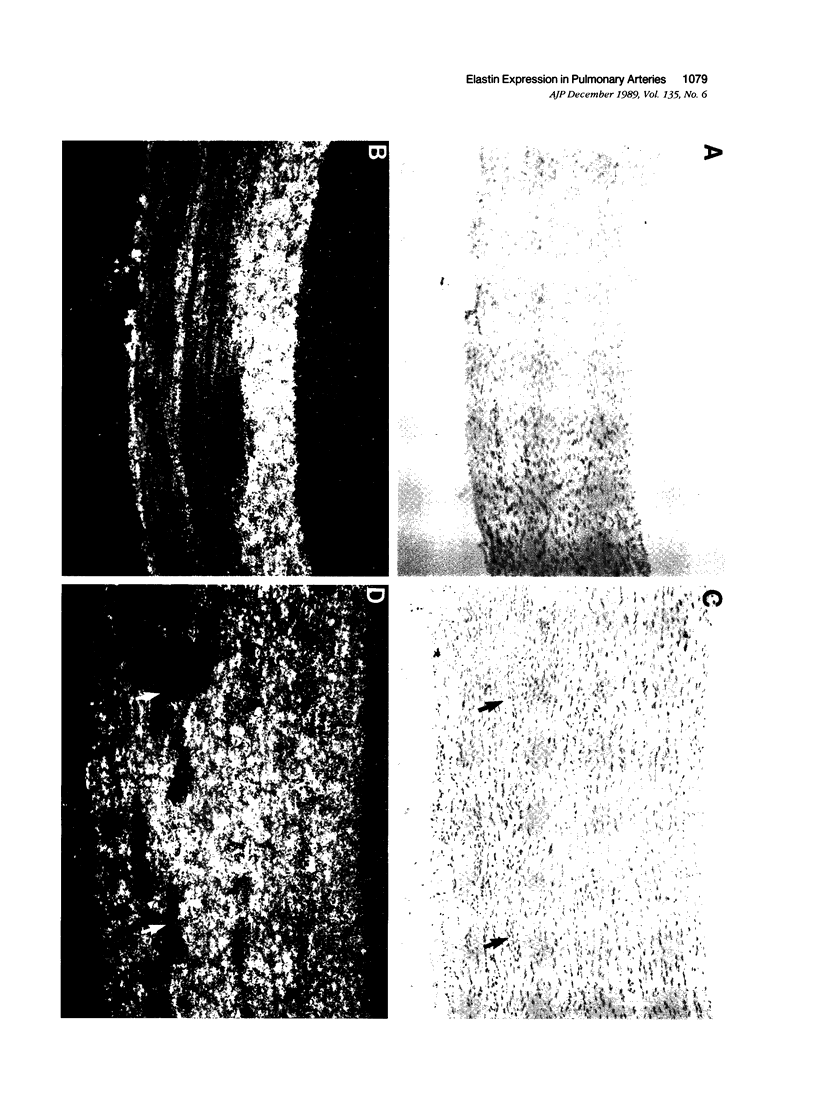
In situ hybridization was used to determine the morphologic distribution of tropoelastin and alpha 1(I) procollagen mRNA expression in elastic intralobar arteries from neonatal calves with hypoxic pulmonary hypertension induced by a 15-day exposure to a simulated altitude of 1500 m. In vessels from normotensive control animals, low levels of hybridizable tropoelastin mRNA were detected in smooth muscle cells (SMC) of the inner media associated with large elastic lamellae. Compared to control arteries, vessels from hypertensive animals demonstrated a markedly different pattern of hybridization. In these arteries, strong hybridization signals for tropoelastin mRNA were seen in SMC lying between the elastic lamellae of the outer media, and the density of labeling associated with these medial cells decreased progressively toward the lumen. Endothelial and adventitial cells in both control and hypertensive arteries were negative for tropoelastin mRNA. Type I procollagen mRNA was dispersed through the media of control arteries, and in hypertensive calves, the hybridization signal was more intense and was unevenly distributed through the media similarly to that for tropoelastin mRNA. Adventitial cells were strongly positive for procollagen mRNA, and the signal was equally intense for both control and hypertensive arteries. Cells that had no detectable tropoelastin mRNA were noted in the outer media of both control and hypertensive vessels. These cells occurred as broad circumferential bands in the normotensive artery and as nodular foci in the hypertensive artery. Immunocytochemical studies with antibodies to smooth muscle specific actin, desmin, and vimentin demonstrated that cells within these foci, as well as tropoelastin mRNA-positive cells, were SMC. These studies demonstrate that expression of tropoelastin and procollagen mRNA was differentially stimulated by pulmonary hypertension within specific regions and SMC populations of the vascular wall.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen K., Haworth S. G. Human postnatal pulmonary arterial remodeling. Ultrastructural studies of smooth muscle cell and connective tissue maturation. Lab Invest. 1988 Nov;59(5):702–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd C. D., Kniep A. C., Pierce R. A., Deak S. B., Karboski C., Miller D. C., Parker M. I., Mackenzie J. W., Rosenbloom J., Scott G. E. Increased elastin mRNA levels associated with surgically induced intimal injury. Connect Tissue Res. 1988;18(2):65–78. doi: 10.3109/03008208809008059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicila G., May M., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Indik Z., Morrow S., Yeh H. S., Rosenbloom J., Boyd C., Rosenbloom J., Yoon K. Structure of the 3' portion of the bovine elastin gene. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3075–3080. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coflesky J. T., Adler K. B., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Mitchell J., Evans J. N. Proliferative changes in the pulmonary arterial wall during short-term hyperoxic injury to the lung. Am J Pathol. 1988 Sep;132(3):563–573. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coflesky J. T., Jones R. C., Reid L. M., Evans J. N. Mechanical properties and structure of isolated pulmonary arteries remodeled by chronic hyperoxia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):388–394. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiano V., Tsang A., Weinbaum G., Christner P., Rosenbloom J. Secretion of elastin in the embryonic chick aorta as visualized by immunoelectron microscopy. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Mar;4(2):153–164. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingemans K. P., Wagenvoort C. A. Pulmonary arteries and veins in experimental hypoxia. An ultrastructural study. Am J Pathol. 1978 Nov;93(2):353–368. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geggel R. L., Reid L. M. The structural basis of PPHN. Clin Perinatol. 1984 Oct;11(3):525–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Ninomiya Y., Parsons J., Hayashi K., Olsen B. R., Trelstad R. L. Differential localization of mRNAs of collagen types I and II in chick fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and corneal cells by in situ hybridization using cDNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2302–2309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ilkiw R., Todorovich-Hunter L., Maruyama K., Shin J., Rabinovitch M. SC-39026, a serine elastase inhibitor, prevents muscularization of peripheral arteries, suggesting a mechanism of monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Circ Res. 1989 Apr;64(4):814–825. doi: 10.1161/01.res.64.4.814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay E. P., Oh S. Modulation of type III collagen synthesis in bovine corneal endothelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1988 Feb;29(2):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay E. P., Smith R. E., Nimni M. E. Type I collagen synthesis by corneal endothelial cells modulated by polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5139–5146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. S., Riley D. J., Frank M. M., Trelstad R. L., Frankel H. M. Reduction of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in the rat by beta-aminopropionitrile. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 Dec;57(6):1760–1766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.57.6.1760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Madaras J., McDonald J. A., Ryan U. Elastin production by cultured calf pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Sep;116(3):282–288. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041160304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P., Whitehouse L. A., Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Griffin G. L., Senior R. M., Crouch E. C., Stenmark K. R., Voelkel N. F. Smooth muscle-mediated connective tissue remodeling in pulmonary hypertension. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):423–426. doi: 10.1126/science.3603030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Hypoxia-induced structural changes in the media and adventitia of the rat hilar pulmonary artery and their regression. Am J Pathol. 1980 Jul;100(1):151–178. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyrick B., Reid L. Normal postnatal development of the media of the rat hilar pulmonary artery and its remodeling by chronic hypoxia. Lab Invest. 1982 May;46(5):505–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. D., Rabinovitch M., Goldstein J. D., Reid L. M. The structural basis of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn infant. J Pediatr. 1981 Jun;98(6):962–967. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80605-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. C., Secrist H., Wu L. C., Mecham R. P. Developmental regulation of tropoelastin isoforms. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4416–4423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Gamble W., Nadas A. S., Miettinen O. S., Reid L. Rat pulmonary circulation after chronic hypoxia: hemodynamic and structural features. Am J Physiol. 1979 Jun;236(6):H818–H827. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1979.236.6.H818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M., Konstam M. A., Gamble W. J., Papanicolaou N., Aronovitz M. J., Treves S., Reid L. Changes in pulmonary blood flow affect vascular response to chronic hypoxia in rats. Circ Res. 1983 Apr;52(4):432–441. doi: 10.1161/01.res.52.4.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinovitch M. Morphology of the developing pulmonary bed: pharmacologic implications. Pediatr Pharmacol (New York) 1985;5(1):31–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Pritzl P., Bornstein P. Characterization of cell matrix associated collagens synthesized by aortic endothelial cells in culture. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 20;20(2):436–442. doi: 10.1021/bi00505a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage H., Pritzl P., Bornstein P. Secretory phenotypes of endothelial cells in culture: comparison of aortic, venous, capillary, and corneal endothelium. Arteriosclerosis. 1981 Nov-Dec;1(6):427–442. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.1.6.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S. M., Campbell G. R., Campbell J. H. Replication of smooth muscle cells in vascular disease. Circ Res. 1986 Apr;58(4):427–444. doi: 10.1161/01.res.58.4.427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soifer S. J., Heymann M. A. Future research directions in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Clin Perinatol. 1984 Oct;11(3):745–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark K. R., Orton E. C., Reeves J. T., Voelkel N. F., Crouch E. C., Parks W. C., Mecham R. P. Vascular remodeling in neonatal pulmonary hypertension. Role of the smooth muscle cell. Chest. 1988 Mar;93(3 Suppl):127S–133S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorovich-Hunter L., Johnson D. J., Ranger P., Keeley F. W., Rabinovitch M. Altered elastin and collagen synthesis associated with progressive pulmonary hypertension induced by monocrotaline. A biochemical and ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1988 Feb;58(2):184–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozzi C. A., Poiani G. J., Harangozo A. M., Boyd C. J., Riley D. J. Pulmonary vascular endothelial cells modulate stretch-induced DNA and connective tissue synthesis in rat pulmonary artery segments. Chest. 1988 Mar;93(3 Suppl):169S–170S. doi: 10.1378/chest.93.3_supplement.169s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn D. S., Mecham R. P. Immunology of elastin. Methods Enzymol. 1987;144:246–259. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)44182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn D. S., Parks W. C., Whitehouse L. A., Crouch E. C., Kucich U., Rosenbloom J., Mecham R. P. Identification of multiple tropoelastins secreted by bovine cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2244–2249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh H., Ornstein-Goldstein N., Indik Z., Sheppard P., Anderson N., Rosenbloom J. C., Cicila G., Yoon K., Rosenbloom J. Sequence variation of bovine elastin mRNA due to alternative splicing. Coll Relat Res. 1987 Sep;7(4):235–247. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(87)80030-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoon K., May M., Goldstein N., Indik Z. K., Oliver L., Boyd C., Rosenbloom J. Characterization of a sheep elastin cDNA clone containing translated sequences. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jan 13;118(1):261–269. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91095-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]