Abstract
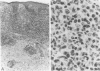
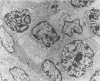
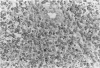
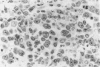
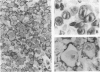
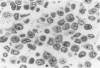
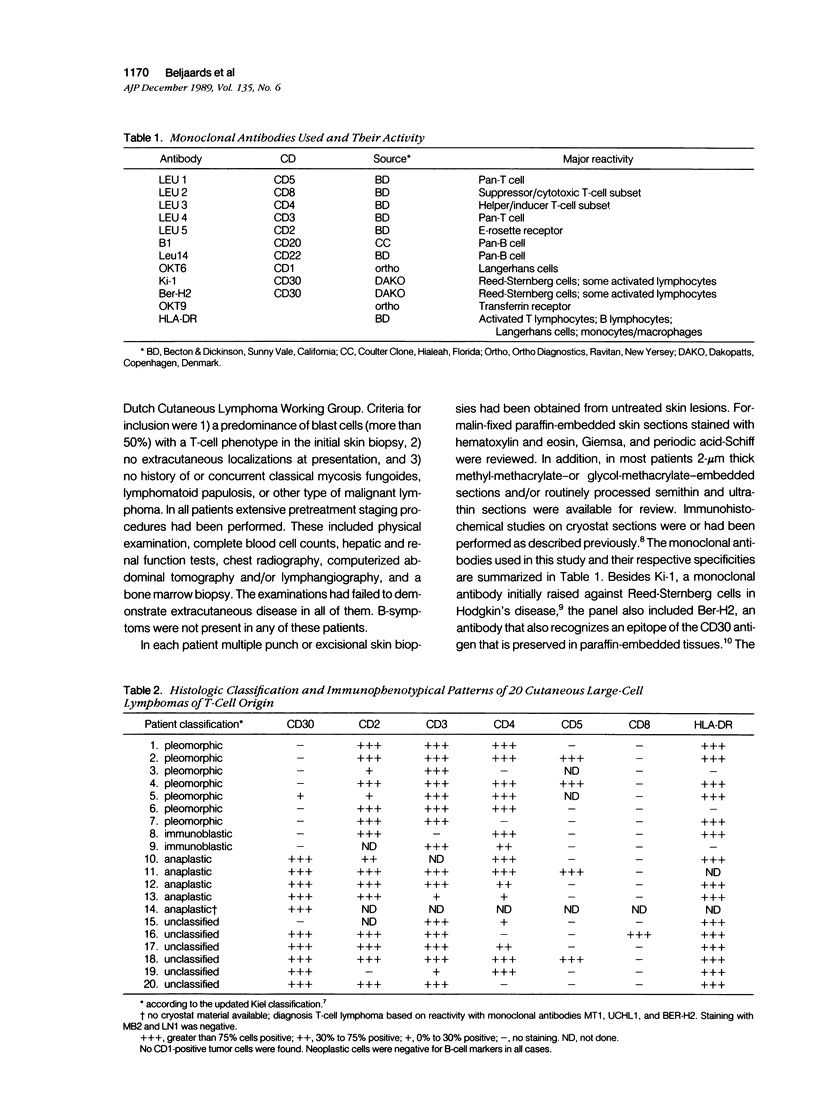
The histologic and immunophenotypical features of 20 primary cutaneous large-cell lymphomas of T-cell origin were investigated and correlated with clinical data to obtain prognostically relevant criteria. Histologic evaluation, using the updated Kiel classification, showed that these large-cell lymphomas represent a morphologic spectrum, often making classification rather arbitrary. It is therefore concluded that the clinical relevance of histologic subtyping is limited for this group of lymphomas. Immunophenotypical studies revealed significant differences between CD30-positive and CD30-negative lymphomas. CD30-positive lymphomas generally presented with localized skin disease, and had a favorable prognosis (9 of 10 patients alive and in complete remission; median survival, 37 months). In contrast, CD30-negative lymphomas often presented with or rapidly developed generalized disease; all patients died of lymphoma (median survival, 17 months). These findings suggest that CD30 expression is an important prognostic parameter for this group of primary cutaneous large-cell lymphomas.
Full text
PDF

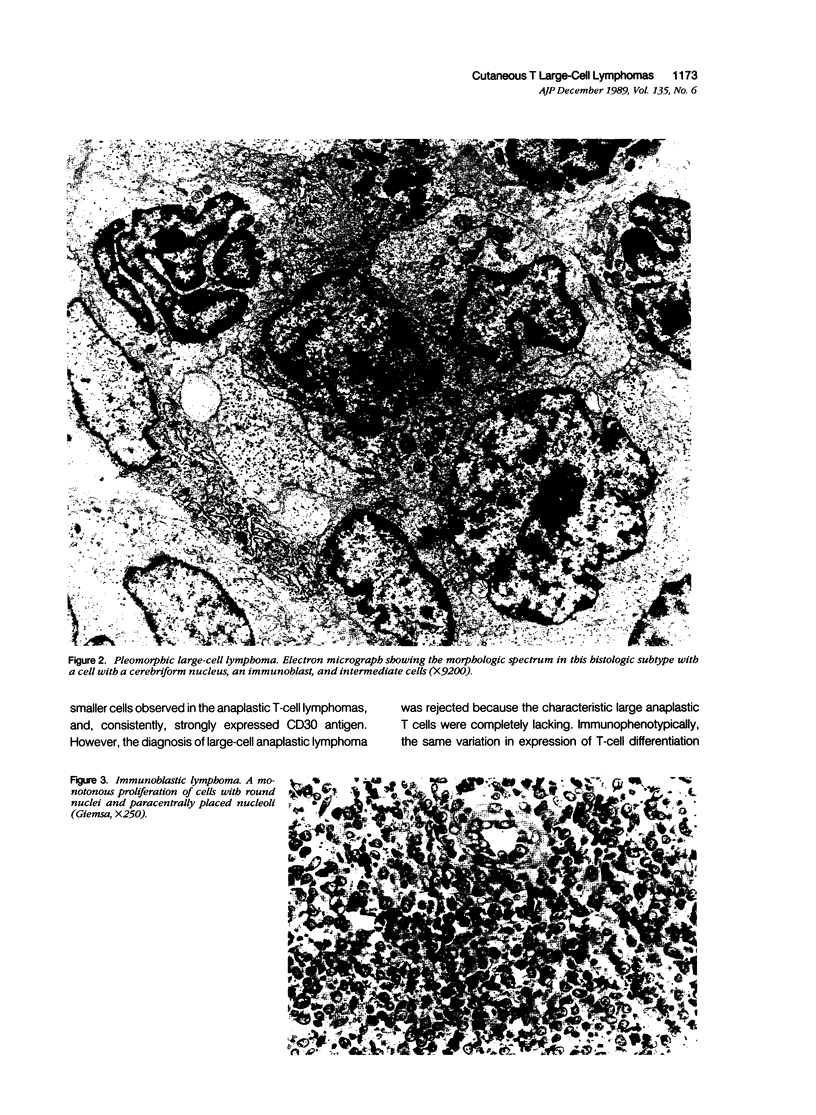

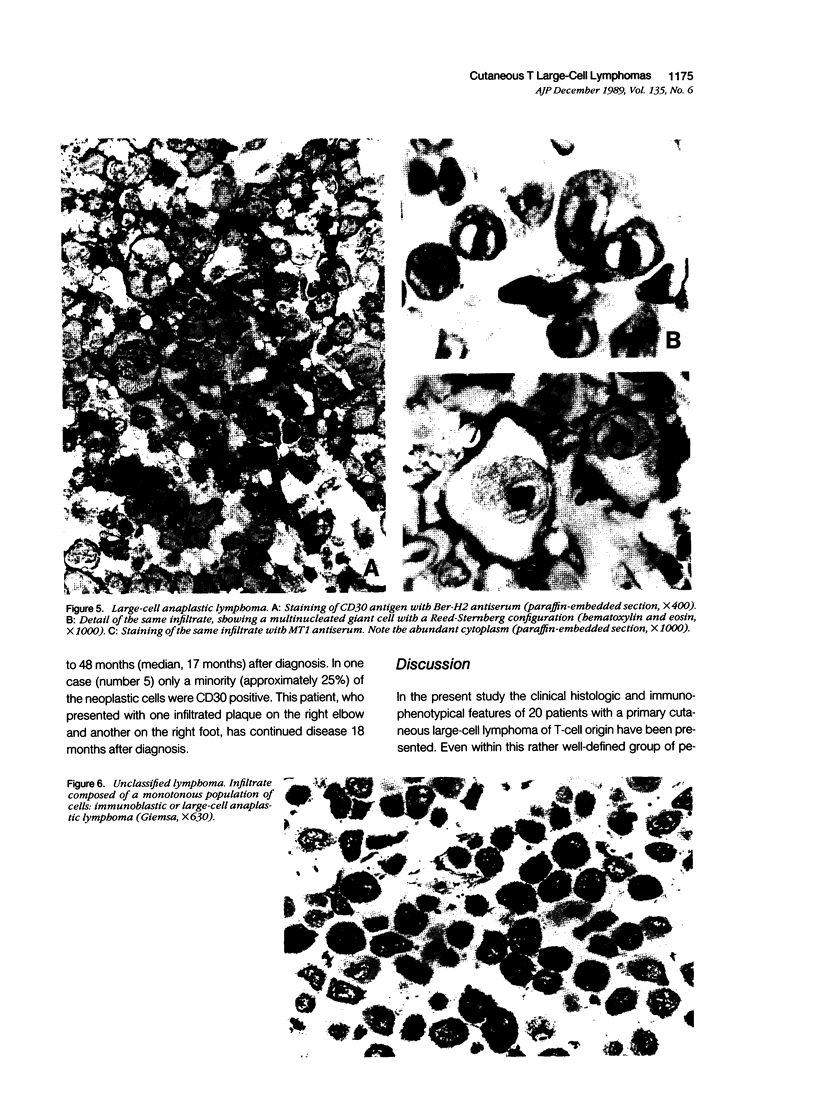
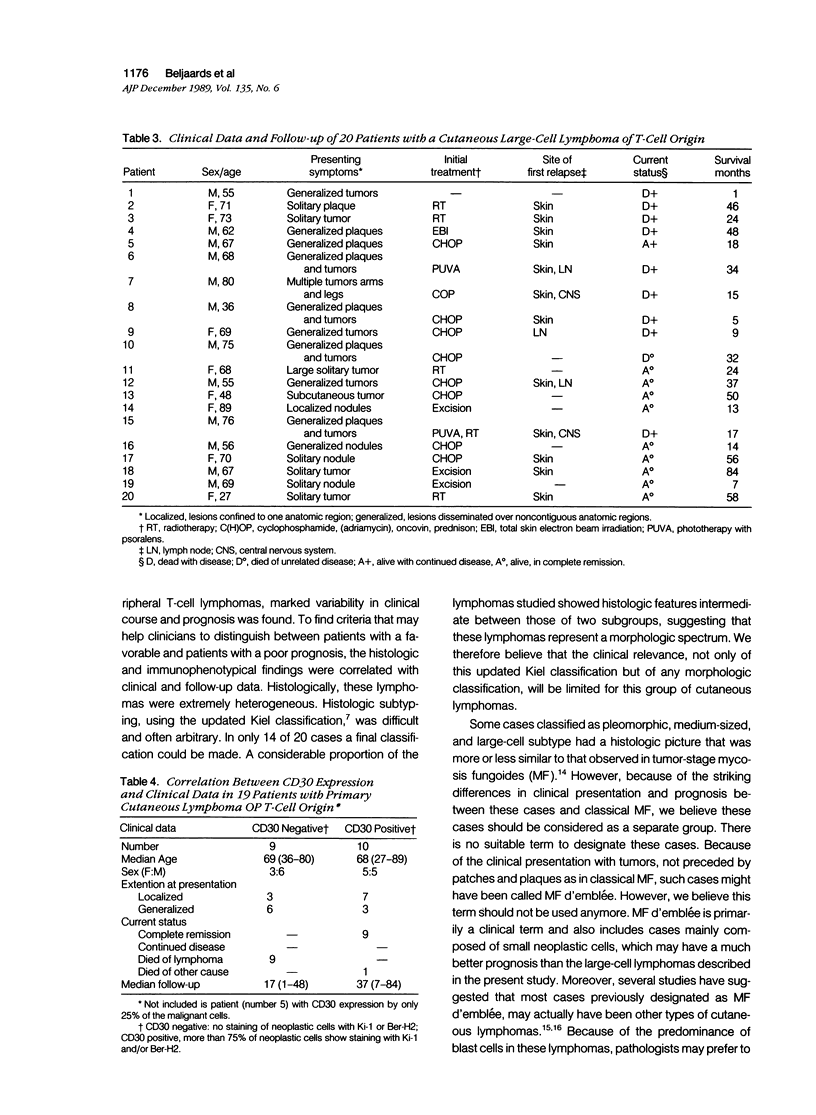


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agnarsson B. A., Kadin M. E. Ki-1 positive large cell lymphoma. A morphologic and immunologic study of 19 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Apr;12(4):264–274. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198804000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitz M. J., Reichert T. A., Brynes R. K., Cousar J. B., Whitcomb C. C., Collins R. D., Crissman J. D., Byrne G. E., Jr The phenotypic diversity of peripheral T-cell lymphomas: the Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jun;17(6):567–574. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan T. M., Fielder K., Rangel C., Jolley C. J., Wirt D. P., Hicks M. J., Miller T. P., Brooks R., Greenberg B., Jones S. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma: aggressive disease with heterogeneous immunotypes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;83(3):279–288. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headington J. T., Roth M. S., Ginsburg D., Lichter A. S., Hyder D., Schnitzer B. T-cell receptor gene rearrangement in regressing atypical histiocytosis. Arch Dermatol. 1987 Sep;123(9):1183–1187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Sako D., Berliner N., Franklin W., Woda B., Borowitz M., Ireland K., Schweid A., Herzog P., Lange B. Childhood Ki-1 lymphoma presenting with skin lesions and peripheral lymphadenopathy. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1042–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., 2nd, Halper J. P. Human T-cell malignancies: Correlative clinical, histopathologic, immunologic, and cytochemical analysis of 23 cases. Am J Pathol. 1982 Feb;106(2):187–203. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krajewski A. S., Myskow M. W., Cachia P. G., Salter D. M., Sheehan T., Dewar A. E. T-cell lymphoma: morphology, immunophenotype and clinical features. Histopathology. 1988 Jul;13(1):19–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1988.tb02001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm J. S., Barron D. R., Williams M. E., Swerdlow S. H. Ki-1-positive cutaneous large cell lymphoma of T cell type: report of an indolent subtype. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1989 Feb;20(2 Pt 2):342–348. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(89)70043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman S. M., Miller T. P., Spier C. M., Slymen D. J., Grogan T. M. The prognostic significance of the immunotype in diffuse large-cell lymphoma: a comparative study of the T-cell and B-cell phenotype. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):436–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. P., Lippman S. M., Spier C. M., Slymen D. J., Grogan T. M. HLA-DR (Ia) immune phenotype predicts outcome for patients with diffuse large cell lymphoma. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jul;82(1):370–372. doi: 10.1172/JCI113598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasu K., Said J., Vonderheid E., Olerud J., Sako D., Kadin M. Immunopathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):436–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noorduyn L. A., van der Valk P., van Heerde P., Vroom T. M., Blok P., Willemze R., Meijer C. J. Stage is a better prognostic indicator than morphologic subtype in primary noncutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1990 Jan;93(1):49–57. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/93.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralfkiaer E., Bosq J., Gatter K. C., Schwarting R., Gerdes J., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Expression of a Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cell associated antigen (Ki-1) in cutaneous lymphoid infiltrates. Arch Dermatol Res. 1987;279(5):285–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00431219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralfkiaer E., Saati T. A., Bosq J., Delsol G., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Immunocytochemical characterisation of cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides. J Clin Pathol. 1986 May;39(5):553–563. doi: 10.1136/jcp.39.5.553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay A. D., Smith W. J., Earl H. M., Souhami R. L., Isaacson P. G. T-cell lymphomas in adults: a clinicopathological study of eighteen cases. J Pathol. 1987 Jun;152(2):63–76. doi: 10.1002/path.1711520202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salhany K. E., Cousar J. B., Greer J. P., Casey T. T., Fields J. P., Collins R. D. Transformation of cutaneous T cell lymphoma to large cell lymphoma. A clinicopathologic and immunologic study. Am J Pathol. 1988 Aug;132(2):265–277. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab U., Stein H., Gerdes J., Lemke H., Kirchner H., Schaadt M., Diehl V. Production of a monoclonal antibody specific for Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells of Hodgkin's disease and a subset of normal lymphoid cells. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):65–67. doi: 10.1038/299065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souteyrand P., Thivolet J. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome. Pathol Res Pract. 1981 Apr;171(2):240–261. doi: 10.1016/s0344-0338(81)80039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stansfeld A. G., Diebold J., Noel H., Kapanci Y., Rilke F., Kelényi G., Sundstrom C., Lennert K., van Unnik J. A., Mioduszewska O. Updated Kiel classification for lymphomas. Lancet. 1988 Feb 6;1(8580):292–293. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90367-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterry W., Korte B., Schubert C. Pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma and large-cell anaplastic lymphoma of the skin. A morphological, immunophenotypical, and ultrastructural study of two typical cases. Am J Dermatopathol. 1989 Apr;11(2):112–123. doi: 10.1097/00000372-198911020-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suchi T., Lennert K., Tu L. Y., Kikuchi M., Sato E., Stansfeld A. G., Feller A. C. Histopathology and immunohistochemistry of peripheral T cell lymphomas: a proposal for their classification. J Clin Pathol. 1987 Sep;40(9):995–1015. doi: 10.1136/jcp.40.9.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tykocinski M., Schinella R., Greco M. A. The pleomorphic cells of advanced mycosis fungoides. An ultrastructural study. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1984 May;108(5):387–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Crabtree G. S., Rouse R. V., Warnke R. A. Morphologic and immunologic characterization of 50 peripheral T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):316–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R. Lymphomatoid papulosis. Dermatol Clin. 1985 Oct;3(4):735–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R., Scheffer E., Meijer C. J. Immunohistochemical studies using monoclonal antibodies on lymph nodes from patients with mycosis fungoides and Sézary's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):46–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Burke J. S., Horning S., Doggett R. S., Levy R., Warnke R. A. The immunologic and clinicopathologic heterogeneity of cutaneous lymphomas other than mycosis fungoides. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):464–472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura T., Aozasa K., Sano S. The cutaneous lymphomas with convoluted nucleus. Analysis of thirty-nine cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984 May;10(5 Pt 1):796–803. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(84)70095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Valk P., Willemze R., Meijer C. J. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: a clinicopathological and immunological study of 10 cases. Histopathology. 1986 Mar;10(3):235–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1986.tb02478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]