Abstract
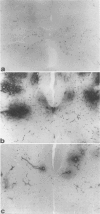
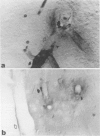
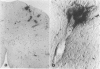
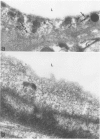
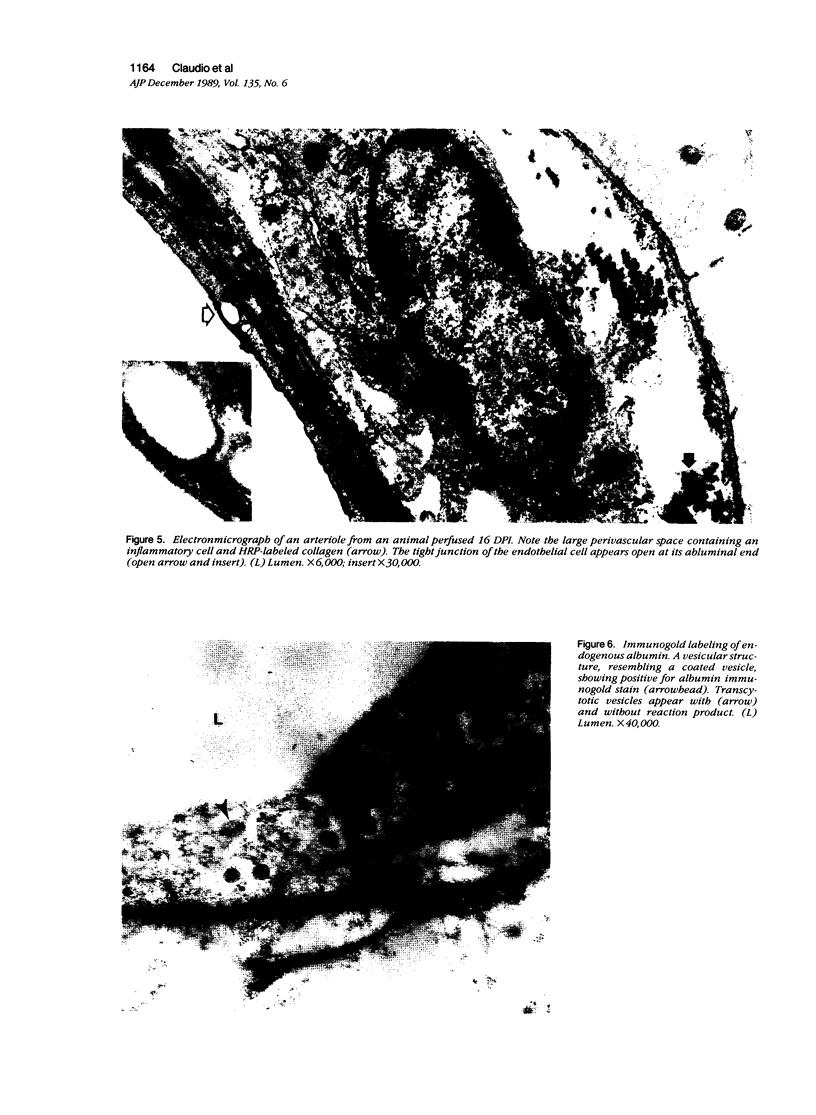
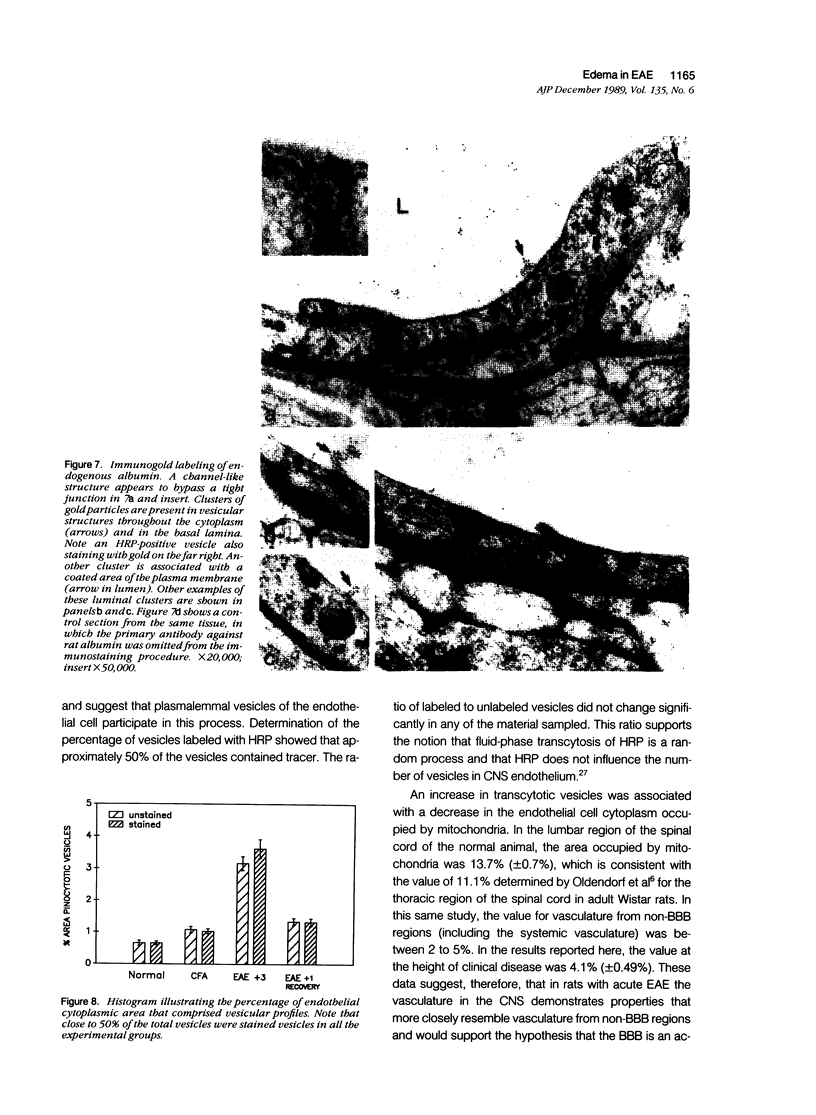
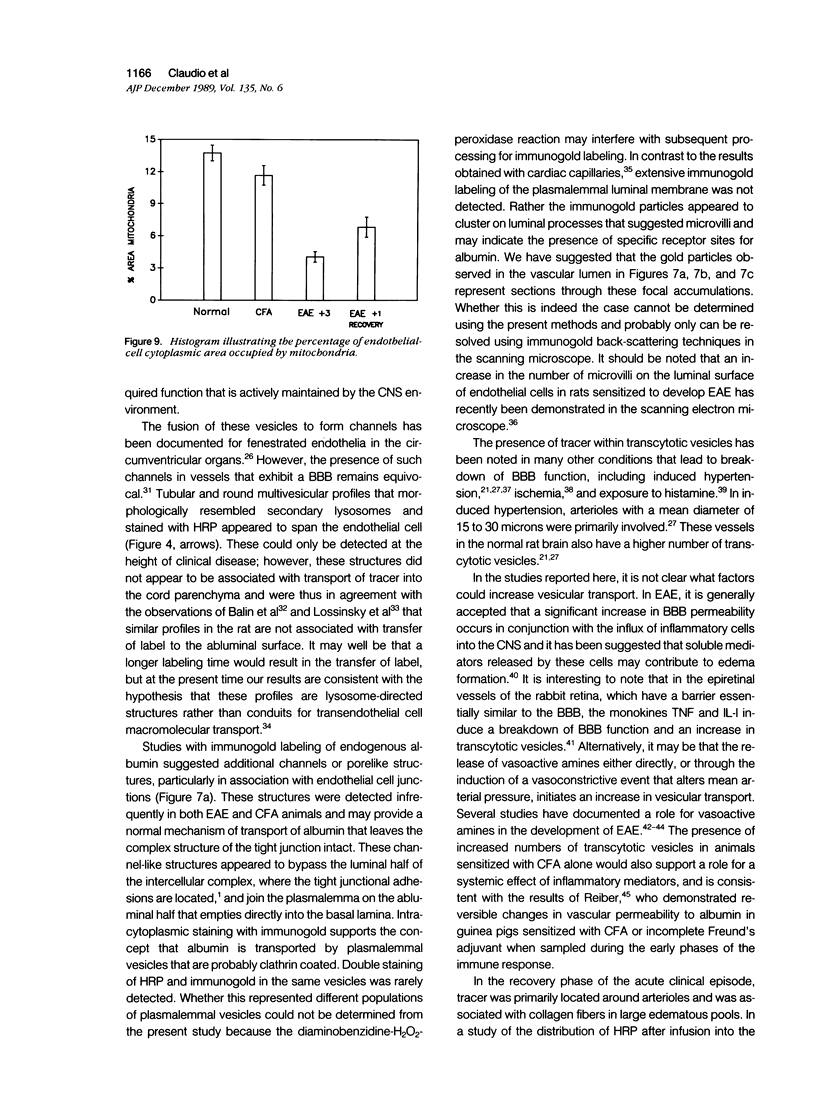
Mechanisms involved in the loss of blood-brain barrier function in Lewis rats with experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) were examined using horseradish peroxidase (HRP) as a tracer. In animals injected with HRP before fixation, tracer was observed in two intracytoplasmic compartments: multivesicular bodies (presumably secondary lysosomes) and transcytotic vesicles. Quantitative morphometry of electron micrographs of capillary endothelial cells demonstrated a 5.2-fold increase in these vesicles. This increase in vesicular transport was associated with a decrease in mitochondrial content from 13.7% of the endothelial cytoplasmic area in the normal rat to 4.2% in EAE rats at the height of clinical disease. These alterations correlated with the clinical course of EAE. In animals infused with tracer after fixation, tracer was restricted to areas of cellular inflammation. Immunogold staining of endogenous albumin demonstrated the presence of albumin in cytoplasmic vesicles and in channel-like tubular structures adjacent to endothelial cell junctions. These results indicate that there is a role for vesicles in transendothelial cell transport and edema formation in animals with EAE.
Full text
PDF


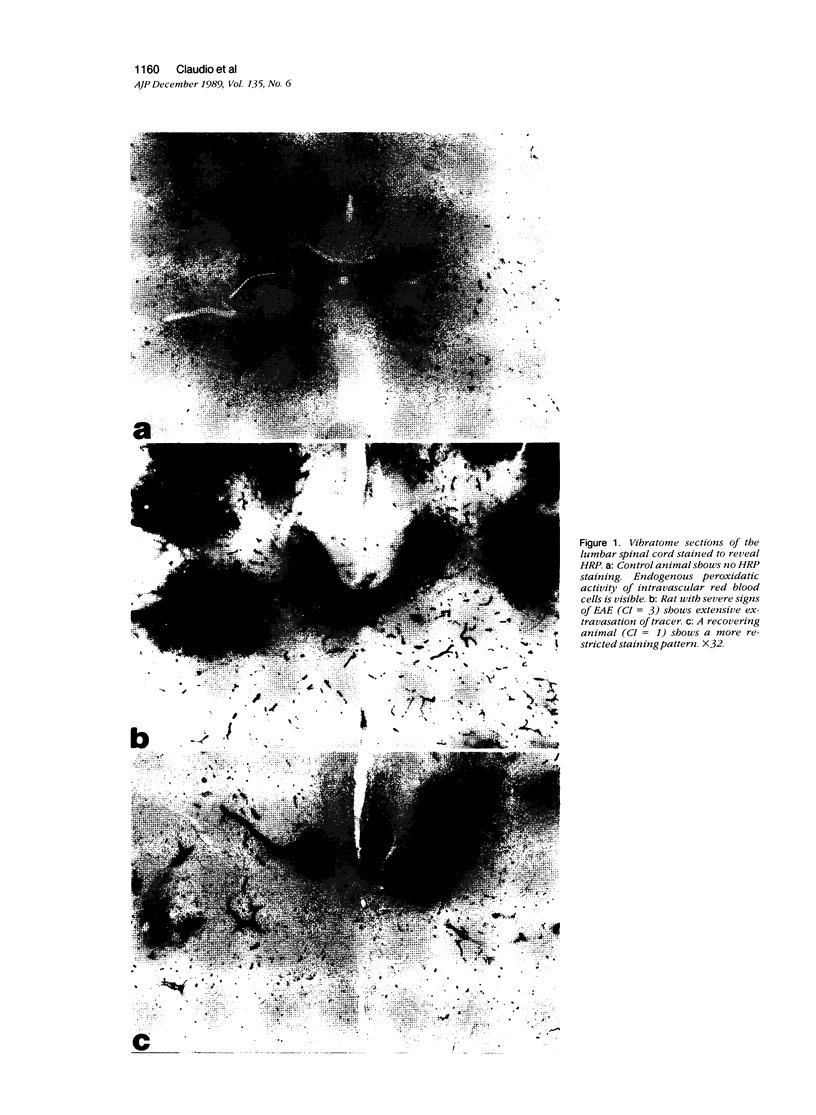

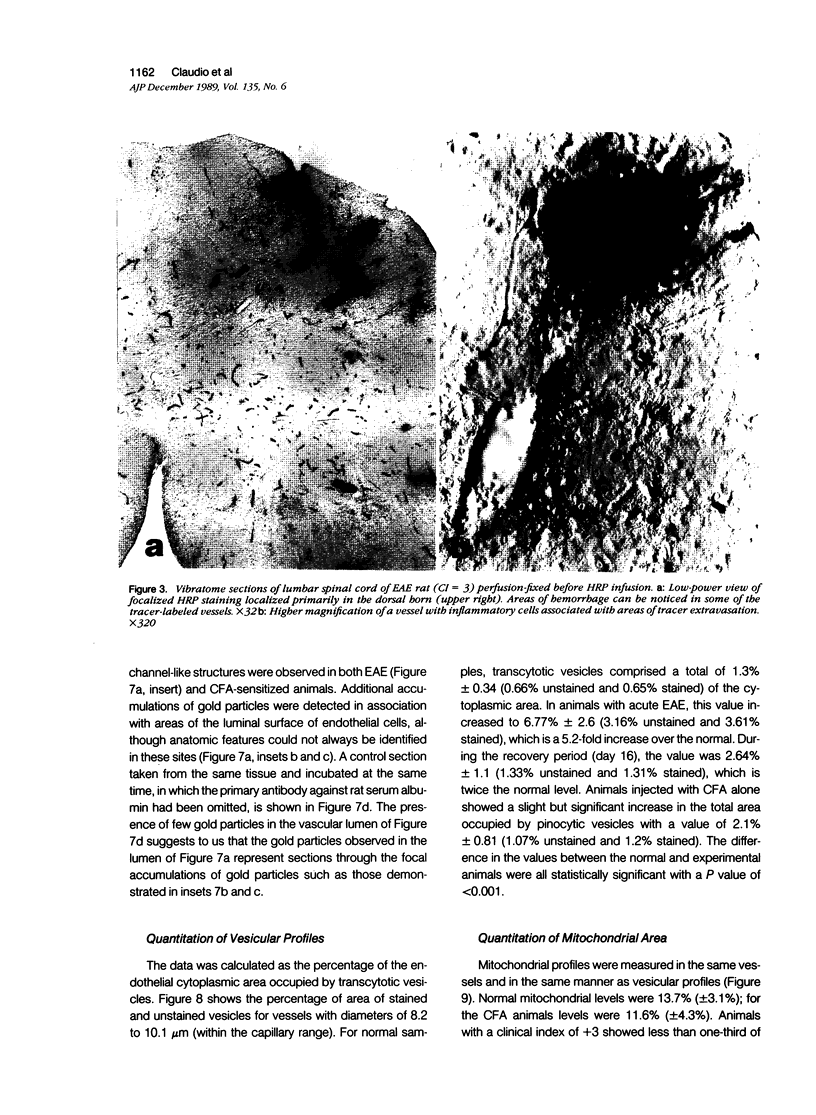



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur F. E., Shivers R. R., Bowman P. D. Astrocyte-mediated induction of tight junctions in brain capillary endothelium: an efficient in vitro model. Brain Res. 1987 Nov;433(1):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balin B. J., Broadwell R. D., Salcman M. Tubular profiles do not form transendothelial channels through the blood-brain barrier. J Neurocytol. 1987 Dec;16(6):721–735. doi: 10.1007/BF01611981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz A. L., Firth J. A., Goldstein G. W. Polarity of the blood-brain barrier: distribution of enzymes between the luminal and antiluminal membranes of brain capillary endothelial cells. Brain Res. 1980 Jun 16;192(1):17–28. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)91004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brightman M. W., Reese T. S. Junctions between intimately apposed cell membranes in the vertebrate brain. J Cell Biol. 1969 Mar;40(3):648–677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broadwell R. D., Balin B. J., Salcman M. Transcytotic pathway for blood-borne protein through the blood-brain barrier. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):632–636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Goldmuntz E. A., Cammer W., Factor S. M., Bloom B. R., Norton W. T. Prazosin, an alpha 1-adrenergic receptor antagonist, suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5915–5919. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosnan C. F., Selmaj K., Schroeder C. E., Litwak M., Raine C. S., Arezzo J. C. Recombinant human lymphokines induce changes in visual evoked potentials in the rabbit. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:571–572. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervós-Navarro J., Artigas J., Mrsulja B. J. Morphofunctional aspects of the normal and pathological blood-brain barrier. Acta Neuropathol Suppl. 1983;8:1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68970-3_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coomber B. L., Stewart P. A. Three-dimensional reconstruction of vesicles in endothelium of blood-brain barrier versus highly permeable microvessels. Anat Rec. 1986 Jul;215(3):256–261. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092150308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone C. The blood-brain barrier as a tight epithelium: where is information lacking? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;481:174–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb27149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dux E., Joó F. Effects of histamine on brain capillaries. Fine structural and immunohistochemical studies after intracarotid infusion. Exp Brain Res. 1982;47(2):252–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00239384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frøkjaer-Jensen J. Three-dimensional organization of plasmalemmal vesicles in endothelial cells. An analysis by serial sectioning of frog mesenteric capillaries. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 Oct;73(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(80)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldmuntz E. A., Brosnan C. F., Norton W. T. Prazosin treatment suppresses increased vascular permeability in both acute and passively transferred experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3444–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M., Becker N. H., Levine S., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structural alterations of the blood-brain barrier in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jul;29(3):432–440. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzer R. C., Raff M. C. Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature. 1987 Jan 15;325(6101):253–257. doi: 10.1038/325253a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhler M., Barry D. I., Offner H., Konat G., Klinken L., Paulson O. B. Blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barrier permeability during the course of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat. Brain Res. 1984 Jun 8;302(2):347–355. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerlero de Rosbo N., Bernard C. C., Simmons R. D., Carnegie P. R. Concomitant detection of changes in myelin basic protein and permeability of blood-spinal cord barrier in acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by electroimmunoblotting. J Neuroimmunol. 1985 Oct;9(6):349–361. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5728(85)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPERT P., CARPENTER S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE VASCULAR PERMEABILITY AND THE MECHANISM OF DEMYELINATION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965 Jan;24:11–24. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196501000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz S., Kennedy L. Cerebral vascular permeability and cellular infiltration in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Immunology. 1972 May;22(5):859–869. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthicum D. S., Munoz J. J., Blaskett A. Acute experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. I. Adjuvant action of Bordetella pertussis is due to vasoactive amine sensitization and increased vascular permeability of the central nervous system. Cell Immunol. 1982 Nov 1;73(2):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90457-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lossinsky A. S., Song M. J., Wisniewski H. M. High voltage electron microscopic studies of endothelial cell tubular structures in the mouse blood-brain barrier following brain trauma. Acta Neuropathol. 1989;77(5):480–488. doi: 10.1007/BF00687249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loud A. V. A quantitative stereological description of the ultrastructure of normal rat liver parenchymal cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Apr;37(1):27–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milici A. J., Watrous N. E., Stukenbrok H., Palade G. E. Transcytosis of albumin in capillary endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2603–2612. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nag S., Robertson D. M., Dinsdale H. B. Quantitative estimate of pinocytosis in experimental acute hypertension. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Apr 12;46(1-2):107–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00684811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Poduslo S. E. Myelination in rat brain: method of myelin isolation. J Neurochem. 1973 Oct;21(4):749–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb07519.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldendorf W. H., Cornford M. E., Brown W. J. The large apparent work capability of the blood-brain barrier: a study of the mitochondrial content of capillary endothelial cells in brain and other tissues of the rat. Ann Neurol. 1977 May;1(5):409–417. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunohistochemical study of allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reese T. S., Karnovsky M. J. Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jul;34(1):207–217. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiber H., Suckling A. J., Rumsby M. G. The effect of Freund's adjuvants on blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier permeability. J Neurol Sci. 1984 Jan;63(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(84)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennels M. L., Gregory T. F., Blaumanis O. R., Fujimoto K., Grady P. A. Evidence for a 'paravascular' fluid circulation in the mammalian central nervous system, provided by the rapid distribution of tracer protein throughout the brain from the subarachnoid space. Brain Res. 1985 Feb 4;326(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91383-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinowara N. L., Michel M. E., Rapoport S. I. Morphological correlates of permeability in the frog perineurium: vesicles and "transcellular channels". Cell Tissue Res. 1982;227(1):11–22. doi: 10.1007/BF00206328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons R. D., Bernard C. C., Singer G., Carnegie P. R. Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. An anatomically-based explanation of clinical progression in rodents. J Neuroimmunol. 1982 Dec;3(4):307–318. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(82)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Kies M. W., Shear C. R. Cell surface endothelial proteins altered in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol. 1989 Feb;21(2-3):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(89)90180-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. A., Wiley M. J. Developing nervous tissue induces formation of blood-brain barrier characteristics in invading endothelial cells: a study using quail--chick transplantation chimeras. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Gonatas N. K. Chronic permeability of the central nervous system to mononuclear cells in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the Lewis rat. J Immunol. 1978 Sep;121(3):844–850. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohl W., Kaplan M. S., Gonatas N. K. A quantitative assay for experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the rat based on permeability of spinal cords to 125I-human gamma-globulin. J Immunol. 1979 Mar;122(3):920–925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorbrodt A. W., Lossinsky A. S., Wisniewski H. M. Enzyme cytochemistry of blood-brain barrier (BBB) disturbances. Acta Neuropathol Suppl. 1983;8:43–57. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68970-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waxman F. J., Taguiam J. M., Whitacre C. C. Modification of the clinical and histopathologic expression of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by the vasoactive amine antagonist cyproheptadine. Cell Immunol. 1984 Apr 15;85(1):82–93. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(84)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard E., Go G., Klatzo I., Spatz M. Increased permeability of cerebral vessels to horseradish peroxidase induced by ischemia in Mongolian Gerbils. Acta Neuropathol. 1976 Aug 16;35(4):307–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard E. Ultrastructural permeability properties of cerebral microvasculature under normal and experimental conditions after application of tracers. Adv Neurol. 1980;28:55–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]