Abstract
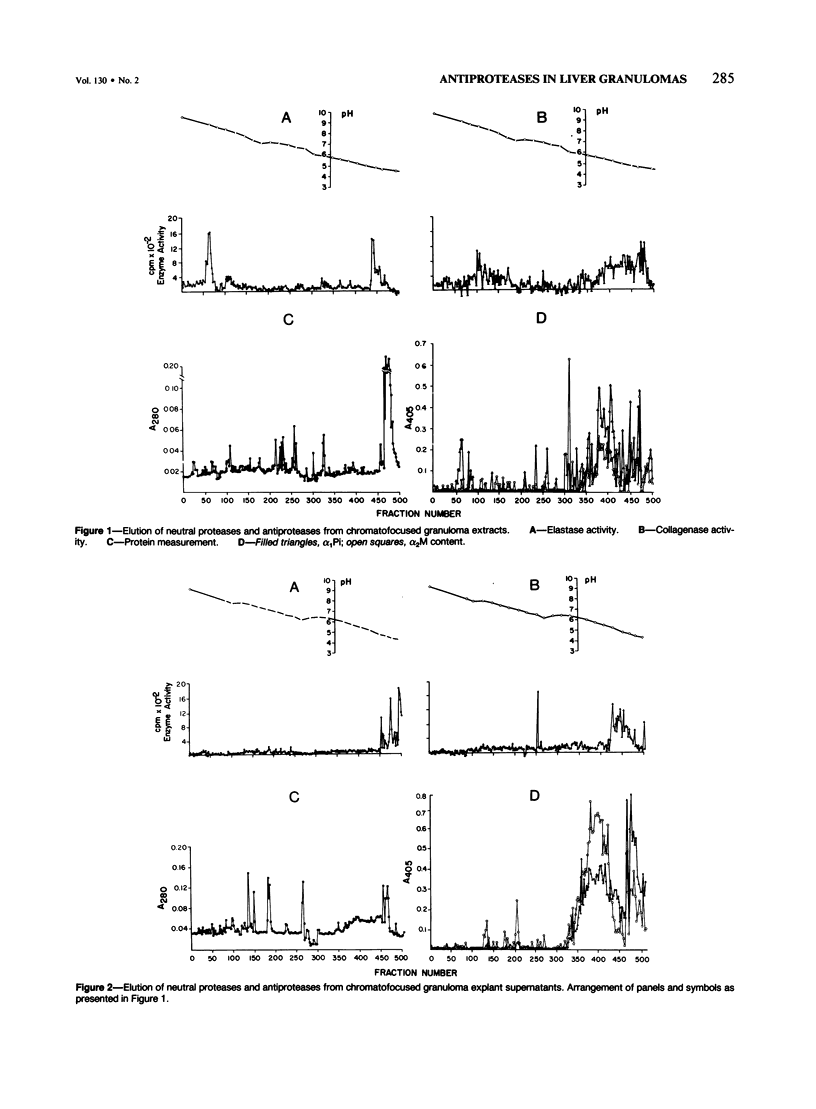
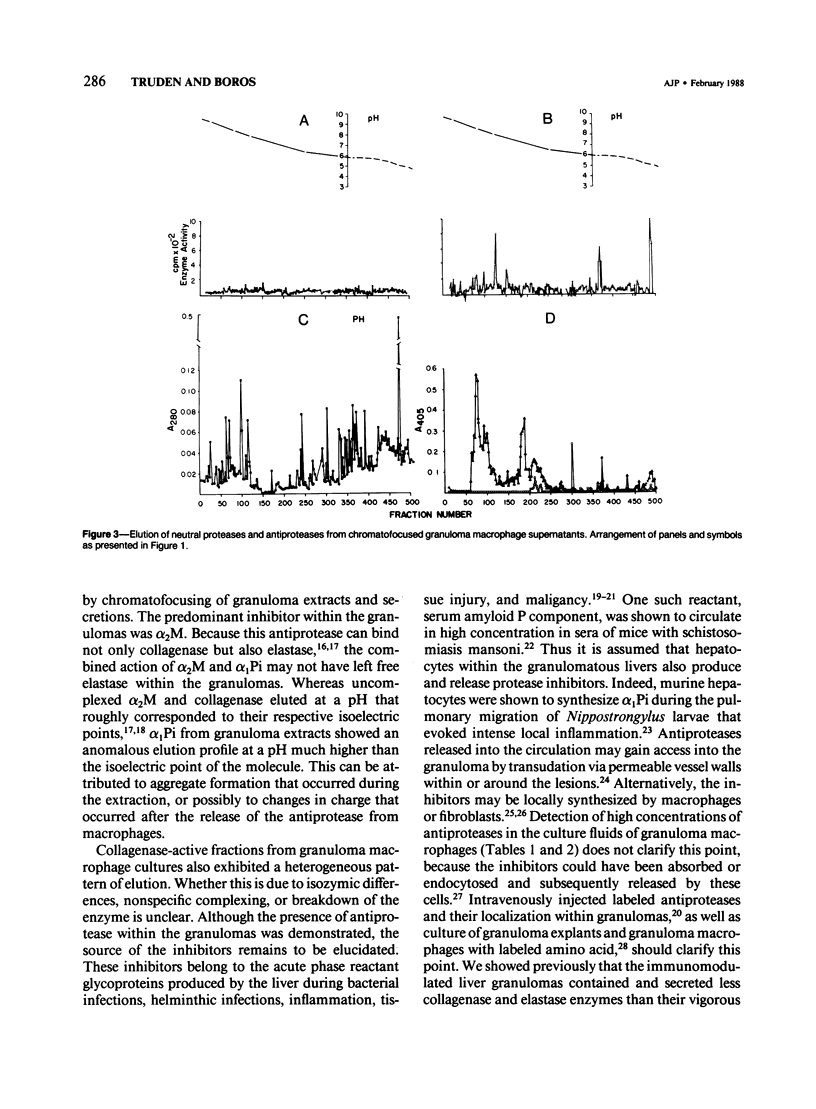
In schistosomiasis mansoni the parasite egg-induced granulomatous tissue inflammations resolve by fibrosis. Intralesional collagen synthesis and deposition are influenced by collagenase, elastase activity that is diminished at the chronic stage of the disease. To determine the cause of diminished neutral protease activity, the authors determined levels of the antiprotease/alpha 2-macroglobulin (alpha 2M) and alpha 1-protease inhibitor (alpha 1Pi) in extracts or secretions of liver granulomas of infected mice. By ELISA, both antiproteases were detected in granuloma-derived substances, as well as supernatants of cultured, adherent granuloma macrophages. In all samples, alpha 2M was the predominant inhibitor. Antiprotease levels were similar in granuloma-derived samples obtained from acutely and chronically infected mice. However, supernatants of cultured adherent macrophages isolated from granulomas of mice with acute infection contained levels of protease inhibitors several times higher than those of similar preparations obtained from chronically infected animals. Gel filtration of samples on Sephacryl S-200 columns did not separate collagenase and elastase from protease inhibitors. By chromatofocusing, a few inhibitor-free collagenase as well as enzyme-free alpha 2M and alpha 1Pi-active peaks were eluted. The bulk of the material that eluted at the acidic region contained protease-antiprotease activity indicating the presence of enzyme-inhibitor complexes. The intragranulomatous presence of antiproteases complexed with protease enzymes emphasizes their importance in the possible enhancement of fibrosis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDRADE Z. A. WARREN KS: MILD PROLONGED SCHISTOSOMIASIS IN MICE: ALTERATIONS IN HOST RESPONSE WITH TIME AND THE DEVELOPMENT OF PORTAL FIBROSIS. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1964 Jan;58:53–57. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(64)90068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abe S., Nagai Y. Interaction between tadpole collagenase and human 2 -macroglobulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 31;278(1):125–132. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(72)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrade Z. A. Hepatic Schistosomiasis. Morphological aspects. Prog Liver Dis. 1965;2:228–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asch H. L., Dresden M. H. Acidic thiol proteinase activity of Schistosoma mansoni egg extracts. J Parasitol. 1979 Aug;65(4):543–549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banda M. J., Clark E. J., Werb Z. Limited proteolysis by macrophage elastase inactivates human alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1563–1570. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Pelley R. P., Warren K. S. Spontaneous modulation of granulomatous hypersensitivity in schistosomiasis mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 May;114(5):1437–1441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boros D. L., Warren K. S. Delayed hypersensitivity-type granuloma formation and dermal reaction induced and elicited by a soluble factor isolated from Schistosoma mansoni eggs. J Exp Med. 1970 Sep 1;132(3):488–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.3.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borth W., Dunky A., Kleesiek K. Alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complexes as correlated with alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor-elastase complexes in synovial fluids of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Mar;29(3):319–325. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cawston T. E., Mercer E., de Silva M., Hazleman B. L. Metalloproteinases and collagenase inhibitors in rheumatoid synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1984 Mar;27(3):285–290. doi: 10.1002/art.1780270306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chensue S. W., Boros D. L., David C. S. Regulation of granulomatous inflammation in murine schistosomiasis. In vitro characterization of T lymphocyte subsets involved in the production and suppression of migration inhibition factor. J Exp Med. 1980 Jun 1;151(6):1398–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.6.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley D. G. Immune responses to a soluble schistosomal egg antigen preparation during chronic primary infection with Schistosoma mansoni. J Immunol. 1975 Jul;115(1):150–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn M. A., Kamel R. Hepatic schistosomiasis. Hepatology. 1981 Nov-Dec;1(6):653–661. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauldie J., Lamontagne L., Stadnyk A. Acute phase response in infectious disease. Surv Synth Pathol Res. 1985;4(2):126–151. doi: 10.1159/000156970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janoff A., Carp H. Proteases, antiproteases, and oxidants: pathways of tissue injury during inflammation. Monogr Pathol. 1982;(23):62–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne L. R., Gauldie J., Befus A. D., McAdam K. P., Baltz M. L., Pepys M. B. The acute phase response in parasite infection. Nippostrongylus brasiliensis in the mouse. Immunology. 1984 Aug;52(4):733–741. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamontagne L. R., Stadnyk A. W., Gauldie J. Synthesis of alpha 1-protease inhibitor by resident and activated mouse alveolar macrophages. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Mar;131(3):321–325. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.131.3.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxfield F. R., Willingham M. C., Haigler H. T., Dragsten P., Pastan I. H. Binding, surface mobility, internalization, and degradation of rhodamine-labeled alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5353–5358. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Sarlo K., Le P. T. Monokine-induced hepatocyte synthesis of acute-phase reactants in mice. Lymphokine Res. 1984;3(1):17–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher D. F. Synthesis of alpha 2-macroglobulin by cultured adherent cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1983;421:327–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1983.tb18121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo H., Ishibashi H., Shibata K., Tsuda-Kawamura K., Yanase T. Distribution of alpha 2-macroglobulin in normal, inflammatory, and tumor tissues in rats. Inflammation. 1984 Jun;8(2):171–179. doi: 10.1007/BF00916092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L. Acute phase proteins with special reference to C-reactive protein and related proteins (pentaxins) and serum amyloid A protein. Adv Immunol. 1983;34:141–212. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60379-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys M. B., Baltz M. L., Musallam R., Doenhoff M. J. Serum protein concentrations during Schistosoma mansoni infection in intact and T-cell deprived mice. I. The acute phase proteins, C3 and serum amyloid P-component (SAP). Immunology. 1980 Feb;39(2):249–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley M. J., Russell D. F., Ridley D. S. An immunoperoxidase study of immunological factors in skin lesions across the spectrum of leprosy. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1982 Mar;50(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Dunn M. A., Seifter S. Liver collagenase in murine schistosomiasis. Gastroenterology. 1980 Jun;78(6):1425–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Koda K. Radioimmunoassay of soluble and insoluble collagenases in fibrotic liver. Biochem J. 1984 May 15;220(1):157–164. doi: 10.1042/bj2200157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi S., Simpser E. Granuloma collagenase and EDTA-sensitive neutral protease production in hepatic murine schistosomiasis. Hepatology. 1981 May-Jun;1(3):211–220. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truden J. L., Boros D. L. Collagenase, elastase, and nonspecific protease production by vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas and granuloma macrophages/eosinophils of S mansoni-infected mice. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):166–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vischer T. L., Flory E., Muirden K. alpha 2M-proteinase complexes are taken up by macrophages during joint inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;155:635–639. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4394-3_69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voller A., Bidwell D. E., Bartlett A. Enzyme immunoassays in diagnostic medicine. Theory and practice. Bull World Health Organ. 1976;53(1):55–65. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. S. The secret of the immunopathogenesis of schistosomiasis: in vivo models. Immunol Rev. 1982;61:189–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellhausen S. R., Boros D. L. Comparison of Fc, C3 receptors and Ia antigens on the inflammatory macrophage isolated from vigorous or immunomodulated liver granulomas of schistosome-infected mice. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1981 Sep;30(3):191–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Habicht G. S., Godfrey H. P., Janoff A., Barton E., Fox C. Secretion of elastase and alpha-2-macroglobulin by cultured murine peritoneal macrophages: studies on their interaction. J Lab Clin Med. 1981 May;97(5):718–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yemul V. L., Sengupta S. R., Dhole T. N. Protease inhibitors activity in lepromatous leprosy and lepra reaction. Lepr India. 1983 Jan;55(1):91–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. C., Jr, Headings V. E., Bose S., Harden K. A., Crockett E. D., Jr, Hackney R. L., Jr Alpha 1 antitrypsin levels in sarcoidosis: relationship to disease activity. Chest. 1973 Jul;64(1):39–45. doi: 10.1378/chest.64.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


