Abstract
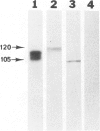
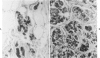
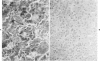
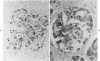
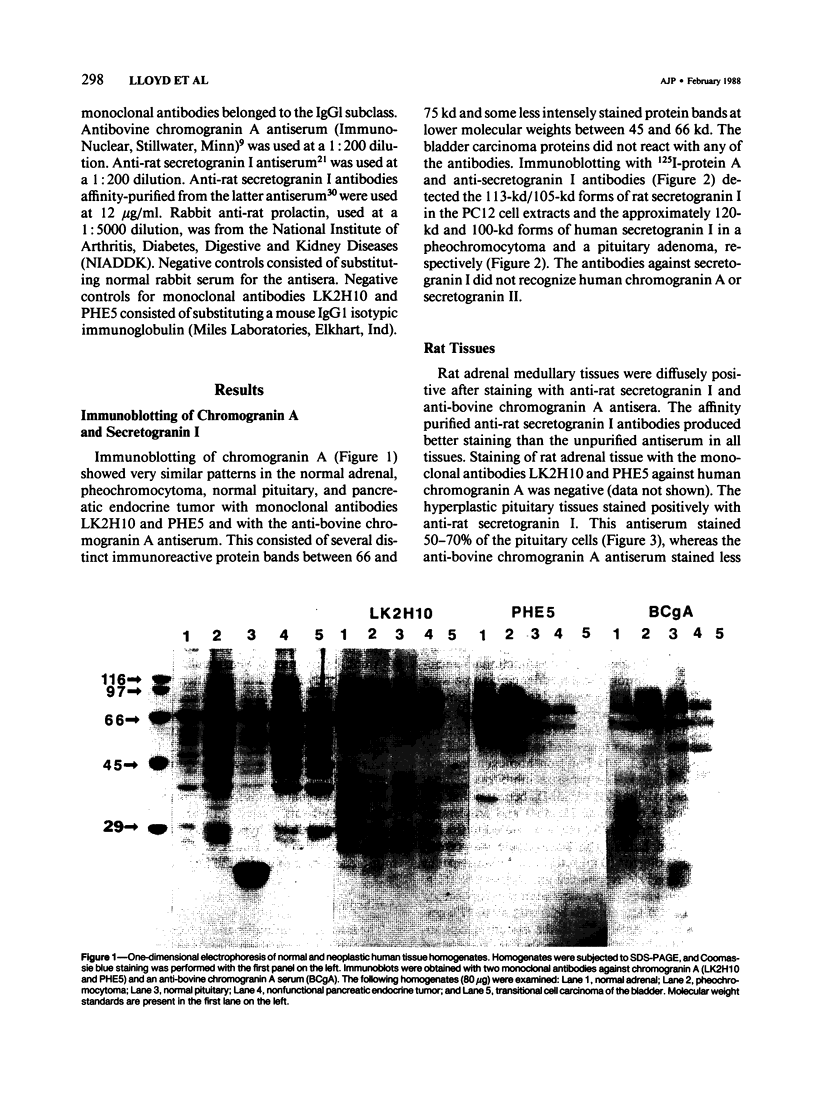
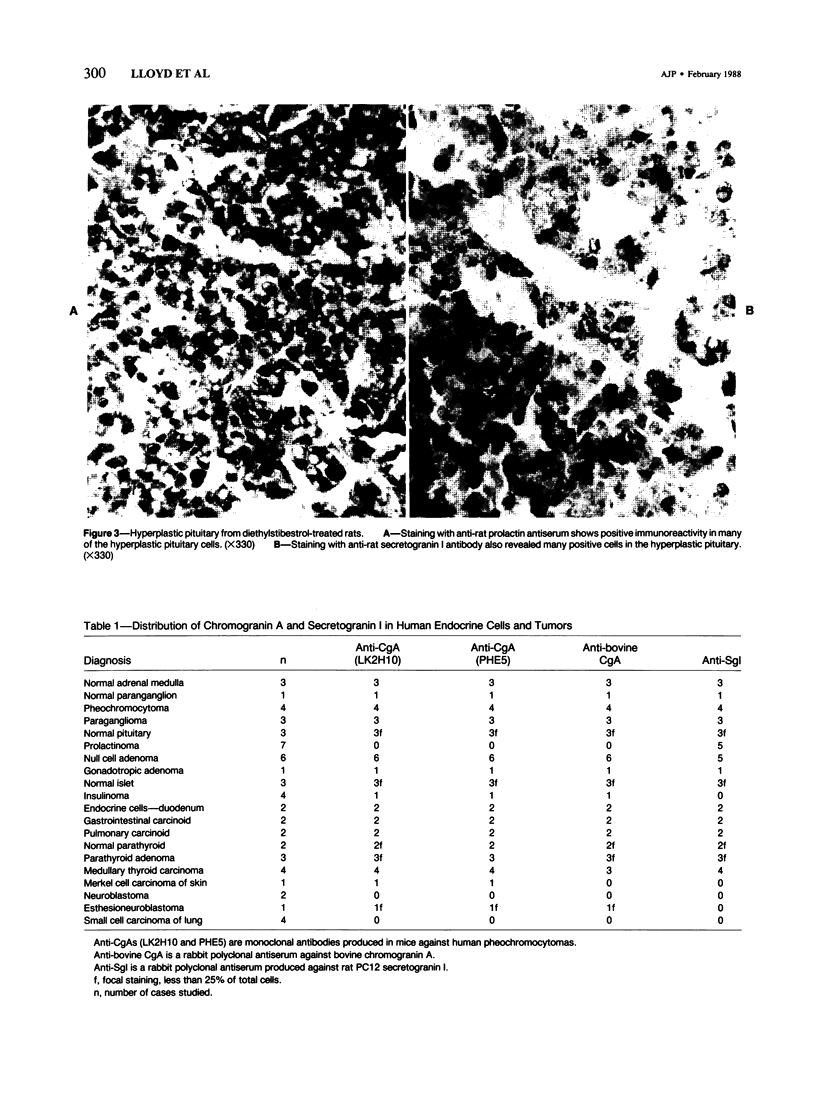
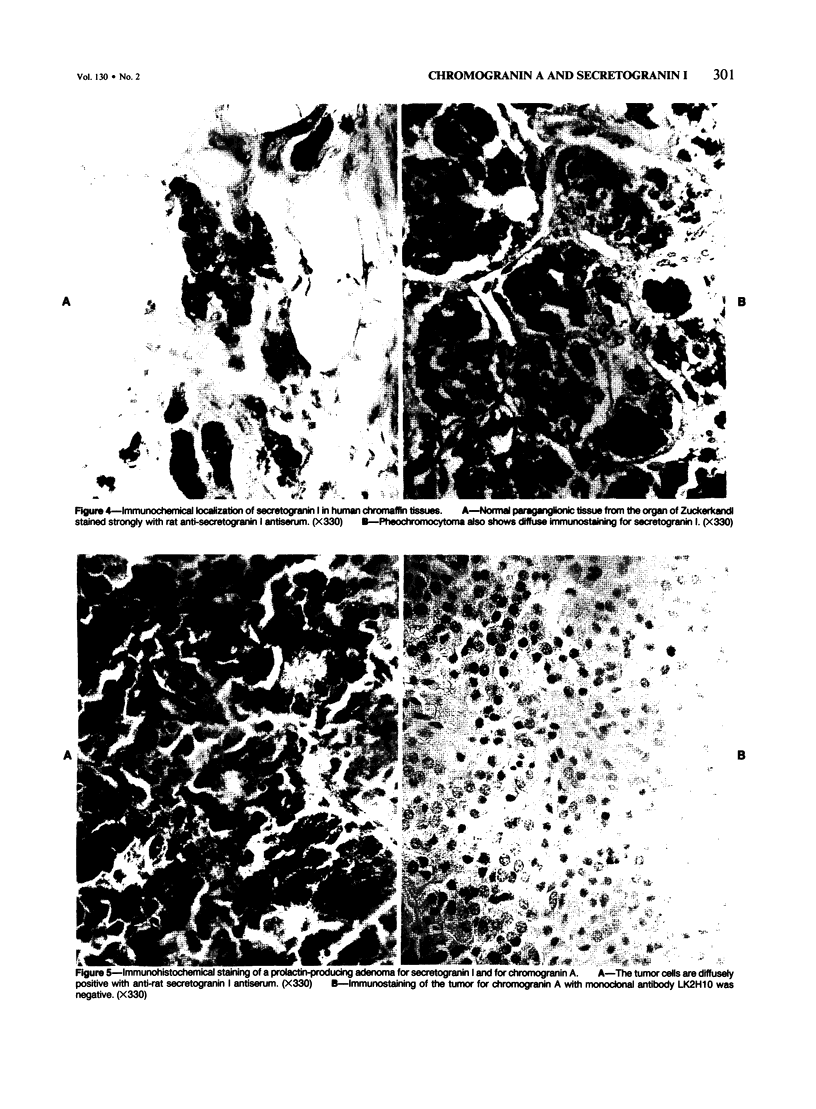
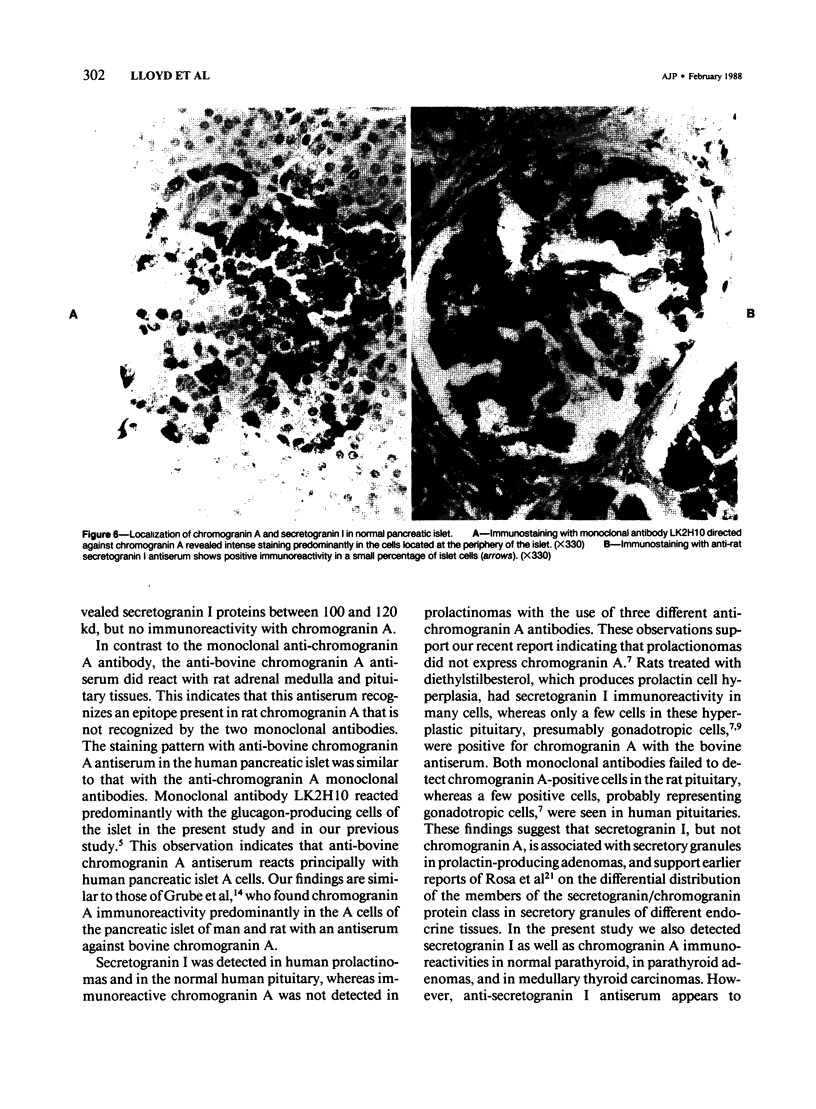
The distribution of chromogranin A and secretogranin I (chromogranin B) in normal and neoplastic human endocrine tissues was analyzed with two human monoclonal antibodies against chromogranin A, anti-bovine antiserum against chromogranin A, and an anti-rat antiserum against secretogranin I. Western blotting analyses showed both chromogranin A and secretogranin I in normal adrenals, pheochromocytomas, a pituitary adenoma, and in normal pituitary glands, but not in a bladder carcinoma. Rat adrenal medullary and anterior pituitary tissues reacted with the polyclonal chromogranin A and secretogranin I antisera, but not with the two monoclonal chromogranin A antibodies. All antibodies reacted with most of the neuroendocrine cells and tumors examined. Pituitary prolactinomas contained immunoreactive secretogranin I, but not chromogranin A. Analysis of the distribution of chromogranin A and secretogranin I in pancreatic islet cells showed that chromogranin A was found predominantly in the glucagon-producing A cells, whereas secretogranin I was present in less than 5% of islet cells. These results indicate that chromogranin A and secretogranin I are both useful in the characterization of some neuroendocrine cells and neoplasms.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Lamouroux A., Konecki D. S., Rosa P., Hille A., Baeuerle P. A., Frank R., Lottspeich F., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human secretogranin I (chromogranin B): comparison with chromogranin A reveals homologous terminal domains and a large intervening variable region. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1203–1211. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02355.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaschko H., Comline R. S., Schneider F. H., Silver M., Smith A. D. Secretion of a chromaffin granule protein, chromogranin, from the adrenal gland after splanchnic stimulation. Nature. 1967 Jul 1;215(5096):58–59. doi: 10.1038/215058a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Elting J. J., Frick M., Elde R. Selective localization of the parathyroid secretory protein-I/adrenal medulla chromogranin A protein family in a wide variety of endocrine cells of the rat. Endocrinology. 1984 Jun;114(6):1963–1974. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-6-1963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Zangerle R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Chu L. L., Elting J. J., Hamilton J. W., Winkler H. Similarity of secretory protein I from parathyroid gland to chromogranin A from adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6056–6059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Huttner W. B., Mallet J., O'Connor D. T., Winkler H., Zanini A. A nomenclature proposal for the chromogranin/secretogranin proteins. Neuroscience. 1987 Jun;21(3):1019–1021. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(87)90056-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E. Is chromogranin a prohormone? Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):301–301. doi: 10.1038/325301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkensammer G., Fischer-Colbrie R., Richter K., Winkler H. Cell-free and cellular synthesis of chromogranin A and B of bovine adrenal medulla. Neuroscience. 1985 Feb;14(2):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90323-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Frischenschlager I. Immunological characterization of secretory proteins of chromaffin granules: chromogranins A, chromogranins B, and enkephalin-containing peptides. J Neurochem. 1985 Jun;44(6):1854–1861. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb07179.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Hagn C., Kilpatrick L., Winkler H. Chromogranin C: a third component of the acidic proteins in chromaffin granules. J Neurochem. 1986 Jul;47(1):318–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02865.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Lassmann H., Hagn C., Winkler H. Immunological studies on the distribution of chromogranin A and B in endocrine and nervous tissues. Neuroscience. 1985 Nov;16(3):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90191-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Wiedenmann B., Lee I., Schwechheimer K., Dockhorn-Dworniczak B., Radosevich J. A., Moll R., Franke W. W. Synaptophysin expression in neuroendocrine neoplasms as determined by immunocytochemistry. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):243–257. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grube D., Aunis D., Bader F., Cetin Y., Jörns A., Yoshie S. Chromogranin A (CGA) in the gastro-entero-pancreatic (GEP) endocrine system. I. CGA in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Histochemistry. 1986;85(6):441–452. doi: 10.1007/BF00508425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagn C., Schmid K. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Chromogranin A, B, and C in human adrenal medulla and endocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):405–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Benedum U. M. Chromogranin A and pancreastatin. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):305–305. doi: 10.1038/325305b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iacangelo A., Affolter H. U., Eiden L. E., Herbert E., Grimes M. Bovine chromogranin A sequence and distribution of its messenger RNA in endocrine tissues. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):82–86. doi: 10.1038/323082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassmann H., Hagn C., Fischer-Colbrie R., Winkler H. Presence of chromogranin A, B and C in bovine endocrine and nervous tissues: a comparative immunohistochemical study. Histochem J. 1986 Jul;18(7):380–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01675219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee R. W., Huttner W. B. Tyrosine-O-sulfated proteins of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells and their sulfation by a tyrosylprotein sulfotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11326–11334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V. Estrogen-induced hyperplasia and neoplasia in the rat anterior pituitary gland. An immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1983 Nov;113(2):198–206. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Mervak T., Schmidt K., Warner T. F., Wilson B. S. Immunohistochemical detection of chromogranin and neuron-specific enolase in pancreatic endocrine neoplasms. Am J Surg Pathol. 1984 Aug;8(8):607–614. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198408000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Sisson J. C., Shapiro B., Verhofstad A. A. Immunohistochemical localization of epinephrine, norepinephrine, catecholamine-synthesizing enzymes, and chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells and tumors. Am J Pathol. 1986 Oct;125(1):45–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Kovacs K., Ryan N. Immunohistochemical localization of chromogranin in human hypophyses and pituitary adenomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1985 Jun;109(6):515–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S. Specific endocrine tissue marker defined by a monoclonal antibody. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):628–630. doi: 10.1126/science.6635661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan J. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Hogue-Angeletti R. Neurons and neuroendocrine cells contain chromogranin: detection of the molecule in normal bovine tissues by immunochemical and immunohistochemical methods. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Aug;33(8):791–798. doi: 10.1177/33.8.3894497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Bernstein K. N. Radioimmunoassay of chromogranin A in plasma as a measure of exocytotic sympathoadrenal activity in normal subjects and patients with pheochromocytoma. N Engl J Med. 1984 Sep 20;311(12):764–770. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198409203111204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Burton D., Deftos L. J. Immunoreactive human chromogranin A in diverse polypeptide hormone producing human tumors and normal endocrine tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1983 Nov;57(5):1084–1086. doi: 10.1210/jcem-57-5-1084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T. Chromogranin: widespread immunoreactivity in polypeptide hormone producing tissues and in serum. Regul Pept. 1983 Jul;6(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(83)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor D. T., Deftos L. J. Secretion of chromogranin A by peptide-producing endocrine neoplasms. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 1;314(18):1145–1151. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605013141803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The diffuse neuroendocrine system and the apud concept: related "endocrine" peptides in brain, intestine, pituitary, placenta, and anuran cutaneous glands. Med Biol. 1977 Jun;55(3):115–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiffen F. U., Gratzl M. Chromogranins, widespread in endocrine and nervous tissue, bind Ca2+. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):327–330. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80187-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindi G., Buffa R., Sessa F., Tortora O., Solcia E. Chromogranin A, B and C immunoreactivities of mammalian endocrine cells. Distribution, distinction from costored hormones/prohormones and relationship with the argyrophil component of secretory granules. Histochemistry. 1986;85(1):19–28. doi: 10.1007/BF00508649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Fumagalli G., Zanini A., Huttner W. B. The major tyrosine-sulfated protein of the bovine anterior pituitary is a secretory protein present in gonadotrophs, thyrotrophs, mammotrophs, and corticotrophs. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):928–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Zanini A. Characterization of adenohypophysial polypeptides by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. II. Sulfated and glycosylated polypeptides. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):181–193. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Zanini A. Purification of a sulfated secretory protein from the adenohypophysis. Immunochemical evidence that similar macromolecules are present in other glands. Eur J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;31(1):94–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., DePotter R. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M., Winkler H., Chubb I. W. Chromogranin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Immunochemical characterisation, distribution and relationship to catecholamine and enkephalin pathways. Brain Res. 1984 Dec;320(2-3):193–230. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varndell I. M., Lloyd R. V., Wilson B. S., Polak J. M. Ultrastructural localization of chromogranin: a potential marker for the electron microscopical recognition of endocrine cell secretory granules. Histochem J. 1985 Sep;17(9):981–992. doi: 10.1007/BF01417947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Lloyd R. V. Detection of chromogranin in neuroendocrine cells with a monoclonal antibody. Am J Pathol. 1984 Jun;115(3):458–468. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson B. S., Phan S. H., Lloyd R. V. Chromogranin from normal human adrenal glands: purification by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography and partial N-terminal amino acid sequence. Regul Pept. 1986 Feb;13(3-4):207–223. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90040-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zanini A., Rosa P. Characterization of adenohypophysial polypeptides by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. I. L-[3H]leucine-labeled polypeptides. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]