Abstract
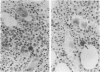
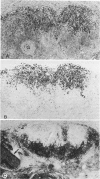
A group of 63 cases of anaplastic large cell lymphomas (variants of diffuse large cell lymphomas often diagnosed as "malignant histiocytosis") was characterized on both morphologic criteria and expression of epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) and Ki-1 antigen (CD30). On the basis of the reactivity of these tumors with anti-EMA and anti-Ki-1 antibodies, four subtypes could be distinguished. In the majority of cases (n = 49), neoplastic cells coexpressed EMA and Ki-1 antigens. Nineteen of these cases were tested for IL-2R, and all were positive (Type I, EMA+, Ki-1+, IL-2R+). In the second group (n = 5), the neoplastic cells expressed EMA but not the Ki-1 antigen. These cases were not tested for the presence of IL-2R (Type II, EMA+, Ki-1-, IL-2R?). There were tumors with similar morphology expressing only Ki-1 antigen (Type III, EMA-, Ki-1+, IL-2R-) or negative for both EMA and Ki-1 antigens (Type IV, EMA-, Ki-1-, IL-2R-). EMA appeared to occur predominantly on activated cells, as has been previously shown for Ki-1 antigen. Analysis using monoclonal antibodies to T-cell, B-cell, or macrophage-associated differentiation antigens showed that these tumors were heterogeneous in terms of cell lineage. Tumors coexpressing EMA, Ki-1, and IL-2R (Type I), were most commonly of T-cell origin (n = 12); the remainder in this type expressed B-cell markers (n = 4), a mixed B/T phenotype (n = 2), or no clear phenotype (n = 9). By contrast, tumors of Types II, III, and IV were mainly from B-cell origin (n = 6) or showed a mixed B/T phenotype (n = 1). Despite the fact that a significant proportion of these cases were initially classified morphologically as "malignant histiocytosis," only 3 of the 63 cases were possibly of histiocytic origin. These results confirm that true malignant histiocytosis is rare and that most tumors with histologic features currently regarded as being consistent with this diagnosis are lymphocytic in origin and express activation antigens such as EMA, Ki-1 antigen, and IL-2R.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Al Saati T., Caveriviere P., Gorguet B., Delsol G., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Epithelial membrane antigen in hematopoietic neoplasms. Hum Pathol. 1986 May;17(5):533–534. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al Saati T., Laurent G., Caveriviere P., Rigal F., Delsol G. Reactivity of Leu 1 and T101 monoclonal antibodies with B cell lymphomas (correlations with other immunological markers). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Dec;58(3):631–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreesen R., Osterholz J., Löhr G. W., Bross K. J. A Hodgkin cell-specific antigen is expressed on a subset of auto- and alloactivated T (helper) lymphoblasts. Blood. 1984 Jun;63(6):1299–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceriani R. L., Thompson K., Peterson J. A., Abraham S. Surface differentiation antigens of human mammary epithelial cells carried on the human milk fat globule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):582–586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell J., Richardson T. C., Pulford K. A., Ghosh A. K., Gatter K. C., Heyderman E., Mason D. Y. Production of monoclonal antibodies against human epithelial membrane antigen for use in diagnostic immunocytochemistry. Br J Cancer. 1985 Sep;52(3):347–354. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delsol G., Gatter K. C., Stein H., Erber W. N., Pulford K. A., Zinne K., Mason D. Y. Human lymphoid cells express epithelial membrane antigen. Implications for diagnosis of human neoplasms. Lancet. 1984 Nov 17;2(8412):1124–1129. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Britton K. E., Mather S., Shepherd J., Granowska M., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Nimmon C. C., Durbin H., Hawkins L. R., Malpas J. S. Targeting of iodine-123-labelled tumour-associated monoclonal antibodies to ovarian, breast, and gastrointestinal tumours. Lancet. 1982 Nov 6;2(8306):999–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90046-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. L., Marder R. J., Winter J. N., Fox R. I. Two new monoclonal antibodies (LN-1, LN-2) reactive in B5 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues with follicular center and mantle zone human B lymphocytes and derived tumors. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):1028–1036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. L., Faldetta T. J., Humphreys R. E., Pratt D. M., Yunis E. J., Schlossman S. F. Peripheral human T cells sensitized in mixed leukocyte culture synthesize and express Ia-like antigens. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1440–1445. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feller A. C., Parwaresch M. R. Simultaneous enzyme-immunocytochemical detection of antigens in monocellular specimens with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Oct 14;63(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90431-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Abdulaziz Z., Beverley P., Corvalan J. R., Ford C., Lane E. B., Mota M., Nash J. R., Pulford K., Stein H. Use of monoclonal antibodies for the histopathological diagnosis of human malignancy. J Clin Pathol. 1982 Nov;35(11):1253–1267. doi: 10.1136/jcp.35.11.1253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gatter K. C., Alcock C., Heryet A., Pulford K. A., Heyderman E., Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Stein H., Mason D. Y. The differential diagnosis of routinely processed anaplastic tumors using monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):33–43. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J., Schwab U., Lemke H., Stein H. Production of a mouse monoclonal antibody reactive with a human nuclear antigen associated with cell proliferation. Int J Cancer. 1983 Jan 15;31(1):13–20. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilkens J., Buijs F., Hilgers J., Hageman P., Calafat J., Sonnenberg A., van der Valk M. Monoclonal antibodies against human milk-fat globule membranes detecting differentiation antigens of the mammary gland and its tumors. Int J Cancer. 1984 Aug 15;34(2):197–206. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacson P. G., O'Connor N. T., Spencer J., Bevan D. H., Connolly C. E., Kirkham N., Pollock D. J., Wainscoat J. S., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Malignant histiocytosis of the intestine: a T-cell lymphoma. Lancet. 1985 Sep 28;2(8457):688–691. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92930-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E. Common activated helper-T-cell origin for lymphomatoid papulosis, mycosis fungoides, and some types of Hodgkin's disease. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):864–865. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadin M. E., Sako D., Berliner N., Franklin W., Woda B., Borowitz M., Ireland K., Schweid A., Herzog P., Lange B. Childhood Ki-1 lymphoma presenting with skin lesions and peripheral lymphadenopathy. Blood. 1986 Nov;68(5):1042–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G., Al Saati T., Olive D., Laurent J. C., Poncelet P., Delsol G. Expression of Tac antigen in B cell lymphomas. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Aug;65(2):354–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naiem M., Gerdes J., Abdulaziz Z., Stein H., Mason D. Y. Production of a monoclonal antibody reactive with human dendritic reticulum cells and its use in the immunohistological analysis of lymphoid tissue. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Feb;36(2):167–175. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallesen G., Plesner T. The third international workshop and conference on human leukocyte differentiation antigens with an up-to-date overview of the CD nomenclature. Leukemia. 1987 Mar;1(3):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Thomas P., Said J. W. Leu-M1--a marker for Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. An immunoperoxidase study of paraffin-embedded tissues. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):244–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding W. H., Coombes R. C., Monaghan P., Clink H. M., Imrie S. F., Dearnaley D. P., Ormerod M. G., Sloane J. P., Gazet J. C., Powles T. J. Detection of micrometastases in patients with primary breast cancer. Lancet. 1983 Dec 3;2(8362):1271–1274. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91150-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarting R., Stein H., Wang C. Y. The monoclonal antibodies alpha S-HCL 1 (alpha Leu-14) and alpha S-HCL 3 (alpha Leu-M5) allow the diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia. Blood. 1985 Apr;65(4):974–983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheibani K., Battifora H., Burke J. S., Rappaport H. Leu-M1 antigen in human neoplasms. An immunohistologic study of 400 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1986 Apr;10(4):227–236. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198604000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Gerdes J., Mason D. Y. The normal and malignant germinal centre. Clin Haematol. 1982 Oct;11(3):531–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Uchánska-Ziegler B., Gerdes J., Ziegler A., Wernet P. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens specific to late cells of granulopoiesis. Int J Cancer. 1982 Mar 15;29(3):283–290. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Uchánska-Ziegler B., Gerdes J., Ziegler A., Wernet P. Hodgkin and Sternberg-Reed cells contain antigens specific to late cells of granulopoiesis. Int J Cancer. 1982 Mar 15;29(3):283–290. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauchen J. A., Breakstone B. A. IL-2 receptor expression in human lymphoid lesions. Immunohistochemical study of 166 cases. Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):506–512. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Papadimitriou J., Peterson J. A., Arklie J., Burchell J., Ceriani R. L., Bodmer W. F. Monoclonal antibodies to epithelium-specific components of the human milk fat globule membrane: production and reaction with cells in culture. Int J Cancer. 1981 Jul 15;28(1):17–21. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910280104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnke R. A., Gatter K. C., Falini B., Hildreth P., Woolston R. E., Pulford K., Cordell J. L., Cohen B., De Wolf-Peeters C., Mason D. Y. Diagnosis of human lymphoma with monoclonal antileukocyte antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1983 Nov 24;309(21):1275–1281. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198311243092102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warnke R. A., Kim H., Dorfman R. F. Malignant histiocytosis (histiocytic medullary reticulosis). I. Clinicopatholigic study of 29 cases. Cancer. 1975 Jan;35(1):215–230. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197501)35:1<215::aid-cncr2820350127>3.0.co;2-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L. M., Trela M. J., Cleary M. L., Turner R. R., Warnke R. A., Sklar J. Frequent immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements in "histiocytic" neoplasms. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):369–373. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek R., Burke J. S., Knowles D. M., 2nd Leu-M1 antigen expression in T-cell neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):374–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]