Abstract
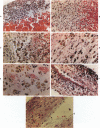
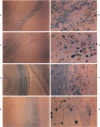
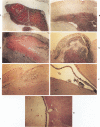
With the development and routine use of real-time ultrasound scanning, it has been possible to collect 20 autopsy cases of infants in whom the ultrasound scan was first normal and then showed evidence of subependymal/intraventricular hemorrhage (SEH/IVH). Analysis of these cases with known postnatal origin of the hemorrhage permitted the development for the first time of a time scale to characterize the temporal evolution of the histopathologic reactions to hemorrhage in the premature human brain. This time scale was then used to define the histologic stage of the lesions in 27 other cases of infants who had a scan demonstrating SEH/IVH prior to death but who had not a previously normal scan. Only 2 cases were found to lie off the original scale, indicating a prenatal onset of the hemorrhage in about 5% of the total cases. Thus, postnatal events immediately preceding the onset of the hemorrhage are more likely to be implicated in the pathogenesis of SEH/IVH than prenatal or obstetric events. Comparison with similar reactions in the adult indicate that the early reactions by macrophages occur at about the same rate but the routine transfer of iron from macrophages to astrocytes and the much slower rate of absorption to form a cyst in the adult combine to form a complicated pattern that requires a different set of criteria for the intermediate and late stages in the adult.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan W. C., Volpe J. J. Periventricular-intraventricular hemorrhage. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Feb;33(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34969-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ando Y., Takashima S., Takeshita K. Cerebral blood flow velocity in preterm neonates. Brain Dev. 1985;7(4):385–391. doi: 10.1016/s0387-7604(85)80135-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. S., Bove K. E., Han B. K. Intracranial hemorrhage in premature infants: sonographic-pathologic correlation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1982 May-Jun;3(3):309–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babcock D. S., Han B. K. The accuracy of high resolution, real-time ultrasonography of the head in infancy. Radiology. 1981 Jun;139(3):665–676. doi: 10.1148/radiology.139.3.7232734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bada H. S., Korones S. B., Anderson G. D., Magill H. L., Wong S. P. Obstetric factors and relative risk of neonatal germinal layer/intraventricular hemorrhage. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Mar 15;148(6):798–804. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(84)90571-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley D. W., Chance G. W., Coates C. F. Intraventricular haemorrhage--timing of occurrence and relationship to perinatal events. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1984 Oct;91(10):1007–1013. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1984.tb03679.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumhagen J. D., Mack L. A. Abnormalities of the neonatal cerebral ventricles. Radiol Clin North Am. 1985 Mar;23(1):13–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein J., Papile L. A., Burstein R. Intraventricular hemorrhage and hydrocephalus in premature newborns: a prospective study with CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Apr;132(4):631–635. doi: 10.2214/ajr.132.4.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervenak F. A., Johnson R. E., Berkowitz R. L., Grannum P., Hobbins J. C. Is routine cesarean section necessary for vertex-breech and vertex-transverse twin gestations? Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Jan 1;148(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(84)80022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfin T., Skidmore M. B., Fong K. W., Hoskins E. M., Milligan J. E., Moore D. C., Shennan A. T. Perinatal factors that influence the incidence of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage in low birthweight infants. Am J Perinatol. 1984 Jan;1(2):107–113. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-999985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis-Hansen B. Perinatal brain injury and cerebral blood flow in newborn infants. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1985 May;74(3):323–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1985.tb10978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haesslein H. C., Goodlin R. C. Delivery of the tiny newborn. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1979 May 15;134(2):192–200. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(79)90885-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambleton G., Wigglesworth J. S. Origin of intraventricular haemorrhage in the preterm infant. Arch Dis Child. 1976 Sep;51(9):651–659. doi: 10.1136/adc.51.9.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S., Spong J., Yu V. Y. Intraventricular hemorrhage. Incidence and outcome in a population of very-low-birth-weight infants. Am J Dis Child. 1984 Feb;138(2):136–139. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1984.02140400022005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horbar J. D., Pasnick M., McAuliffe T. L., Lucey J. F. Obstetric events and risk of periventricular hemorrhage in premature infants. Am J Dis Child. 1983 Jul;137(7):678–681. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1983.02140330062017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchen W., Ford G. W., Doyle L. W., Rickards A. L., Lissenden J. V., Pepperell R. J., Duke J. E. Cesarean section or vaginal delivery at 24 to 28 weeks' gestation: comparison of survival and neonatal and two-year morbidity. Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Aug;66(2):149–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech R. W., Kohnen P. Subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhages in the newborn. Am J Pathol. 1974 Dec;77(3):465–475. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko S. M., Mitchell A. A., Epstein M. F., Louik C., Giacoia G. P., Shapiro S. Heparin use as a risk factor for intraventricular hemorrhage in low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 1986 May 1;314(18):1156–1160. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198605013141805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveno K. J., Cunningham F. G., Roark M. L., Nelson S. D., Williams M. L. Prenatal care and the low birth weight infant. Obstet Gynecol. 1985 Nov;66(5):599–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leviton A., Gilles F., Strassfeld R. The influence of route of delivery and hyaline membranes on the risk of neonatal intracranial hemorrhages. Ann Neurol. 1977 Dec;2(6):451–454. doi: 10.1002/ana.410020602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack L. A., Rumack C. M., Johnson M. L. Ultrasound evaluation of cystic intracranial lesions in the neonate. Radiology. 1980 Nov;137(2):451–455. doi: 10.1148/radiology.137.2.6968920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mack L. A., Wright K., Hirsch J. H., Alvord E. C., Guthrie R. D., Shuman W. P., Rogers J. V., Bolender N. F. Intracranial hemorrhage in premature infants: accuracy in sonographic evaluation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Aug;137(2):245–250. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.2.245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main D. M., Main E. K., Maurer M. M. Cesarean section versus vaginal delivery for the breech fetus weighing less than 1,500 grams. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Jul 1;146(5):580–584. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(83)90807-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald M. M., Koops B. L., Johnson M. L., Guggenheim M. A., Rumack C. M., Mitchell S. A., Hathaway W. E. Timing and antecedents of intracranial hemorrhage in the newborn. Pediatrics. 1984 Jul;74(1):32–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Duncan C. C., Ehrenkranz R. A., Lange R. C., Taylor K. J., Kleinman C. S., Scott D. T., Sivo J., Gettner P. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the preterm neonate: timing and cerebral blood flow changes. J Pediatr. 1984 Mar;104(3):419–425. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)81109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ment L. R., Ehrenkranz R. A., Duncan C. C., Lange R. C. Delayed hemorrhagic infarction. A cause of late neonatal germinal matrix and intraventricular hemorrhage. Arch Neurol. 1984 Oct;41(10):1036–1039. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1984.04050210034010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morales W. J., Koerten J. Obstetric management and intraventricular hemorrhage in very-low-birth-weight infants. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jul;68(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton E. R., Haering W. A., Kennedy J. L., Jr, Herschel M., Cetrulo C. L., Feingold M. Effect of mode of delivery on morbidity and mortality of infants at early gestational age. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Apr;67(4):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papile L. A., Burstein J., Burstein R., Koffler H. Incidence and evolution of subependymal and intraventricular hemorrhage: a study of infants with birth weights less than 1,500 gm. J Pediatr. 1978 Apr;92(4):529–534. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(78)80282-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., Goodman S., Kreusser K. L., Volpe J. J. Reduction in intraventricular hemorrhage by elimination of fluctuating cerebral blood-flow velocity in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 23;312(21):1353–1357. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505233122104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M. Neonatal cerebral blood flow velocity measurement. Clin Perinatol. 1985 Feb;12(1):179–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlman J. M., Volpe J. J. Suctioning in the preterm infant: effects on cerebral blood flow velocity, intracranial pressure, and arterial blood pressure. Pediatrics. 1983 Sep;72(3):329–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayburn W. F., Donn S. M., Kolin M. G., Schork M. A. Obstetric care and intraventricular hemorrhage in the low birth weight infant. Obstet Gynecol. 1983 Oct;62(4):408–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushton D. I., Preston P. R., Durbin G. M. Structure and evolution of echo dense lesions in the neonatal brain. A combined ultrasound and necropsy study. Arch Dis Child. 1985 Sep;60(9):798–808. doi: 10.1136/adc.60.9.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott D. T., Ment L. R., Ehrenkranz R. A., Warshaw J. B. Evidence for late developmental deficit in very low birth weight infants surviving intraventricular hemorrhage. Childs Brain. 1984;11(4):261–269. doi: 10.1159/000120186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackelford G. D., Fulling K. H., Glasier C. M. Cysts of the subependymal germinal matrix: sonographic demonstration with pathologic correlation. Radiology. 1983 Oct;149(1):117–121. doi: 10.1148/radiology.149.1.6310678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw C. M., Alvord E. C., Jr Subependymal germinolysis. Arch Neurol. 1974 Dec;31(6):374–381. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1974.00490420040003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman W. P., Rogers J. V., Mack L. A., Alvord E. C., Jr, Christie D. P. Real-time sonographic sector scanning of the neonatal cranium: technique and normal anatomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981 Oct;137(4):821–828. doi: 10.2214/ajr.137.4.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szymonowicz W., Yu V. Y., Wilson F. E. Antecedents of periventricular haemorrhage in infants weighing 1250 g or less at birth. Arch Dis Child. 1984 Jan;59(1):13–17. doi: 10.1136/adc.59.1.13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarby T. J., Volpe J. J. Intraventricular hemorrhage in the premature infant. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1982 Oct;29(5):1077–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34248-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejani N., Rebold B., Tuck S., Ditroia D., Sutro W., Verma U. Obstetric factors in the causation of early periventricular--intraventricular hemorrhage. Obstet Gynecol. 1984 Oct;64(4):510–515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpe J. J. Neonatal intraventricular hemorrhage. N Engl J Med. 1981 Apr 9;304(15):886–891. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198104093041506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch R. A., Bottoms S. F. Reconsideration of head compression and intraventricular hemorrhage in the vertex very-low-birth-weight fetus. Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jul;68(1):29–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]