Abstract
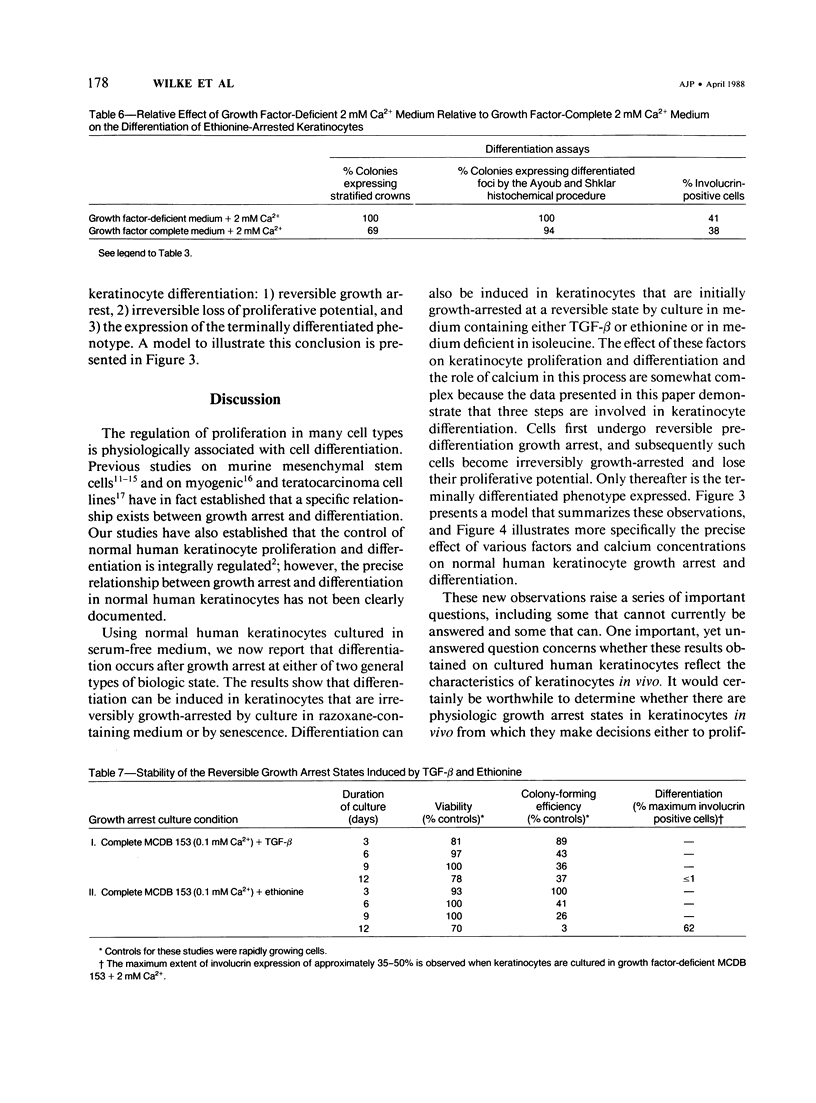
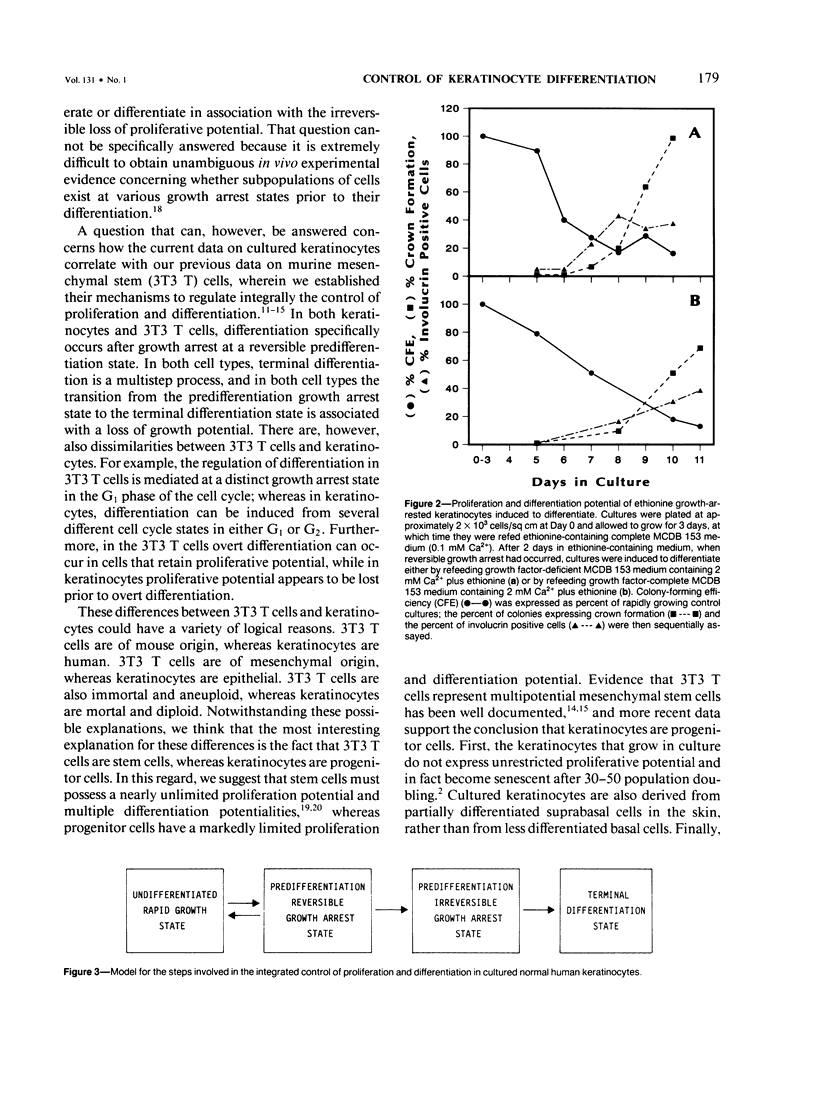
Normal human keratinocytes can be grown in serum-free medium, and the integrated control of their proliferation and differentiation can be modulated experimentally. The growth of cultured human keratinocytes can also be specifically arrested at either reversible or irreversible growth arrest states. Reversible growth arrest is induced by culture in medium containing TGF-beta or ethionine or in medium deficient of isoleucine. Irreversible growth arrest is induced by culture in razoxane-containing medium or by routine passage of keratinocytes until senescence results. The current studies were performed to determine from which growth arrest states keratinocyte differentiation occurs. Cells were therefore growth-arrested at each state, and they were then incubated in several different differentiation-promoting culture conditions. The results show that differentiation, as determined by morphologic, cytochemical, and immunofluorescent assays, can be induced from multiple reversible and irreversible growth arrest states by a series of complex biologic mechanisms. More specifically, at least three distinct stages appear to be involved in the process of keratinocyte differentiation. First, cells arrest their growth at a reversible predifferentiation state. Second, cells irreversibly lose their proliferative potential. Finally, cells express the terminally differentiated keratinocyte phenotype.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AYOUB P., SHKLAR G. A modification of the Mallory connective tissue stain as a stain for keratin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1963 May;16:580–581. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(63)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawisz B. R., Scott R. E. Coupling of proadipocyte growth arrest and differentiation. I. Induction by heparinized medium containing human plasma. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):394–399. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop B., Thomas K., Glaser L. Control of myogenic differentiation by fibroblast growth factor is mediated by position in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2194–2198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcelo C. L., Kim Y. G., Kaine J. L., Voorhees J. J. Stratification, specialization, and proliferation of primary keratinocyte cultures. Evidence of a functioning in vitro epidermal cell system. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):356–370. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierce G. B. The cancer cell and its control by the embryo. Rous-Whipple Award lecture. Am J Pathol. 1983 Oct;113(1):117–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittelkow M. R., Scott R. E. New techniques for the in vitro culture of human skin keratinocytes and perspectives on their use for grafting of patients with extensive burns. Mayo Clin Proc. 1986 Oct;61(10):771–777. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)64815-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittelkow M. R., Wille J. J., Jr, Scott R. E. Two functionally distinct classes of growth arrest states in human prokeratinocytes that regulate clonogenic potential. J Invest Dermatol. 1986 Apr;86(4):410–417. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12285684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S. Cell replacement in epidermis (keratopoiesis) via discrete units of proliferation. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;69:271–318. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62326-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potten C. S. The epidermal proliferative unit: the possible role of the central basal cell. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1974 Jan;7(1):77–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1974.tb00401.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Florine D. L., Wille J. J., Jr, Yun K. Coupling of growth arrest and differentiation at a distinct state in the G1 phase of the cell cycle: GD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):845–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Hoerl B. J., Wille J. J., Jr, Florine D. L., Krawisz B. R., Yun K. Coupling of proadipocyte growth arrest and differentiation. II. A cell cycle model for the physiological control of cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):400–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott R. E., Wille J. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R., Sparks R. L. Biological mechanisms of stem cell carcinogenesis: a concept for multiple phases in the initiation of carcinogenesis and the role of differentiation control defects. Carcinog Compr Surv. 1985;9:67–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg M. L., Defendi V. Altered pattern of growth and differentiation in human keratinocytes infected by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):801–805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsao M. C., Walthall B. J., Ham R. G. Clonal growth of normal human epidermal keratinocytes in a defined medium. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):219–229. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M. Involucrin and other markers of keratinocyte terminal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):100s–103s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille J. J., Jr, Pittelkow M. R., Shipley G. D., Scott R. E. Integrated control of growth and differentiation of normal human prokeratinocytes cultured in serum-free medium: clonal analyses, growth kinetics, and cell cycle studies. J Cell Physiol. 1984 Oct;121(1):31–44. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041210106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]