Abstract
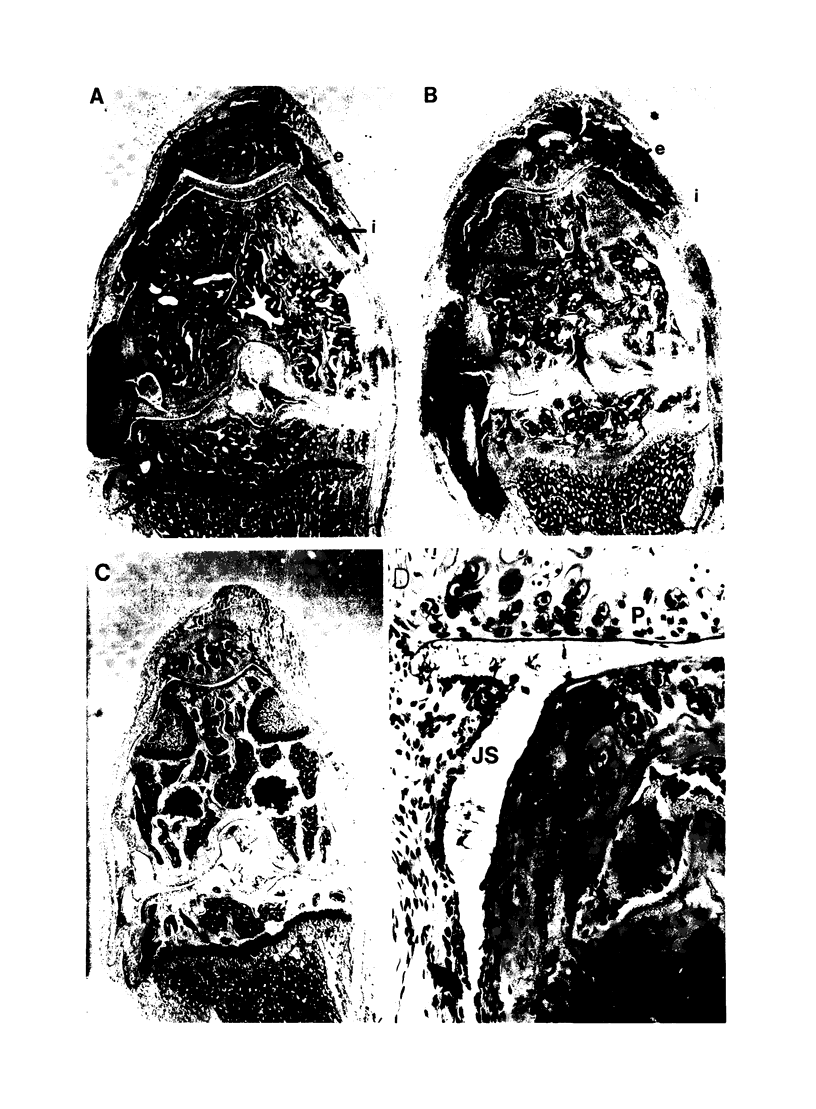
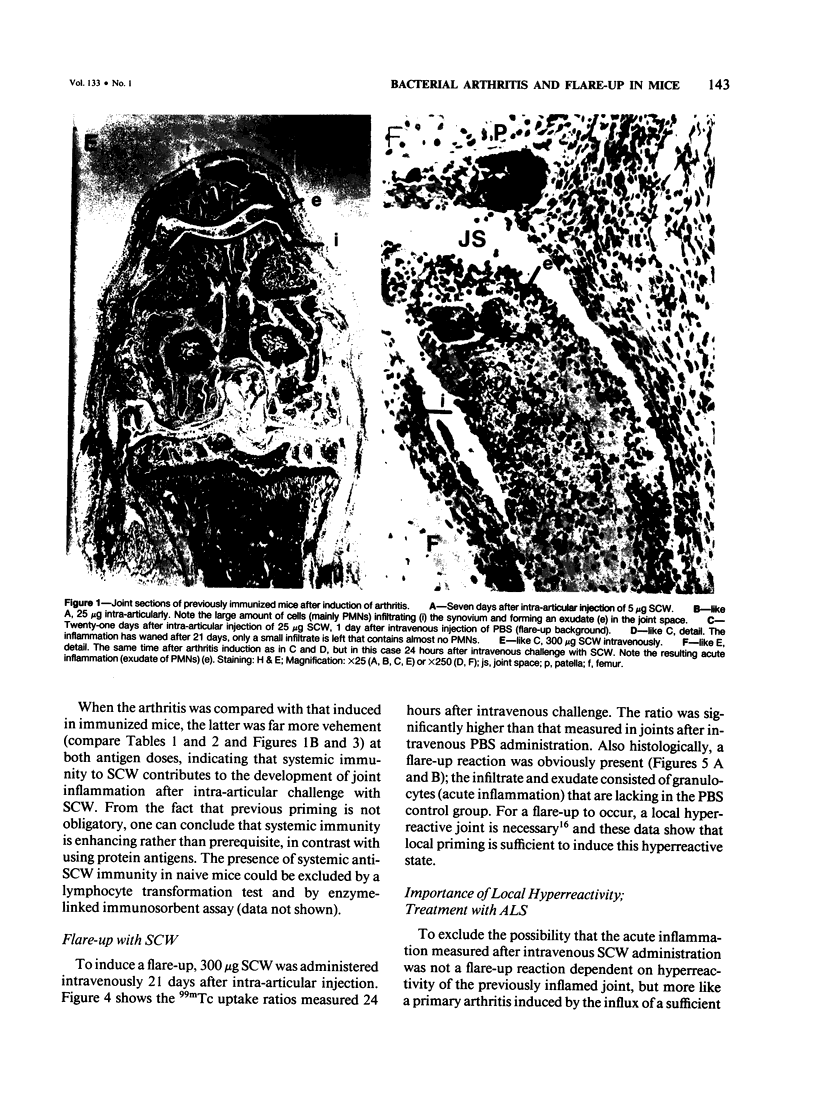
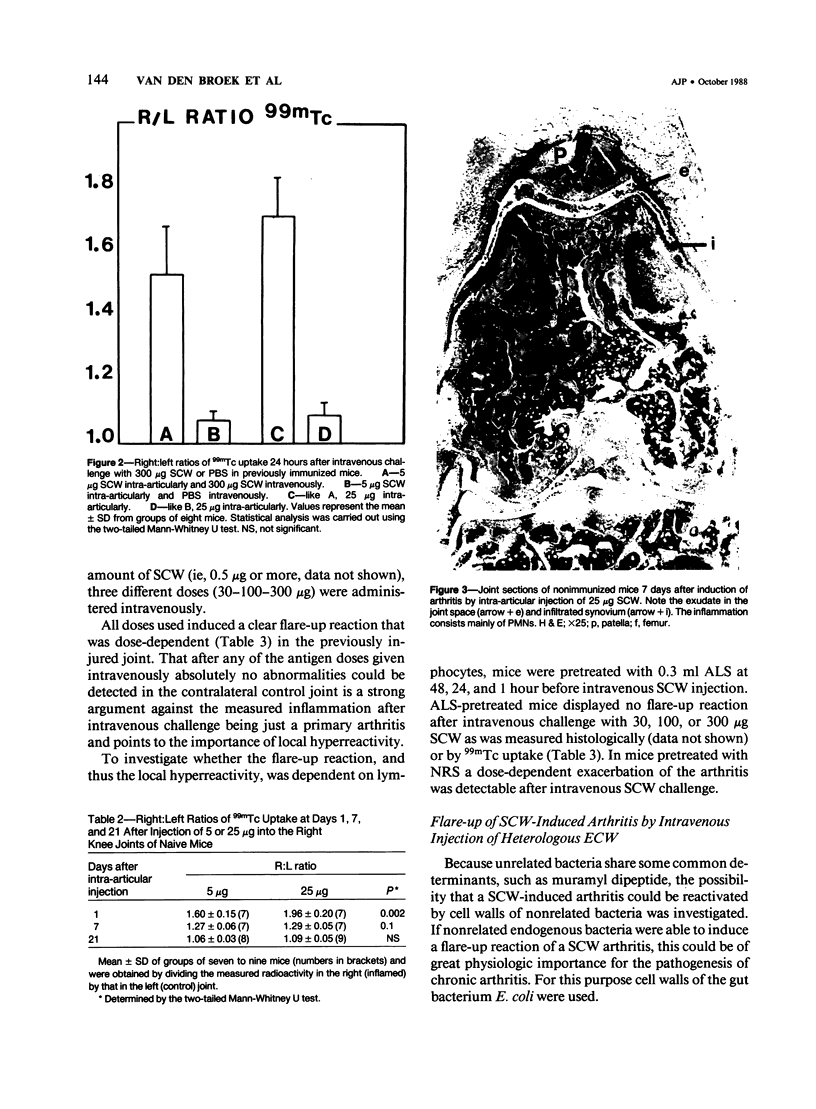
Intra-articular injection of cell walls from the gram-positive bacterium Streptococcus pyogenes induces an arthritis in both streptococcal cell wall (SCW)-primed and naive mice. This joint inflammation subsides after 2 weeks but it could be reactivated by systemic injection of SCW in a dose-dependent way. The primary arthritis as well as the flare-up reaction were more vehement in immunized than naive mice. Pretreatment with antilymphocyte serum of nonimmunized arthritic mice before systemic challenge completely inhibits the flare-up reaction, suggesting the involvement of lymphocytes in the reactivation. Dose-response studies showed that intravenous challenge with SCW amounts too small to induce a primary arthritis were able to reactivate a chronic arthritis, implying that an inflamed joint is in a hyperreactive state, probably due to locally retained lymphocytes. Arthritis as a result of injection with SCW can be reactivated by fragments of a nonrelated, gram negative endogenous bacterium, Escherichia coli. The latter finding might be of importance for the understanding of the pathogenesis of chronic arthritis: once an arthritis is induced by one bacterium, other (unrelated) bacteria, probably derived from an endogenous source, may be able to reactivate the inflammatory process, thus contributing to chronicity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen J. B., Calandra G. B., Wilder R. L. Cutaneous inflammatory reactions to group A streptococcal cell wall fragments in Fisher and Lewis inbred rats. Infect Immun. 1983 Nov;42(2):796–801. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.2.796-801.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. C. The infectious etiology of rheumatoid arthritis. New considerations. Arthritis Rheum. 1978 Jun;21(5):531–538. doi: 10.1002/art.1780210507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brackertz D., Mitchell G. F., Mackay I. R. Antigen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Induction of arthritis in various strains of mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Apr;20(3):841–850. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke T. D., Hurd E. R., Ziff M., Jasin H. E. The pathogenesis of chronic inflammation in experimental antigen-induced arthritis. II. Preferential localization of antigen-antibody complexes to collagenous tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):323–338. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cromartie W. J., Craddock J. G., Schwab J. H., Anderle S. K., Yang C. H. Arthritis in rats after systemic injection of streptococcal cells or cell walls. J Exp Med. 1977 Dec 1;146(6):1585–1602. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUMONDE D. C., GLYNN L. E. The production of arthritis in rabbits by an immunological reaction to fibrin. Br J Exp Pathol. 1962 Aug;43:373–383. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esser R. E., Stimpson S. A., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Reactivation of streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis by homologous and heterologous cell wall polymers. Arthritis Rheum. 1985 Dec;28(12):1402–1411. doi: 10.1002/art.1780281213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A., Brown R. R., Anderle S. K., Chetty C., Cromartie W. J., Gooder H., Schwab J. H. Arthropathic properties related to the molecular weight of peptidoglycan-polysaccharide polymers of streptococcal cell walls. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):1003–1010. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.1003-1010.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gery I., Gershon R. K., Waksman B. H. Potentiation of the T-lymphocyte response to mitogens. I. The responding cell. J Exp Med. 1972 Jul 1;136(1):128–142. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadler N. M. A pathogenetic model for erosive synovitis: lessons from animal arthritides. Arthritis Rheum. 1976 Mar-Apr;19(2):256–266. doi: 10.1002/art.1780190222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadzija O. A simple method for the quantitative determination of muramic acid. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):512–517. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90261-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janusz M. J., Chetty C., Eisenberg R. A., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Treatment of experimental erosive arthritis in rats by injection of the muralytic enzyme mutanolysin. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1360–1374. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koga T., Kakimoto K., Hirofuji T., Kotani S., Ohkuni H., Watanabe K., Okada N., Okada H., Sumiyoshi A., Saisho K. Acute joint inflammation in mice after systemic injection of the cell wall, its peptidoglycan, and chemically defined peptidoglycan subunits from various bacteria. Infect Immun. 1985 Oct;50(1):27–34. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.1.27-34.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Berden J. H., Lems S. P. Flare-up of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after challenge with intravenous antigen: effects of pre-treatment with cobra venom factor and anti-lymphocyte serum. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Sep;57(3):520–528. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Flare-up of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after challenge with intravenous antigen: studies on the characteristics of and mechanisms involved in the reaction. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):287–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Quantitation of arthritis by 99mTc-uptake measurements in the mouse knee-joint: correlation with histological joint inflammation scores. Agents Actions. 1984 Jun;14(5-6):723–728. doi: 10.1007/BF01978915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A. Flare of antigen-induced arthritis in mice after intravenous challenge. Kinetics of antigen in the circulation and localization of antigen in the arthritic and noninflamed joint. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 May;29(5):665–674. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushima K., Procopio A., Abe H., Scala G., Ortaldo J. R., Oppenheim J. J. Production of interleukin 1 activity by normal human peripheral blood B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1132–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettipher E. R., Higgs G. A., Henderson B. Interleukin 1 induces leukocyte infiltration and cartilage proteoglycan degradation in the synovial joint. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8749–8753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridge S. C., Zabriske J. B., Oronsky A. L., Kerwar S. S. Streptococcal cell wall arthritis: studies with nude (athymic) inbred Lewis rats. Cell Immunol. 1985 Nov;96(1):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimpson S. A., Esser R. E., Carter P. B., Sartor R. B., Cromartie W. J., Schwab J. H. Lipopolysaccharide induces recurrence of arthritis in rat joints previously injured by peptidoglycan-polysaccharide. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1688–1702. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Hansen C. Thymus-dependent and -independent regulation of Ia antigen expression in situ by cells in the synovium of rats with streptococcal cell wall-induced arthritis. Differences in site and intensity of expression in euthymic, athymic, and cyclosporin A-treated LEW and F344 rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 Apr;79(4):1160–1171. doi: 10.1172/JCI112933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Allen J. B., Wahl L. M., Calandra G. B., Wahl S. M. The pathogenesis of group A streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Comparative studies in arthritis resistant and susceptible inbred rat strains. Arthritis Rheum. 1983 Dec;26(12):1442–1451. doi: 10.1002/art.1780261205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder R. L., Calandra G. B., Garvin A. J., Wright K. D., Hansen C. T. Strain and sex variation in the susceptibility to streptococcal cell wall-induced polyarthritis in the rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Sep;25(9):1064–1072. doi: 10.1002/art.1780250906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lent P. L., van den Berg W. B., Schalkwijk J., van de Putte L. B., van den Bersselaar L. Allergic arthritis induced by cationic antigens: relationship of chronicity with antigen retention and T-cell reactivity. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):265–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte L. B., Lens J. W., van den Berg W. B., Kruijsen M. W. Exacerbation of antigen-induced arthritis after challenge with intravenous antigen. Immunology. 1983 May;49(1):161–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van Beusekom H. J., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., van der Sluis M. Antigen handling in antigen-induced arthritis in mice: an autoradiographic and immunofluorescence study using whole joint sections. Am J Pathol. 1982 Jul;108(1):9–16. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Electrical charge of the antigen determines its localization in the mouse knee joint. Deep penetration of cationic BSA in hyaline articular cartilage. Am J Pathol. 1985 Nov;121(2):224–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B., Zwarts W. A., Joosten L. A. Electrical charge of the antigen determines intraarticular antigen handling and chronicity of arthritis in mice. J Clin Invest. 1984 Nov;74(5):1850–1859. doi: 10.1172/JCI111604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., van den Berg W. B., Arntz O. J., van de Putte L. B. Reaction of bacterium-primed murine T cells to cartilage components: a clue for the pathogenesis of arthritis? Clin Exp Immunol. 1988 Apr;72(1):9–14. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. Monoclonal anti-Ia antibodies suppress the flare up reaction of antigen induced arthritis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Nov;66(2):320–330. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Broek M. F., van den Berg W. B., van de Putte L. B. The role of MHC class II antigens in the flare up reaction of antigen-induced arthritis in mice. Agents Actions. 1986 Dec;19(5-6):328–330. doi: 10.1007/BF01971241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






