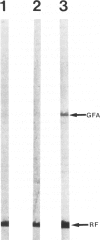
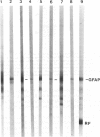
Abstract
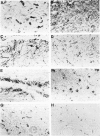
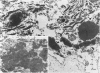
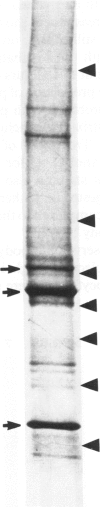
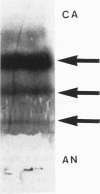
Rosenthal fibers (RFs) are inclusions within astrocytes, characteristic of Alexander's disease, but also seen in astrocytic tumors and occasionally in glial scar tissue. They are granular deposits, intimately associated with intermediate filaments. Their composition has been unknown. The authors have isolated a protein of about 19 kd from partially purified RFs from Alexander's disease central nervous system tissue. Antibodies were raised to this protein and shown to react with it on nitrocellulose blots and to bind to RFs in tissue sections. Small amounts of this protein were detected in normal brain and in cultured rat astrocytes. Charge heterogeneity was inferred because several species were separated by isoelectric focusing.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALEXANDER W. S. Progressive fibrinoid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in a hydrocephalic infant. Brain. 1949 Sep;72(3):373-81, 3 pl. doi: 10.1093/brain/72.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averback P. Spheroidal filamentous inclusion body cells in von Recklinghausen's disease. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1978 Apr 17;377(4):363–368. doi: 10.1007/BF00507136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrett D., Becker L. E. Alexander's disease. A disease of astrocytes. Brain. 1985 Jun;108(Pt 2):367–385. doi: 10.1093/brain/108.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L. Megalencephaly associated with hyaline pan-neuropathy. Brain. 1953 Jun;76(2):215–228. doi: 10.1093/brain/76.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu F. C., Goldman J. E. Synthesis and turnover of cytoskeletal proteins in cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):166–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09713.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEDE R. L. ALEXANDER'S DISEASE. Arch Neurol. 1964 Oct;11:414–422. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460220076010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebel H. H., Bode G., Caesar R., Kohlschütter A. Bulbar palsy with Rosenthal fiber formation in the medulla of a 15-year-old girl. Localized form of Alexander's disease? Neuropediatrics. 1981 Nov;12(4):382–391. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1059669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Chiu F. C. Growth kinetics, cell shape, and the cytoskeleton of primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):175–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Horoupian D. S., Johnson A. B. Granulofilamentous inclusions in a meningioma. Cancer. 1980 Jul 1;46(1):156–161. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800701)46:1<156::aid-cncr2820460126>3.0.co;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman J. E., Schaumburg H. H., Norton W. T. Isolation and characterization of glial filaments from human brain. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):426–440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullotta F., Fliedner E. Spongioblastomas, astrocytomas and Rosenthal fibers. Ultrastructural, tissue culture and enzyme histochemical investigations. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;22(1):68–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00687551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpern R., Schiffenbauer J., Solomon G., Diamond B. Detection of masked anti-DNA antibodies in lupus sera by a monoclonal anti-idiotype. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon R. M., Rubinstein L. J., Freeman J. M., Mathieson G. Light and electron microscopic observations on Rosenthal fibers in Alexander's disease and in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Oct;29(4):524–551. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197010000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzer R. C., Friede R. L. Do Rosenthal fibers contain glial fibrillary acid protein? Acta Neuropathol. 1981;55(1):75–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00691535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress Y., Gaskin F., Horoupian D. S., Brosnan C. Nickel induction of Rosenthal fibers in rat brain. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 6;210(1-2):419–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90920-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ksiezak-Reding H., Yen S. H. Two monoclonal antibodies recognize Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles, neurofilament, and microtubule-associated proteins. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):455–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastri A. R., Sung J. H. Diffuse Rosenthal fiber formation in the adult: a report of four cases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1973 Jul;32(3):424–436. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197307000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Kondo J., Ihara Y. Ubiquitin is a component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1641–1644. doi: 10.1126/science.3029875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N. Multiple Sklerose mit Rosenthalschen Fasern. Acta Neuropathol. 1965 Oct 4;5(1):61–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00689163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Friedman R., Shaw G., Chau V. Ubiquitin is detected in neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaque neurites of Alzheimer disease brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):3033–3036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.3033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rizzuto N., Ferrari G., Piscioli A. Diffuse Rosenthal fiber formation in adults. A case report. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;50(3):237–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00688761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochet S. S., Jr, Lampert P. W., Earle K. M. Alexander's disease. A case report with electron microscopic observations. Neurology. 1968 Jun;18(6):543–549. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.6.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J., Schochet S. S., Jr, Earle K. M. Alexander's disease in an adult. Report of a case. Arch Neurol. 1968 Nov;19(5):494–502. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00480050064006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soffer D., Horoupian D. S. Rosenthal fibers formation in the central nervous system. Its relation to Alexander's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Jun 15;47(1):81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00698278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tihen W. S. Central pontine myelinolysis and Rosenthal fibers of the brainstem. Association with emaciation and prolonged intravenous hyperalimentation. Neurology. 1972 Jul;22(7):710–716. doi: 10.1212/wnl.22.7.710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towfighi J., Young R., Sassani J., Ramer J., Horoupian D. S. Alexander's disease: further light-, and electron-microscopic observations. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;61(1):36–42. doi: 10.1007/BF00688384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walls T. J., Jones R. A., Cartlidge N., Saunders M. Alexander's disease with Rosenthal fibre formation in an adult. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984 Apr;47(4):399–403. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.47.4.399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]