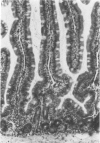
Abstract
Oxygen-derived free radicals, particularly superoxide anion, are considered important mediators of intestinal injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion based on the protective effects of superoxide dismutase and allopurinol. A role for free radicals was investigated in a model of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) which was initiated by a luminal, as opposed to a vascular, insult. Intestinal loops of weanling rabbits received either saline (control loops) or a solution of 10 mg/ml casein and 50 mg/ml calcium gluconate acidified to pH 4 with proprionic acid (treated loops). When the animals were sacrificed 3 hours later, severe damage was noted in the treated loops, which included blunting of villi and edema, with all animals surviving. At 16 hours only 5 of 8 rabbits survived, and 3 had hemorrhagic necrosis. Control loops were normal in each case. Intravenous infusion of superoxide dismutase (4 mg/kg/hr), commencing 15 minutes after NEC induction, totally prevented intestinal injury. On the other hand, pretreatment with allopurinol, an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, for 2 days (30 and 60 mg/kg by mouth) was not protective against intestinal damage. A cellular infiltration in treated loops was not histologically evident in the majority of animals at 3 hours after treatment, a finding confirmed by the minimal accumulation of 111In-labeled leukocytes in damaged and intact intestinal tissue. These results suggest that superoxide generated locally from sources other than xanthine oxidase play a critical and early role in experimental NEC and that superoxide dismutase may prove to be an effective therapy in this devastating neonatal disease.
Full text
PDF



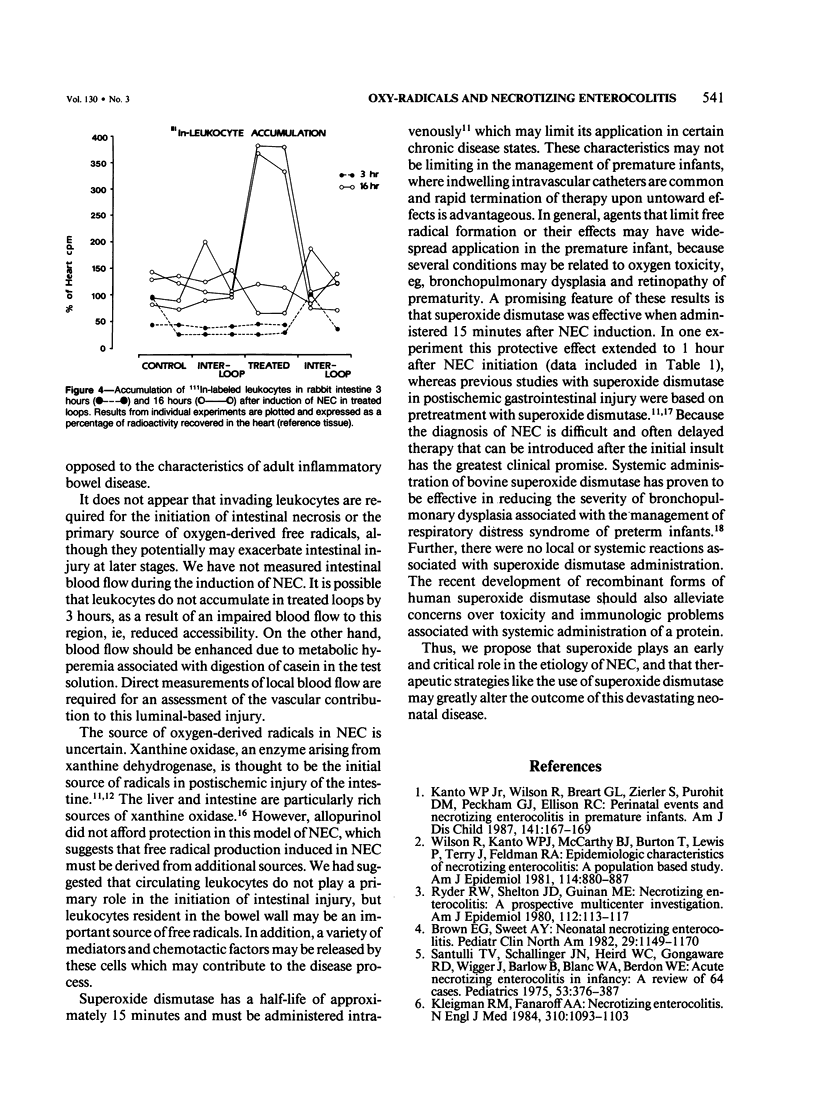

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkison D., Höllwarth M. E., Benoit J. N., Parks D. A., McCord J. M., Granger D. N. Role of free radicals in ischemia-reperfusion injury to the liver. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. G., Sweet A. Y. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1982 Oct;29(5):1149–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)34252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. A., Thompson J. E., Weiner L. B., McMillan J. A., Schneider A. J., Rokahr J. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis: intraluminal biochemistry in human neonates and a rabbit model. Pediatr Res. 1985 Sep;19(9):919–921. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198509000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz I. D., 3rd, L'heureux P., Engel R. R., Hunt C. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis. J Pediatr. 1975 Feb;86(2):259–263. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80485-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger D. N., Rutili G., McCord J. M. Superoxide radicals in feline intestinal ischemia. Gastroenterology. 1981 Jul;81(1):22–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham M. B., Hernandez L. A., Granger D. N. Xanthine oxidase and neutrophil infiltration in intestinal ischemia. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):G567–G574. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1986.251.4.G567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanto W. P., Jr, Wilson R., Breart G. L., Zierler S., Purohit D. M., Peckham G. J., Ellison R. C. Perinatal events and necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. Am J Dis Child. 1987 Feb;141(2):167–169. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1987.04460020057026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai G. J., Burrows W. The titration of cholera toxin and antitoxin in the rabbit ileal loop. J Infect Dis. 1966 Dec;116(5):606–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.5.606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliegman R. M., Fanaroff A. A. Necrotizing enterocolitis. N Engl J Med. 1984 Apr 26;310(17):1093–1103. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198404263101707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. A., Granger D. N. Xanthine oxidase: biochemistry, distribution and physiology. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:87–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld W., Evans H., Concepcion L., Jhaveri R., Schaeffer H., Friedman A. Prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by administration of bovine superoxide dismutase in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1984 Nov;105(5):781–785. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. W., Shelton J. D., Guinan M. E. Necrotizing enterocolitis: a prospective multicenter investigation. Am J Epidemiol. 1980 Jul;112(1):113–123. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sántulli T. V., Schullinger J. N., Heird W. C., Gongaware R. D., Wigger J., Barlow B., Blanc W. A., Berdon W. E. Acute necrotizing enterocolitis in infancy: a review of 64 cases. Pediatrics. 1975 Mar;55(3):376–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virnig N. L., Reynolds J. W. Epidemiological aspects of neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Am J Dis Child. 1974 Aug;128(2):186–190. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1974.02110270060012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J. Oxygen, ischemia and inflammation. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1986;548:9–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Kanto W. P., Jr, McCarthy B. J., Burton T., Lewin P., Terry J., Feldman R. A. Epidemiologic characteristics of necrotizing enterocolitis: a population-based study. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Dec;114(6):880–887. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]