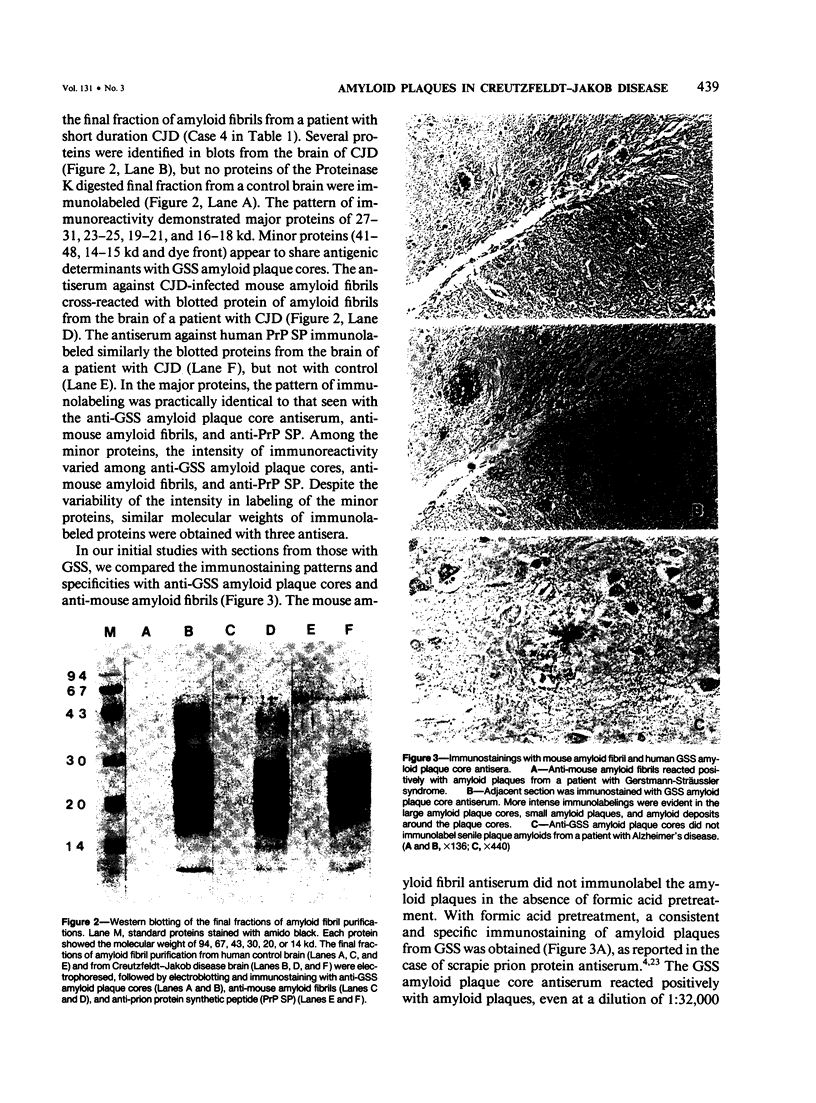
Abstract
Amyloid plaques have been found in the brains of some patients with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and all patients with Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome (GSS). We examined paraffin sections from 45 patients with CJD or GSS and from 51 patients with other neurologic diseases, using an antiserum against GSS amyloid plaque cores. The GSS amyloid plaque core antiserum revealed not only birefringent amyloid plaques but also small plaques that cannot be detected by the staining with Congo red dye. Positive immunolabeling was demonstrated in 59% of 34 Japanese patients with CJD, in 100% of 11 patients with GSS, and in none with other neurologic diseases. All cases of CJD of short duration (less than 11 months) were evaluated as being negative, and 95% of 21 long survivors (over 12 months) were positive. This immunohistochemical approach revealed that amyloid plaque is a hallmark of CJD with a long clinical course.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Bockman J. M., McKinley M. P., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins share physical properties and antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Prusiner S. B., Tateishi J., Kingsbury D. T. Immunoblotting of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins: host species-specific epitopes. Ann Neurol. 1987 Jun;21(6):589–595. doi: 10.1002/ana.410210611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Cathala F., Castaigne P., Gajdusek D. C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: clinical analysis of a consecutive series of 230 neuropathologically verified cases. Ann Neurol. 1986 Nov;20(5):597–602. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Coker-Vann M., Pomeroy K., Franko M., Asher D. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by Western blot identification of marker protein in human brain tissue. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 27;314(9):547–551. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602273140904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN A. S., CALKINS E. THE ISOLATION OF AMYLOID FIBRILS AND A STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF COLLAGENASE AND HYALURONIDASE. J Cell Biol. 1964 Jun;21:481–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.21.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopra I. J. A radioimmunoassay for measurement of 3,3',5'-triiodothyronine (reverse T3). J Clin Invest. 1974 Sep;54(3):583–592. doi: 10.1172/JCI107795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou S. M., Martin J. D. Kuru-plaques in a case of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;17(2):150–155. doi: 10.1007/BF00687490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., Mobley W. C., DeMott D. L., Barry R. A., Beckstead J. H., Prusiner S. B. Changes in the localization of brain prion proteins during scrapie infection. Neurology. 1987 Aug;37(8):1271–1280. doi: 10.1212/wnl.37.8.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field E. J., Mathews J. D., Raine C. S. Electron microscopic observations on the cerebellar cortex in kuru. J Neurol Sci. 1969 Mar-Apr;8(2):209–224. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(69)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilmert H., Diringer H. A rapid and efficient method to enrich SAF-protein from scrapie brains of hamsters. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Hikita K., Tashima T., Tateishi J., Sato Y. Scrapie-associated fibrils (SAF) purification method yields amyloid proteins from systemic and cerebral amyloidosis. Biosci Rep. 1986 May;6(5):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF01116137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Ogomori K., Tateishi J., Prusiner S. B. Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest. 1987 Aug;57(2):230–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Hikita K., Nagara H., Takeshita I. A new method to classify amyloid fibril proteins. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;67(3-4):272–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00687812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Tashima T., Takeshita I., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Amyloid plaques in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease stain with prion protein antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):204–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretzschmar H. A., Stowring L. E., Westaway D., Stubblebine W. H., Prusiner S. B., Dearmond S. J. Molecular cloning of a human prion protein cDNA. DNA. 1986 Aug;5(4):315–324. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
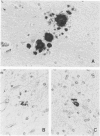
- Masters C. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome with an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus-induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain. 1981 Sep;104(3):559–588. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Richardson E. P., Jr Subacute spongiform encephalopathy (Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease). The nature and progression of spongiform change. Brain. 1978 Jun;101(2):333–344. doi: 10.1093/brain/101.2.333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani T., Morimatsu Y., Shiraki H. [Clinical pictures of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease based on 97 autopsy cases in Japan--with special reference to clinicopathological correlation of cerebellar symptoms]. Rinsho Shinkeigaku. 1984 Jan;24(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashima T., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Sato Y. Congophilia in cerebral amyloidosis is modified by inactivation procedures on slow transmissible pathogens. Brain Res. 1986 Dec 3;399(1):80–86. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90602-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Doi H., Sato Y., Suetsugu M., Ishii K., Kuroiwa Y. Experimental transmission of human subacute spongiform encephalopathy to small rodents. III. Further transmission from three patients and distribution patterns of lesions in mice. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53(2):161–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00689997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Koga M., Mori R. Experimental transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1981 Nov;31(6):943–951. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1981.tb02008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Nagara H., Hikita K., Sato Y. Amyloid plaques in the brains of mice with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 1984 Mar;15(3):278–280. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Ohta M., Koga M., Sato Y., Kuroiwa Y. Transmission of chronic spongiform encephalopathy with kuru plaques from humans to small rodents. Ann Neurol. 1979 Jun;5(6):581–584. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Sato Y., Koga M., Doi H., Ohta M. Experimental transmission of human subacute spongiform encephalopathy to small rodents. I. Clinical and histological observations. Acta Neuropathol. 1980;51(2):127–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00690454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Sato Y., Nagara H., Boellaard J. W. Experimental transmission of human subacute spongiform encephalopathy to small rodents. IV. Positive transmission from a typical case of Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;64(1):85–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00695613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Kuroiwa Y. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in Japan. Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1503–1506. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]