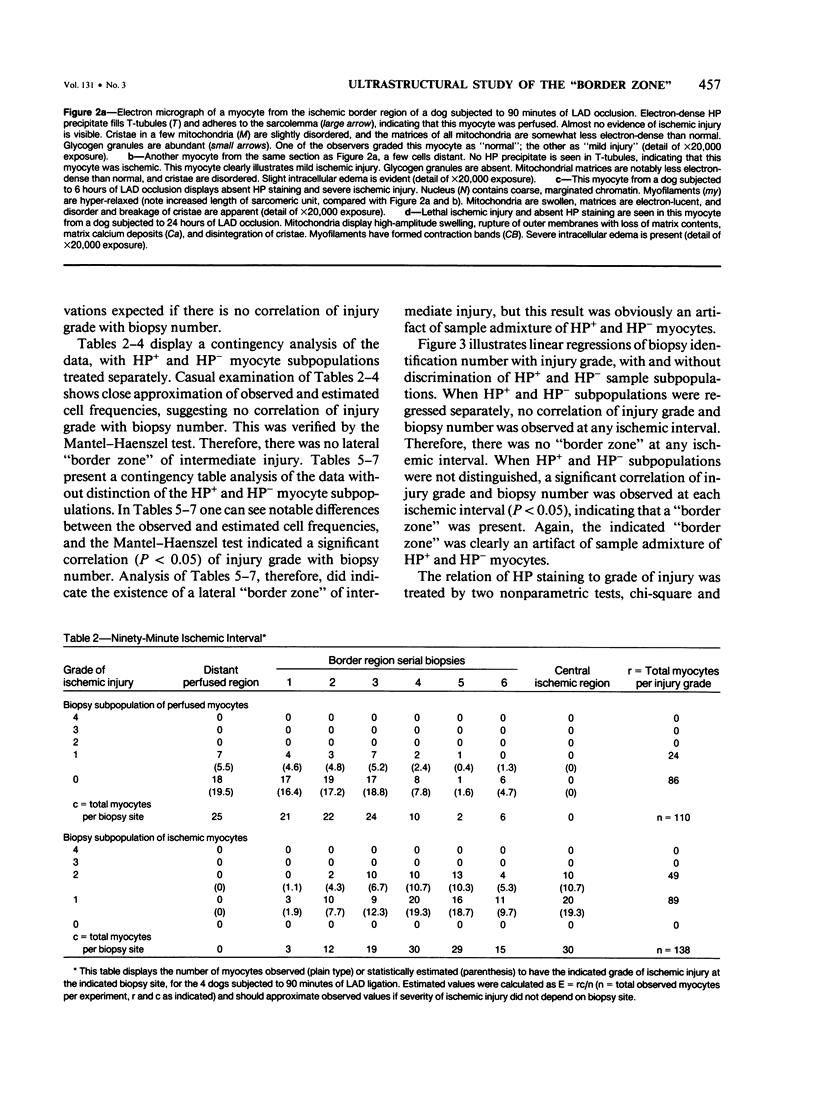
Abstract
There is controversy over the existence of a lateral "border zone" of intermediately injured tissue in the developing myocardial infarct (MI). The authors attempted an ultrastructural demonstration of this zone in serial subepicardial biopsies from developing MIs in dogs subjected to 90 minutes, 6 hours, or 24 hours of left anterior descending coronary artery ligation (4 dogs per group). After ligation, 400,000 units of horseradish peroxidase was infused through the left atrial appendage as a blood flow marker, to allow distinction of perfused and ischemic myocytes under electron microscopy. Evans blue stain was infused in the same way for gross guidance in harvesting biopsies across the lateral margins of the ischemic region. Interdigitation of perfused and ischemic tissue was observed over a lateral margin 6 mm wide, which caused admixture of perfused and ischemic myocytes in biopsies from this region. Ultrastructural ischemic injury was graded on a five-level qualitative scale (normal, mild, moderate, severe, lethal). Perfused myocytes from control and border sites were equivalently well preserved (79% normal, 21% mild injury, n = 353). Ischemic myocyte injury increased with duration of ischemia. At 90 minutes, 65% of ischemic myocytes had mild injury, 35% moderate (n = 138); at 6 hours, 17% of ischemic myocytes had moderate injury, 81% severe, 2% lethal (n = 115); at 24 hr, 100% of ischemic myocytes had lethal injury (n = 148). Severity of ischemic myocyte injury did not vary from the lateral border to the center of the ischemic region: there was no lateral "border zone." However, if myocytes were not separated into perfused and ischemic subpopulations before statistical comparison of biopsy site to severity of injury, false evidence of a "border zone" was obtained.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox J. L., McLaughlin V. W., Flowers N. C., Horan L. G. The ischemic zone surrounding acute myocardial infarction. Its morphology as detected by dehydrogenase staining. Am Heart J. 1968 Nov;76(5):650–659. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(68)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor S. M., Okun E. M., Kirk E. S. The histological lateral border of acute canine myocardial infarction. A function of microcirculation. Circ Res. 1981 May;48(5):640–649. doi: 10.1161/01.res.48.5.640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Factor S. M., Sonnenblick E. H., Kirk E. S. The histologic border zone of acute myocardial infarction--islands or peninsulas? Am J Pathol. 1978 Jul;92(1):111–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein M. A. Ultrastructure of the ischemic myocardium. Cardiovasc Res Cent Bull. 1979 Jul-Sep;18(1):1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb G. J., Kubo S. H., Alonso D. R. Ultrastructural characterization of the border zone surrounding early experimental myocardial infarcts in dogs. Am J Pathol. 1981 May;103(2):292–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grizzle J. E., Starmer C. F., Koch G. G. Analysis of categorical data by linear models. Biometrics. 1969 Sep;25(3):489–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harden W. R., Simson M. B., Barlow C. H., Soriano R., Harken A. H. Display of epicardial ischemia by reduced nicotamide adenine dinucleotide fluorescence photography, electron microscopy, and ST segment mapping. Surgery. 1978 Jun;83(6):732–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harken A. H., Barlow C. H., Harden W. R., 3rd, Chance B. Two and three dimensional display of myocardial ischemic "border zone" in dogs. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Dec;42(6):954–959. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90681-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harken A. H., Simson M. B., Haselgrove J., Wetstein L., Harden W. R., 3rd, Barlow C. H. Early ischemia after complete coronary ligation in the rabbit, dog, pig, and monkey. Am J Physiol. 1981 Aug;241(2):H202–H210. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1981.241.2.H202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearse D. J., Yellon D. M. The "Border zone" and myocardial protection: a time for reassessment? Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1981;651:37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearse J. D., Opie L. H., Katzeff I. E., Lubbe W. F., Van der Werff T. J., Peisach M., Boulle G. Characterization of the "border zone" in acute regional ischemia in the dog. Am J Cardiol. 1977 Nov;40(5):716–726. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(77)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfant R. H., Banka V. S., Bodenheimer M. M. Perplexities and complexities concerning the myocardial infarction border zone and its salvage. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Feb;41(2):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90178-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirzel H. O., Sonnenblick E. H., Kirk E. S. Absence of a lateral border zone of intermediate creatine phosphokinase depletion surrounding a central infarct 24 hours after acute coronary occlusion in the dog. Circ Res. 1977 Nov;41(5):673–683. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.5.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hüttner I., More R. H., Rona G. Fine structural evidence of specific mechanism for increased endothelial permeability in experimental hypertension. Am J Pathol. 1970 Dec;61(3):395–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janse M. J., Cinca J., Moréna H., Fiolet J. W., Kléber A. G., de Vries G. P., Becker A. E., Durrer D. The "border zone" in myocardial ischemia. An electrophysiological, metabolic, and histochemical correlation in the pig heart. Circ Res. 1979 Apr;44(4):576–588. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.4.576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings R. B., Ganote C. E., Reimer K. A. Ischemic tissue injury. Am J Pathol. 1975 Oct;81(1):179–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jugdutt B. I., Hutchins G. M., Bulkley B. H., Becker L. C. Myocardial infarction in the conscious dog: three-dimensional mapping of infarct, collateral flow and region at risk. Circulation. 1979 Nov;60(5):1141–1150. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.60.5.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloner R. A., Braunwald E., Maroko P. R. Long-term preservation of ischemic myocardium in the dog by hyaluronidase. Circulation. 1978 Aug;58(2):220–226. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.58.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsunami K., Fukuhara T., Kato S., Bito K., Kinoshita M., Kawakita S. The border zone in acute myocardial ischemia in the dog--a histochemical, biochemical and ultrastructural study. Jpn Circ J. 1984 Jan;48(1):18–31. doi: 10.1253/jcj.48.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okun E. M., Factor S. M., Kirk E. S. End-capillary loops in the heart: an explanation for discrete myocardial infarctions without border zones. Science. 1979 Nov 2;206(4418):565–567. doi: 10.1126/science.493960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page E., Polimeni P. I. Ultrastructural changes in the ischemic zone bordering experimental infarcts in rat left ventricles. Am J Pathol. 1977 Apr;87(1):81–104. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regitz V., Paulson D. J., Hodach R. J., Little S. E., Schaper W., Shug A. L. Mitochondrial damage during myocardial ischemia. Basic Res Cardiol. 1984 Mar-Apr;79(2):207–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01908307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Jennings R. B., Tatum A. H. Pathobiology of acute myocardial ischemia: metabolic, functional and ultrastructural studies. Am J Cardiol. 1983 Jul 20;52(2):72A–81A. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(83)90180-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Jennings R. B. The "wavefront phenomenon" of myocardial ischemic cell death. II. Transmural progression of necrosis within the framework of ischemic bed size (myocardium at risk) and collateral flow. Lab Invest. 1979 Jun;40(6):633–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer K. A., Lowe J. E., Rasmussen M. M., Jennings R. B. The wavefront phenomenon of ischemic cell death. 1. Myocardial infarct size vs duration of coronary occlusion in dogs. Circulation. 1977 Nov;56(5):786–794. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.56.5.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaper J., Mulch J., Winkler B., Schaper W. Ultrastructural, functional, and biochemical criteria for estimation of reversibility of ischemic injury: a study on the effects of global ischemia on the isolated dog heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1979 Jun;11(6):521–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(79)90428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sládek T., Filkuka J., Dolezel S., Vasků J., Hartmannová B., Trávnícková J. The border zone of the early myocardial infarction in dogs; its characteristics and viability. Basic Res Cardiol. 1984 May-Jun;79(3):344–349. doi: 10.1007/BF01908035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vokonas P. S., Malsky P. M., Paul S. J., Robbins S. L., Hood W. B., Jr Radioautographic studies in experimental myocardial infarction: profiles of ischemic blood flow and quantification of infarct size in relation to magnitude of ischemic zone. Am J Cardiol. 1978 Jul;42(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(78)90987-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walfridsson H., Lewis D. H., Sjöberg F., Lund N. Acute coronary occlusion: oxygen pressure in the border zone studied in the pig. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1985;4(2):109–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellon D. M. A multiple biopsy gun for the study of three-dimensional metabolic geometry [proceedings]. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:5P–6P. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellon D. M., Downey J. M., Hearse D. J. Myocardial infarct size limitation. Principles, problems and possibilities. G Ital Cardiol. 1984 Nov;14(11):892–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellon D. M., Hearse D. J., Crome R., Grannell J., Wyse R. K. Characterization of the lateral interface between normal and ischemic tissue in the canine heart during evolving myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 1981 Jun;47(6):1233–1239. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(81)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yellon D. M., Hearse D. J., Crome R., Wyse R. K. Temporal and spatial characteristics of evolving cell injury during regional myocardial ischemia in the dog: the "border zone" controversy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1983 Oct;2(4):661–670. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(83)80306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



