Abstract
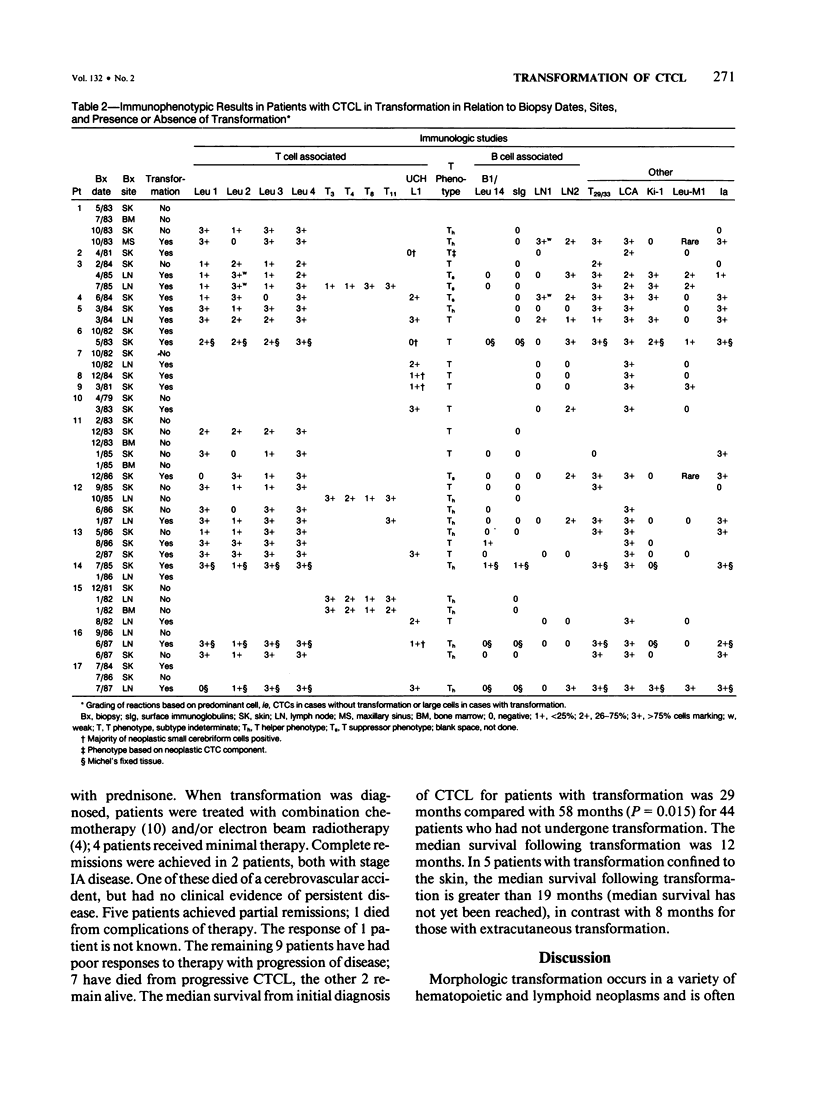
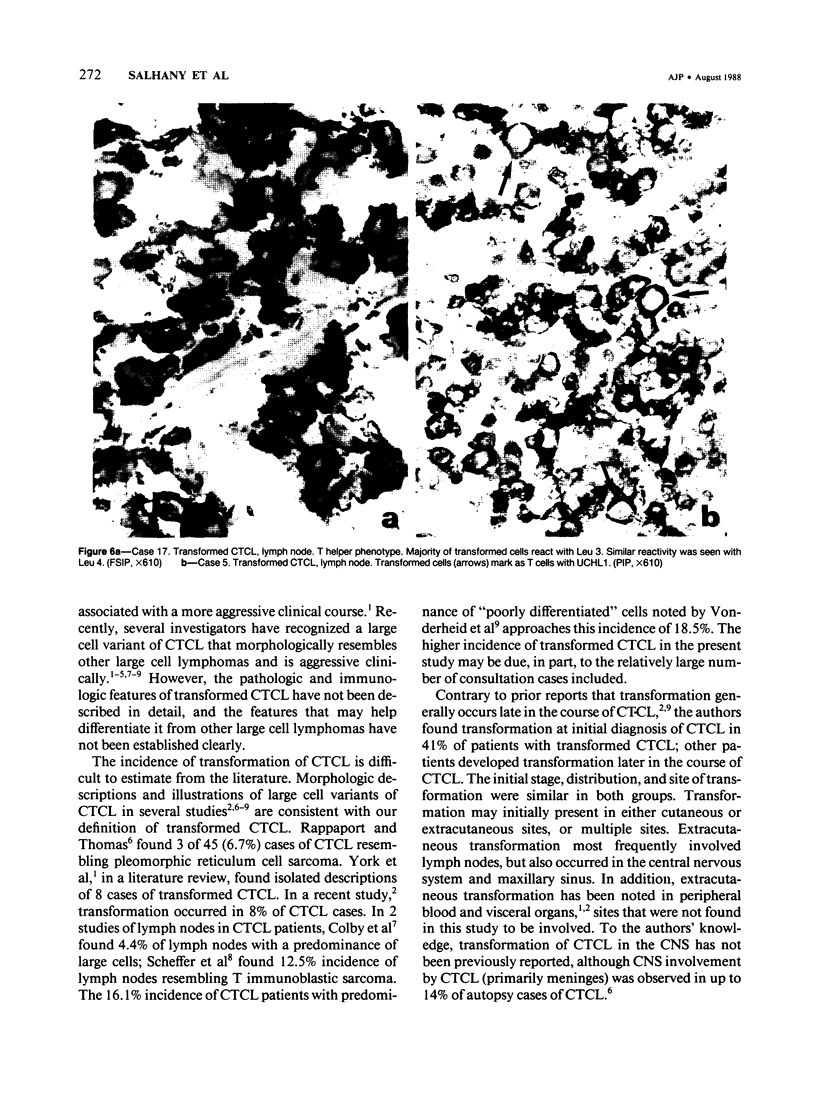
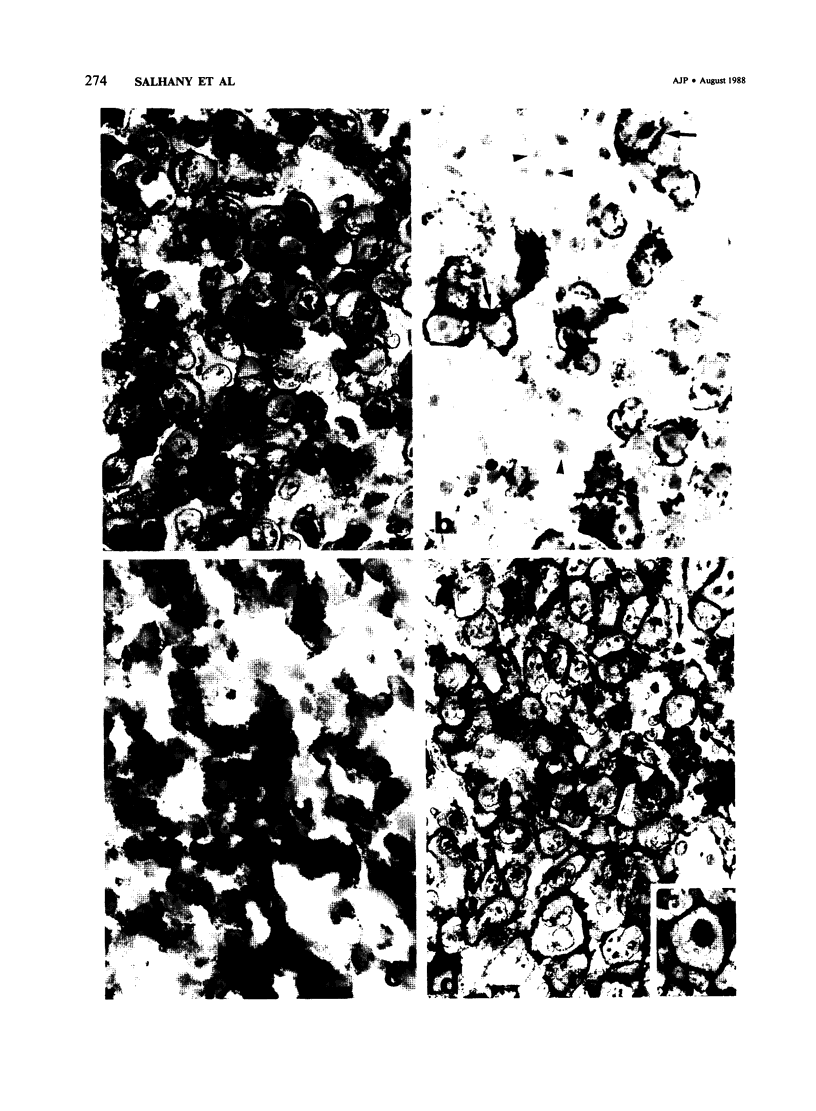
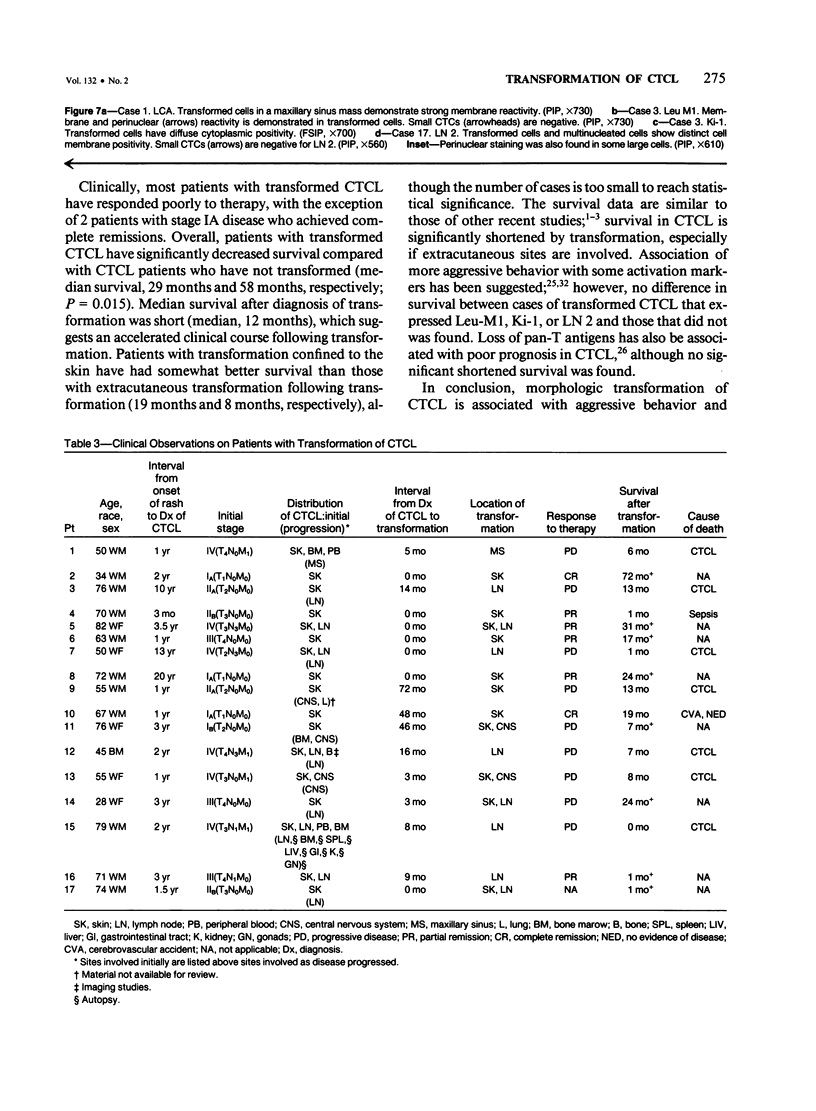
Some patients with cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL) develop a high-grade, large-cell lymphoma associated with rapid deterioration of clinical status. This change in histologic appearance and clinical behavior of CTCL is similar to transformations of other hematopoietic and lymphoid neoplasms. From a group of 92 cases of CTCL, morphologic, immunologic and clinical features were studied in 17 cases of transformed CTCL. Transformation was noted, at presentation or subsequently, in either cutaneous or extracutaneous sites; remarkably, transformation was found at initial diagnosis of CTCL in 7 of 17 patients. T cell characteristics were maintained in all 17 cases of transformed CTCL; in 11 cases with complete phenotypes, there were 6 T-helper, 3 T-suppressor, and 2 aberrant T subtypes. The pre- and posttransformation phenotypes were similar in 3 of 7 cases tested over time (all T-helper); retention of T-suppressor phenotype was suggested in another case. T cell features were maintained in the other 3 cases, but the T subtypes were altered in 2 of these cases. Absent or diminished pan-T antigens (CD 5, CD 3, or UCHL1) were found in 9 of 17 cases. Leu-M1, Ki-1, or LN 2 antigens were expressed by transformed cells in 10 of 17 cases, often in patterns identical to Reed-Sternberg cells. Survival in patients with transformed CTCL was significantly shorter (median, 29 months) than in 44 CTCL patients without transformation (58 months, P = 0.015); survival after diagnosis of transformation was short (12 months). Patients with extracutaneous transformation had a shorter median survival after transformation (8 months) than those with transformation limited to skin (19 months). It is concluded that CTCL can transform morphologically to a large cell variant associated with aggressive behavior and shortened survival. Extracutaneous transformation apparently indicates a poorer prognosis than cutaneous transformation. Although transformed CTCL usually retains a T cell phenotype, some antigens are lost while other new antigens may be expressed. Recognition of transformed CTCL is facilitated by identification of the dysplastic cerebriform cell component, but often requires correlation of immunologic and clinical features.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett S. R., Greer J. P., Stein R. S., Glick A. D., Cousar J. B., Collins R. D. Death due to splenic rupture in suppressor cell mycosis fungoides: a case report. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):104–109. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitz M. J., Croker B. P., Burchette J. Immunocytochemical detection of lymphocyte surface antigens in fixed tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Feb;30(2):171–174. doi: 10.1177/30.2.7037938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borowitz M. J., Reichert T. A., Brynes R. K., Cousar J. B., Whitcomb C. C., Collins R. D., Crissman J. D., Byrne G. E., Jr The phenotypic diversity of peripheral T-cell lymphomas: the Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. Hum Pathol. 1986 Jun;17(6):567–574. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(86)80128-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehmer-Andersson E. Mycosis fungoides and its relation to Sézary's syndrome, lymphomatoid papulosis, and primary cutaneous Hodgkin's disease. A clinical, histopathologic and cytologic study of fourteen cases and a critical review of the literature. Acta Derm Venereol Suppl (Stockh) 1976;56(75):3–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey T. T., Posey D. H., McCurley T. L. OKT4 epitope deficiency in significant proportions of the black population. A cause for underestimation of helper/suppressor lymphocyte ratios. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1986 Aug;110(8):702–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan W. C., Griem M. L., Grozea P. N., Freel R. J., Variakojis D. Mycosis fungoides and Hodgkin's disease occurring in the same patient: report of three cases. Cancer. 1979 Oct;44(4):1408–1413. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197910)44:4<1408::aid-cncr2820440435>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu A., Patterson J., Berger C., Vonderheid E., Edelson R. In situ study of T-cell subpopulations in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Diagnostic criteria. Cancer. 1984 Dec 1;54(11):2414–2422. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841201)54:11<2414::aid-cncr2820541118>3.0.co;2-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby T. V., Burke J. S., Hoppe R. T. Lymph node biopsy in mycosis fungoides. Cancer. 1981 Jan 15;47(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810115)47:2<351::aid-cncr2820470224>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dmitrovsky E., Matthews M. J., Bunn P. A., Schechter G. P., Makuch R. W., Winkler C. F., Eddy J., Sausville E. A., Ihde D. C. Cytologic transformation in cutaneous T cell lymphoma: a clinicopathologic entity associated with poor prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 1987 Feb;5(2):208–215. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1987.5.2.208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEHAN E. A. A GENERALIZED WILCOXON TEST FOR COMPARING ARBITRARILY SINGLY-CENSORED SAMPLES. Biometrika. 1965 Jun;52:203–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan T. M., Fielder K., Rangel C., Jolley C. J., Wirt D. P., Hicks M. J., Miller T. P., Brooks R., Greenberg B., Jones S. Peripheral T-cell lymphoma: aggressive disease with heterogeneous immunotypes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Mar;83(3):279–288. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/83.3.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Hensley L. L., Jegasothy B. V. Phenotypic characterization of skin-infiltrating T cells in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: comparison with benign cutaneous T-cell infiltrates. Blood. 1982 Aug;60(2):463–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Jaffe E. S. Leu M1 and peanut agglutinin stain the neoplastic cells of Hodgkin's disease. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Jul;82(1):29–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/82.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Yang K., Jaffe E. S. Phenotypic expression of Hodgkin's and Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. Am J Pathol. 1985 Feb;118(2):209–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Glick A. D., Waldron J. A., Flexner J. M., Horn R. G., Collins R. D. Malignant lymphomas of follicular center cell origin in man. I. Immunologic studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):11–21. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder J., Ye Y. L., Harrington D. S., Armitage J. O., Weisenburger D. D. Monoclonal antibodies marking T lymphocytes in paraffin-embedded tissue. Am J Pathol. 1987 Apr;127(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukes R. J., Collins R. D. Immunologic characterization of human malignant lymphomas. Cancer. 1974 Oct;34(4 Suppl):suppl–suppl:1503. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197410)34:8+<1488::aid-cncr2820340822>3.0.co;2-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder R. J., Variakojis D., Silver J., Epstein A. L. Immunohistochemical analysis of human lymphomas with monoclonal antibodies to B cell and Ia antigens reactive in paraffin sections. Lab Invest. 1985 May;52(5):497–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasu K., Said J., Vonderheid E., Olerud J., Sako D., Kadin M. Immunopathology of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jun;119(3):436–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picker L. J., Weiss L. M., Medeiros L. J., Wood G. S., Warnke R. A. Immunophenotypic criteria for the diagnosis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Am J Pathol. 1987 Jul;128(1):181–201. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Said J. W. Hodgkin's disease, lymphocyte predominance type, nodular--a distinct entity? Unique staining profile for L&H variants of Reed-Sternberg cells defined by monoclonal antibodies to leukocyte common antigen, granulocyte-specific antigen, and B-cell-specific antigen. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jan;118(1):1–6. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkus G. S., Thomas P., Said J. W. Leu-M1--a marker for Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin's disease. An immunoperoxidase study of paraffin-embedded tissues. Am J Pathol. 1985 May;119(2):244–252. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralfkiaer E., Wantzin G. L., Mason D. Y., Hou-Jensen K., Stein H., Thomsen K. Phenotypic characterization of lymphocyte subsets in mycosis fungoides. Comparison with large plaque parapsoriasis and benign chronic dermatoses. Am J Clin Pathol. 1985 Nov;84(5):610–619. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/84.5.610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappaport H., Thomas L. B. Mycosis fungoides: the pathology of extracutaneous involvement. Cancer. 1974 Oct;34(4):1198–1229. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197410)34:4<1198::aid-cncr2820340431>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheen S. R., 3rd, Banks P. M., Winkelmann R. K. Morphologic heterogeneity of malignant lymphomas developing in mycosis fungoides. Mayo Clin Proc. 1984 Feb;59(2):95–106. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)60243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer E., Meijer C. J., Van Vloten W. A. Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy and lymph node involvement in mycosis fungoides. Cancer. 1980 Jan 1;45(1):137–148. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19800101)45:1<137::aid-cncr2820450124>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarze E. W., Ude P. Immunoblastic sarcoma with leukemic blood picture in the terminal stage of mycosis fungoides. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1975 Dec 31;369(2):165–172. doi: 10.1007/BF00433242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrod A. E., Felder B., Levy N., Epstein A., Marder R., Lukes R. J., Taylor C. R. Immunohistologic identification of phenotypic antigens associated with Hodgkin and Reed-Sternberg cells. A paraffin section study. Cancer. 1986 Jun 1;57(11):2135–2140. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860601)57:11<2135::aid-cncr2820571109>3.0.co;2-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H., Mason D. Y., Gerdes J., O'Connor N., Wainscoat J., Pallesen G., Gatter K., Falini B., Delsol G., Lemke H. The expression of the Hodgkin's disease associated antigen Ki-1 in reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):848–858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vonderheid E. C., Tam D. W., Johnson W. C., Van Scott E. J., Wallner P. E. Prognostic significance of cytomorphology in the cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. Cancer. 1981 Jan 1;47(1):119–125. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<119::aid-cncr2820470120>3.0.co;2-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek R., Burke J. S., Knowles D. M., 2nd Leu-M1 antigen expression in T-cell neoplasia. Am J Pathol. 1985 Dec;121(3):374–380. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek R., Suhrland M., Ramsay D., Reed M. L., Knowles D. M., 2nd Leu-M1 antigen expression in advanced (tumor) stage mycosis fungoides. Am J Clin Pathol. 1986 Jul;86(1):25–32. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/86.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R., Scheffer E., Meijer C. J. Immunohistochemical studies using monoclonal antibodies on lymph nodes from patients with mycosis fungoides and Sézary's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1985 Jul;120(1):46–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willemze R., de Graaff-Reitsma C. B., Cnossen J., Van Vloten W. A., Meijer C. J. Characterization of T-cell subpopulations in skin and peripheral blood of patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphomas and benign inflammatory dermatoses. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jan;80(1):60–66. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12531102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood G. S., Deneau D. G., Miller R. A., Levy R., Hoppe R. T., Warnke R. A. Subtypes of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma defined by expression of leu-1 and Ia. Blood. 1982 May;59(5):876–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagihara E. T., Parker J. W., Meyer P. R., Cain M. J., Hofman F., Lukes R. J. Mycosis fungoides/Sezary's syndrome progressing to immunoblastic sarcoma. A T-cell lymphoproliferation with both helper and suppressor phenotypes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1984 Feb;81(2):249–257. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/81.2.249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- York J. C., Glick A. D., Cousar J. B., Collins R. D. Changes in the appearance of hematopoietic and lymphoid neoplasms: clinical, pathologic, and biologic implications. Hum Pathol. 1984 Jan;15(1):11–38. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]