Abstract
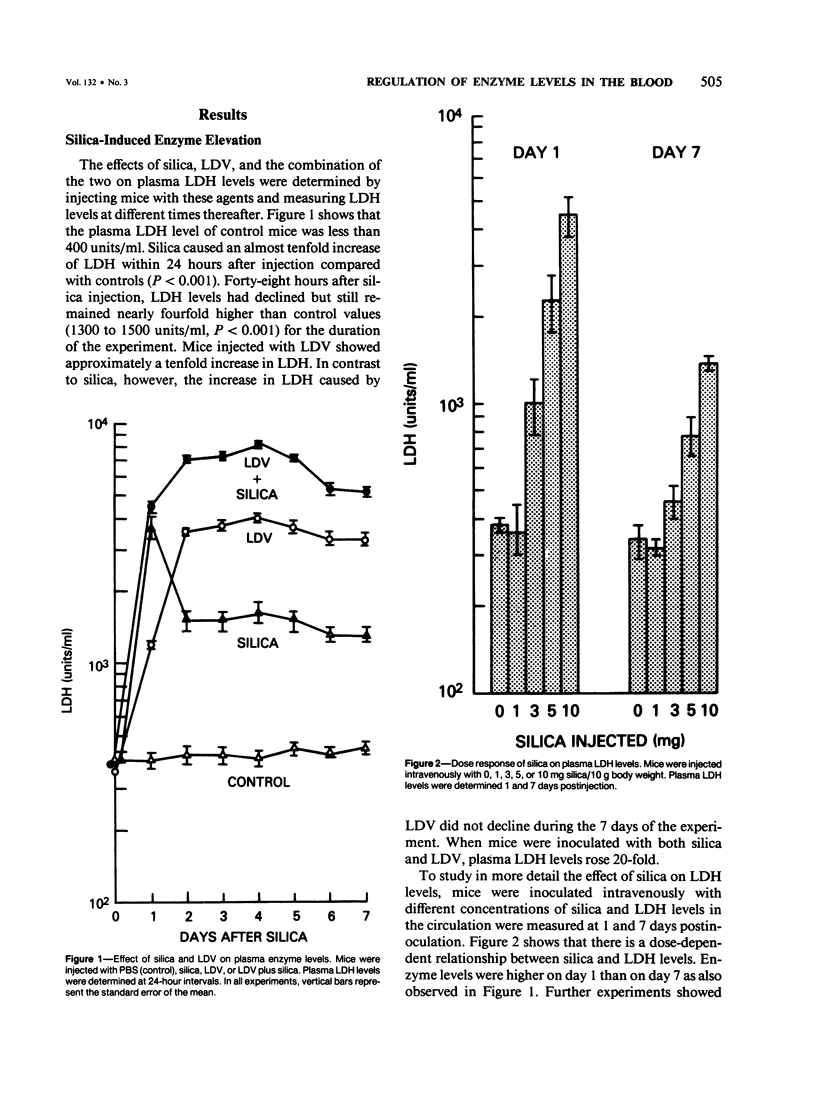
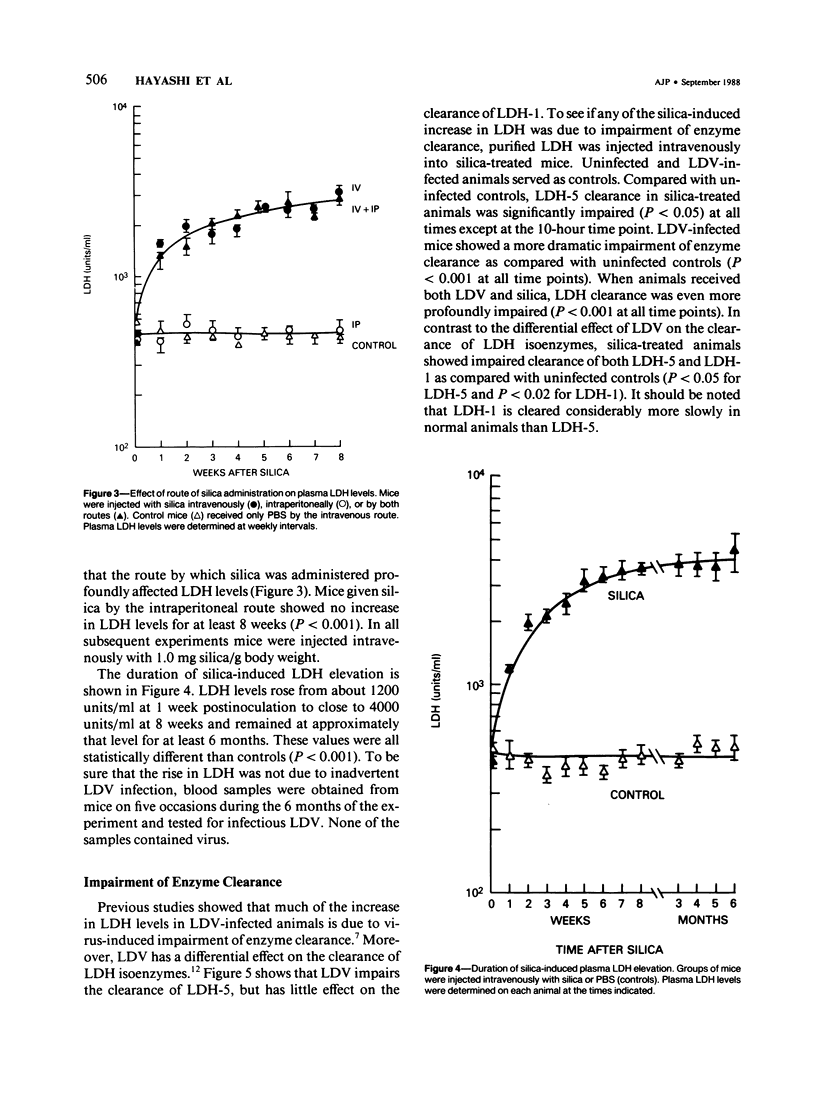
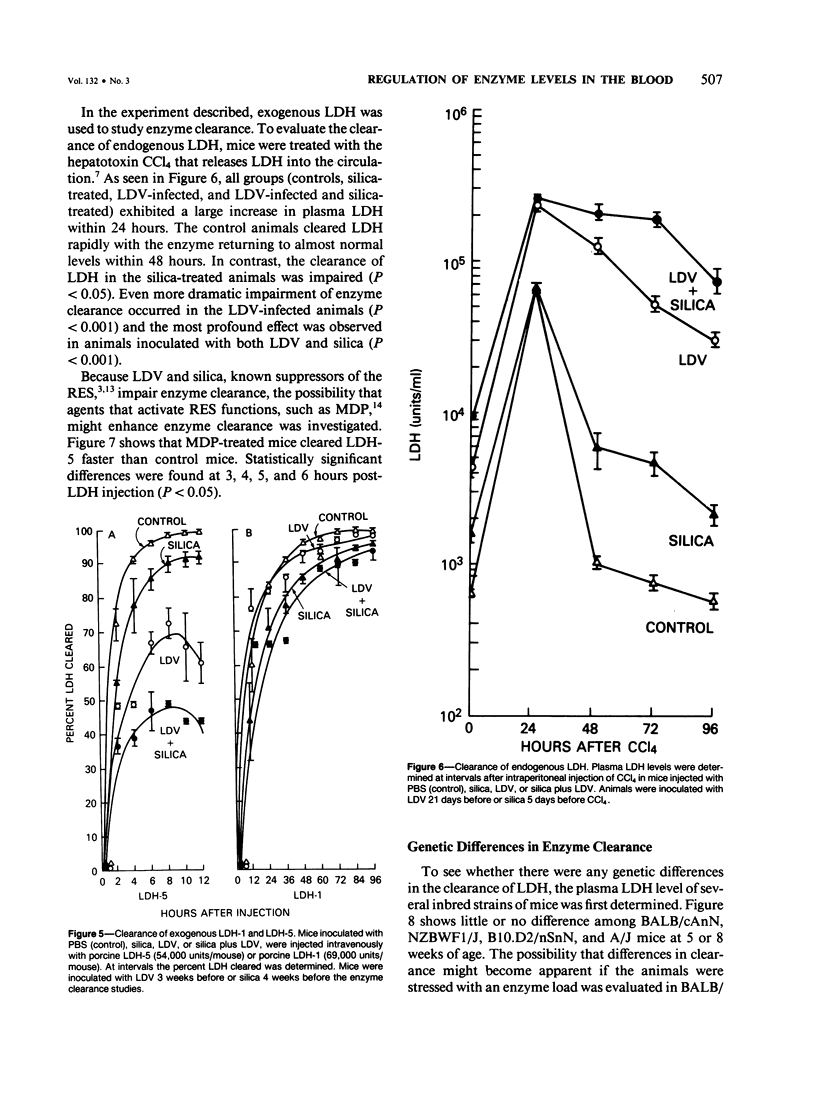
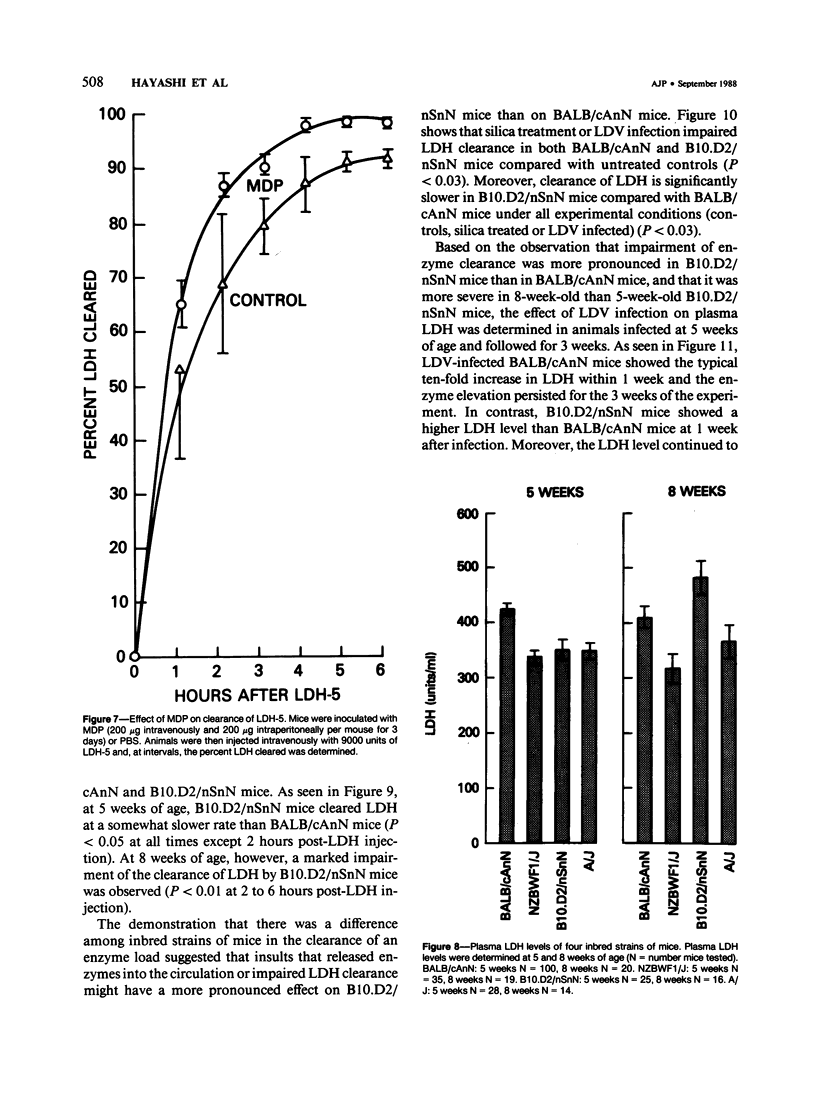
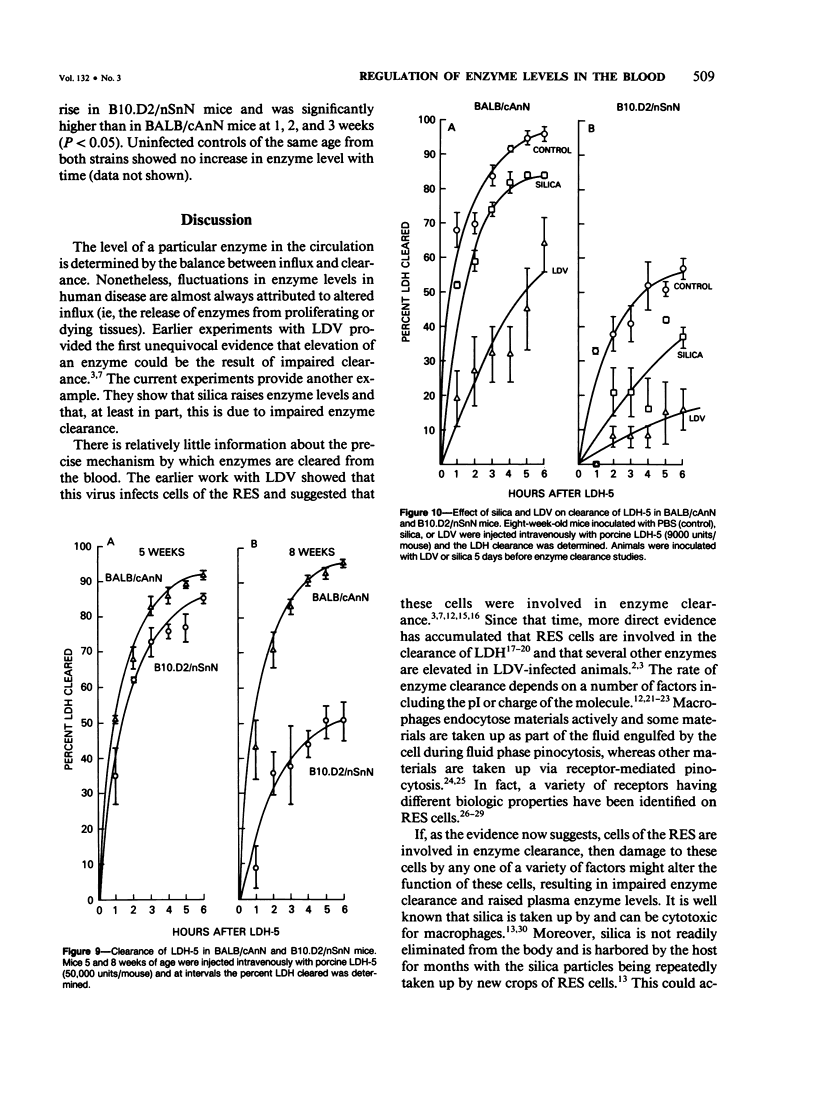
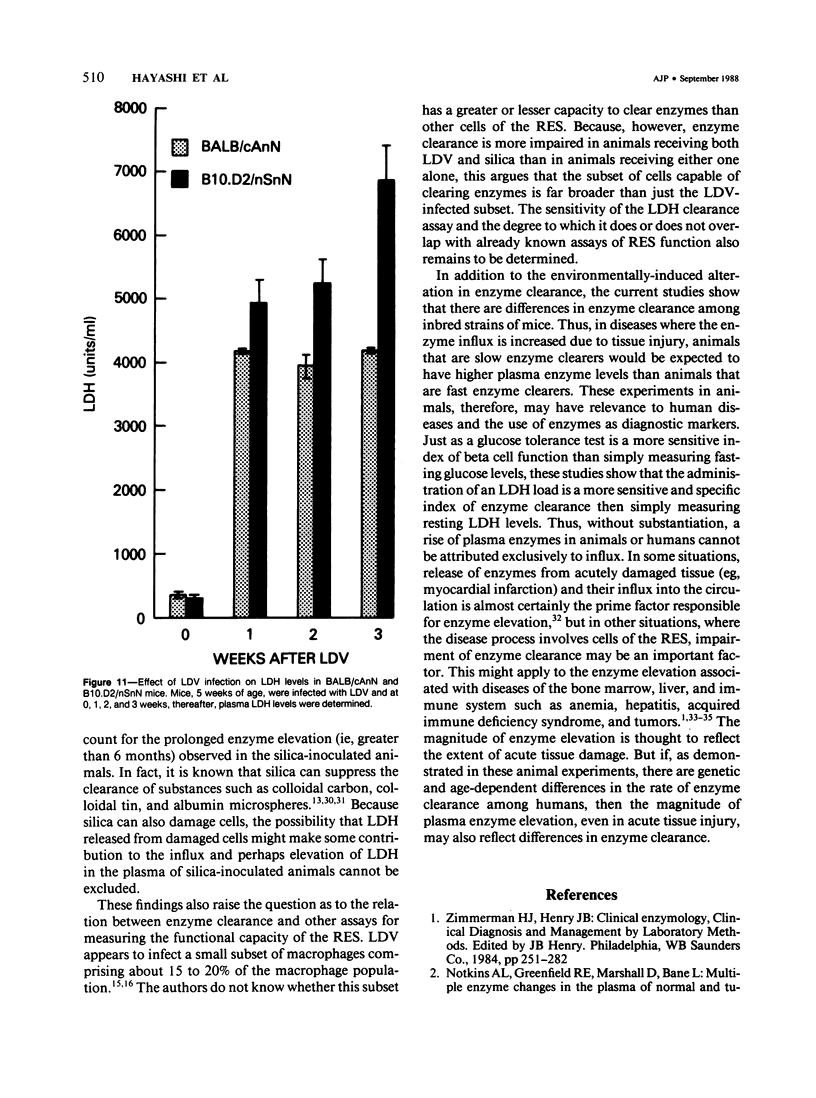
Since its discovery, lactic dehydrogenase virus (LDV) has remained unique as a model of long-term enzyme elevation due to impairment of enzyme clearance. The present study shows that mice inoculated with silica develop an increase in plasma lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) lasting for at least 6 months and that the enzyme elevation is due, at least in part, to impairment of clearance. The extent of the enzyme elevation is dependent on both the dose and route of silica administration and mice that had received both silica and LDV showed a more profound impairment of LDH clearance than mice that had received silica or LDV alone. Examination of the factors that regulate circulating enzyme levels in normal mice revealed that whereas there was no difference in resting enzyme levels among several inbred strains of mice (BALB/cAnN, NZBWF1/J,B10.D2/nSnN, and A/J mice), when mice were stressed by the administration of an enzyme load, certain inbred strains (BALB/cAnN) cleared the enzyme rapidly and others (B10.D2/nSnN) cleared the enzyme slowly. Moreover, in B10.D2/nSnN mice, enzyme clearance was age-related. When different strains of mice were infected with LDV, LDH levels were substantially higher in the circulation of slow enzyme clearers as compared to rapid enzyme clearers. It is concluded that both environmental and genetic factors influence the clearance of LDH and that impairment of enzyme clearance may be a more important factor than previously suspected in regulating enzyme levels in disease states.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashwell G., Harford J. Carbohydrate-specific receptors of the liver. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:531–554. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Duursma A. M., Bouma J. M., Gruber M., Nieuwenhuis P. Plasma clearance and endocytosis of mitochondrial malate dehydrogenase in the rat. Biochem J. 1981 Oct 15;200(1):115–121. doi: 10.1042/bj2000115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chadwick S. J., Aldridge M., Dudley H. A. Detection of reticulo-endothelial blockade with low-dose test agent. Br J Exp Pathol. 1985 Aug;66(4):483–491. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapelle J. P., Albert A., Smeets J. P., Maréchal J. P., Heusghem C., Kulbertus H. E. Does lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme-5 contribute to the predictive power of total lactate dehydrogenase in myocardial infarction? Clin Chem. 1983 May;29(5):774–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn Z. A. The macrophage--versatile element of inflammation. Harvey Lect. 1981 1982;77:63–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DETHE G., NOTKINS A. L. ULTRASTRUCTURE OF THE LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE VIRUS (LDV) AND CELL-VIRUS RELATIONSHIPS. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:512–516. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Jong A. S., Bouma J. M., Gruber M. O-(4-Diazo-3,5-di[125I]iodobenzoyl)sucrose, a novel radioactive label for determining organ sites of catabolism of plasma proteins. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):45–51. doi: 10.1042/bj1980045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genin C., Cosio F., Michael A. F. Macromolecular charge and reticuloendothelial function: comparison between the kinetics of administered native and cationized ferritins and the corresponding immune complexes in the mouse. Immunology. 1984 Feb;51(2):225–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Ho Y. K., Basu S. K., Brown M. S. Binding site on macrophages that mediates uptake and degradation of acetylated low density lipoprotein, producing massive cholesterol deposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):333–337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han T., Emrich L. J., Ozer H., Reese P. A., Gajera R., Gomez G. A., Henderson E. S., Bloom M. L., Bhargava A., Fitzpatrick J. Clinical significance of serum lactate dehydrogenase in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Y State J Med. 1985 Dec;85(12):685–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horiuchi S., Takata K., Maeda H., Morino Y. Scavenger function of sinusoidal liver cells. Acetylated low-density lipoprotein is endocytosed via a route distinct from formaldehyde-treated serum albumin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):53–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahy B. W., Rowson K. E., Parr C. W. Studies on the mechanism of action of Riley virus. IV. The reticuloendothelial system and impaired plasma enzyme clearance in infected mice. J Exp Med. 1967 Feb 1;125(2):277–288. doi: 10.1084/jem.125.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merion R. M. Measurements of reticuloendothelial system phagocytic activity in the rat after treatment with silica, liposomes, and cyclosporine. Transplantation. 1985 Jul;40(1):86–90. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198507000-00017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOTKINS A. L., GREENFIELD R. E., MARSHALL D., BANE L. Multiple enzyme changes in the plasma of normal and tumor-bearing mice following infection with the lactic dehydrogenase agent. J Exp Med. 1963 Feb 1;117:185–195. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.2.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOTKINS A. L. LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE VIRUS. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Jun;29:143–160. doi: 10.1128/br.29.2.143-160.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOTKINS A. L., SCHEELE C. IMPAIRED CLEARANCE OF ENZYMES IN MICE INFECTED WITH THE LACTIC DEHYDROGENASE AGENT. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Oct;33:741–749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOTKINS A. L., SHOCHAT S. J. Studies on the multiplication and the properties of the lactic dehydrogenase agent. J Exp Med. 1963 May 1;117:735–747. doi: 10.1084/jem.117.5.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickle E. C., Solomon R. D., Torchia T. E., Wriston J. C., Jr Chemical modifications of Escherichia coli L-asparaginase and their effect on plasma clearance rate and other properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 4;704(2):345–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90164-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L. Enzymatic and immunologic alterations in mice infected with lactic dehydrogenase virus. Am J Pathol. 1971 Sep;64(3):733–746. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notkins A. L., Mahar S., Scheele C., Goffman J. Infectious virus-antibody complex in the blood of chronically infected mice. J Exp Med. 1966 Jul 1;124(1):81–97. doi: 10.1084/jem.124.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pui C. H., Dodge R. K., Dahl G. V., Rivera G., Look A. T., Kalwinsky D., Bowman W. P., Ochs J., Abromowitch M., Mirro J. Serum lactic dehydrogenase level has prognostic value in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):778–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritzi D. M., Holth M., Smith M. S., Swart W. J., Cafruny W. A., Plagemann G. W., Stueckemann J. A. Replication of lactate dehydrogenase-elevating virus in macrophages. 1. Evidence for cytocidal replication. J Gen Virol. 1982 Apr;59(Pt 2):245–262. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-2-245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman B. A., Rubinstein A. Serum lactate dehydrogenase levels in adults and children with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex: possible indicator of B cell lymphoproliferation and disease activity. Effect of intravenous gammaglobulin on enzyme levels. Am J Med. 1985 May;78(5):728–736. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(85)90275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinke J., Bouma J. M., Kooistra T., Gruber M. Endocytosis and breakdown of 125I-labelled lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme M4 by rat liver and spleen in vivo. Biochem J. 1979 Apr 15;180(1):1–9. doi: 10.1042/bj1800001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M., Mellman I. S., Muller W. A., Cohn Z. A. Endocytosis and the recycling of plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;96(1):1–27. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka A., Nagao S., Nagao R., Kotani S., Shiba T., Kusumoto S. Stimulation of the reticuloendothelial system of mice by muramyl dipeptide. Infect Immun. 1979 May;24(2):302–307. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.2.302-307.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uber C. L., McReynolds R. A. Immunotoxicology of silica. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1982 Oct;10(4):303–319. doi: 10.3109/10408448209003370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlassara H., Brownlee M., Cerami A. Novel macrophage receptor for glucose-modified proteins is distinct from previously described scavenger receptors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1301–1309. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WROBLEWSKI F., LADUE J. S. Lactic dehydrogenase activity in blood. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Oct;90(1):210–213. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-21985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkelhake J. L., Elcombe B. M., Chang R. J. Protracted circulating lifetimes of mannose-terminated glycoproteins and aggregated albumin in mice infected with LDH-elevating virus. Physiol Chem Phys. 1978;10(4):305–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


