Abstract
The vascularity of 20 primary skin melanomas was assessed histologically. These cases were selected from patients with intermediate thickness melanomas (0.76-4.0 mm thick) treated surgically to provide two groups of ten patients. One group had no evidence of recurrence with a minimum follow-up of 9 years. The second group of ten patients developed locoregional or systemic metastasis under follow-up, and seven of these patients died of disseminated melanoma. Age, sex, Breslow's tumor thickness, and Clark's level of invasion were similar in the two groups. Vascular quantitation was carried out by image analysis after vascular definition by Ulex europaeus-I agglutinin staining. The percentage vascular area at the tumor base in the recurrence group was more than twice that in the recurrence-free group. This study suggests that increased vascularity at the tumor base may have prognostic significance in intermediate thickness melanomas.
Full text
PDF
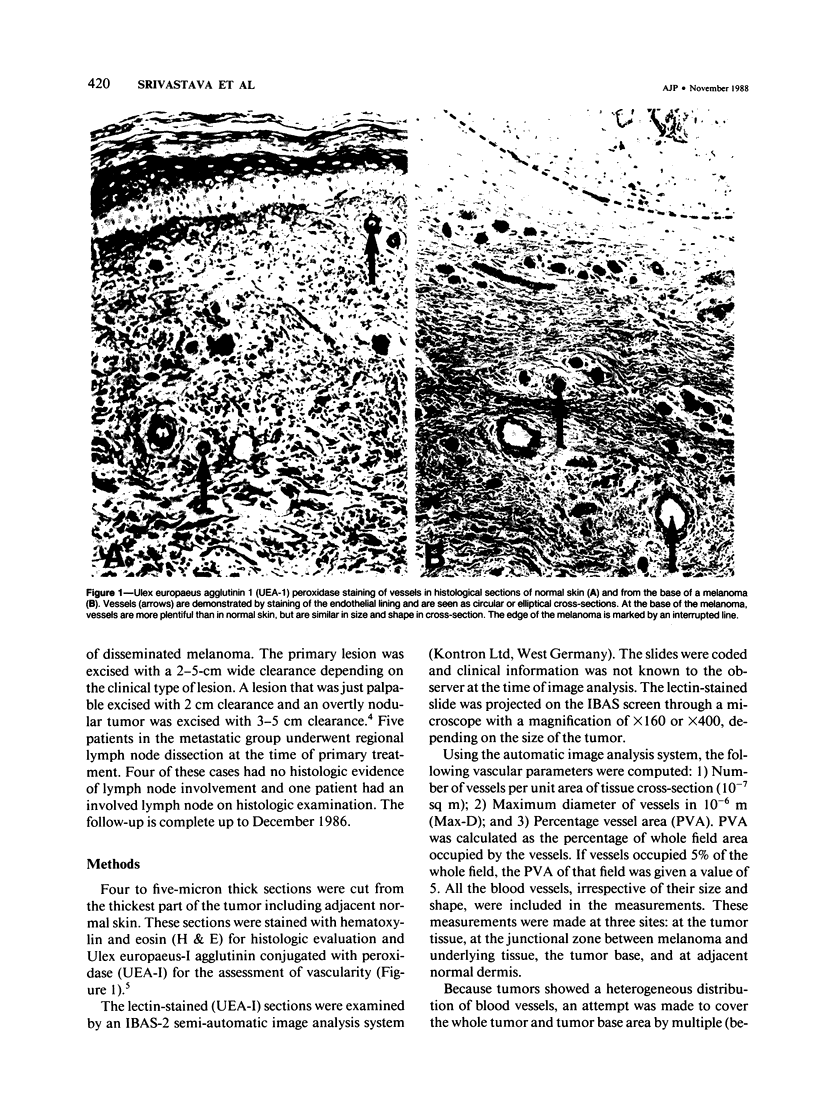

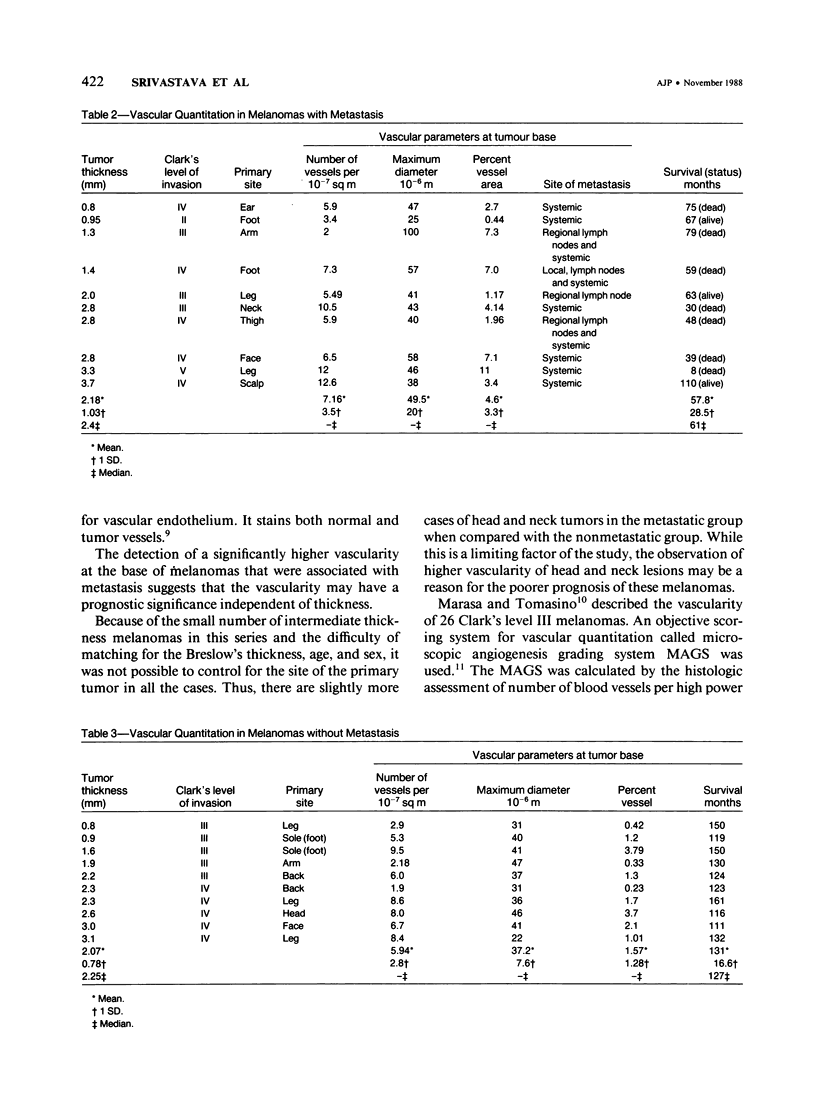
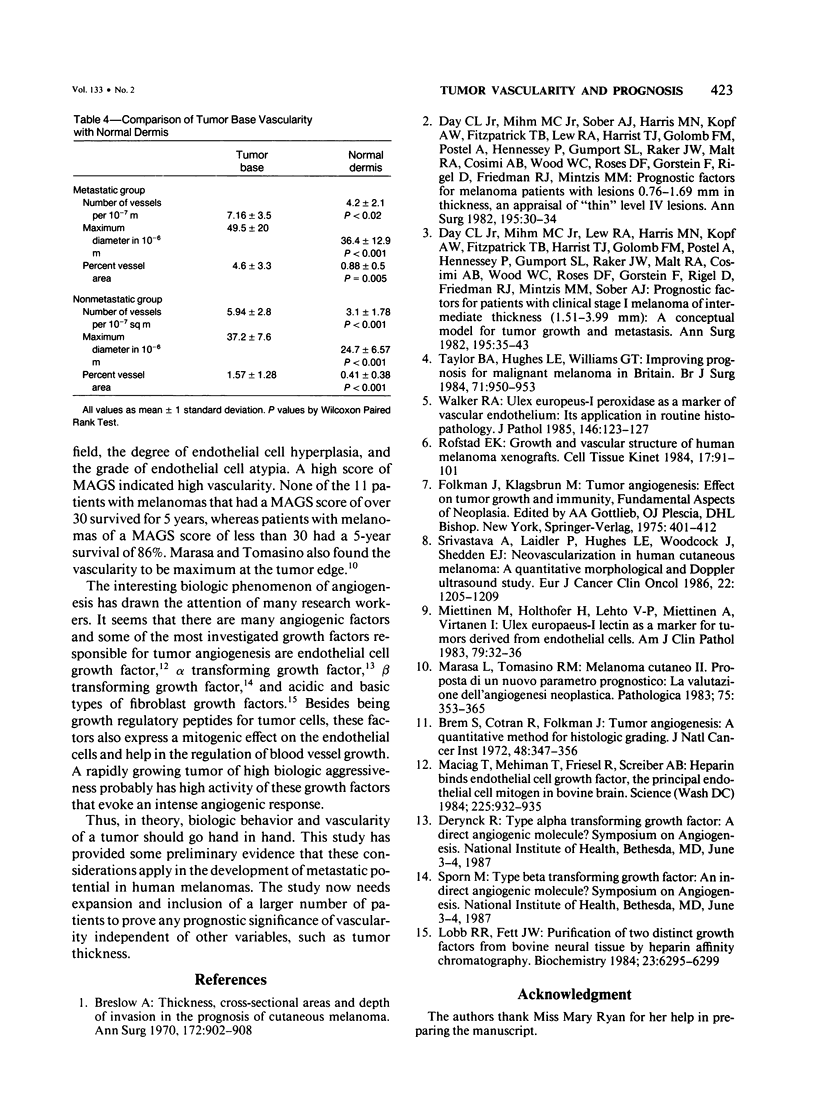
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brem S., Cotran R., Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Feb;48(2):347–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breslow A. Thickness, cross-sectional areas and depth of invasion in the prognosis of cutaneous melanoma. Ann Surg. 1970 Nov;172(5):902–908. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197011000-00017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. L., Jr, Mihm M. C., Jr, Lew R. A., Harris M. N., Kopf A. W., Fitzpatrick T. B., Harrist T. J., Golomb F. M., Postel A., Hennessey P. Prognostic factors for patients with clinical stage I melanoma of intermediate thickness (1.51 - 3.39 mm). A conceptual model for tumor growth and metastasis. Ann Surg. 1982 Jan;195(1):35–43. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198201001-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day C. L., Jr, Mihm M. C., Jr, Sober A. J., Harris M. N., Kopf A. W., Fitzpatrick T. B., Lew R. A., Harrist T. J., Golomb F. M., Postel A. Prognostic factors for melanoma patients with lesions 0.76 - 1.69 mm in thickness. An appraisal of "thin" level IV lesions. Ann Surg. 1982 Jan;195(1):30–34. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198201001-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Fett J. W. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6295–6299. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marasà L., Tomasino R. M. Melanoma cutaneo. II. Proposta di un nuovo parametro prognostico: la valutazione dell'angiogenesi neoplastica. Pathologica. 1983 May-Jun;75(1037):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Holthofer H., Lehto V. P., Miettinen A., Virtanen I. Ulex europaeus I lectin as a marker for tumors derived from endothelial cells. Am J Clin Pathol. 1983 Jan;79(1):32–36. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/79.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rofstad E. K. Growth and vascular structure of human melanoma xenografts. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1984 Jan;17(1):91–101. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1984.tb00571.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava A., Laidler P., Hughes L. E., Woodcock J., Shedden E. J. Neovascularization in human cutaneous melanoma: a quantitative morphological and Doppler ultrasound study. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Oct;22(10):1205–1209. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90322-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Hughes L. E., Williams G. T. Improving prognosis for malignant melanoma in Britain. Br J Surg. 1984 Dec;71(12):950–953. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800711213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. A. Ulex europeus I--peroxidase as a marker of vascular endothelium: its application in routine histopathology. J Pathol. 1985 Jun;146(2):123–127. doi: 10.1002/path.1711460207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



